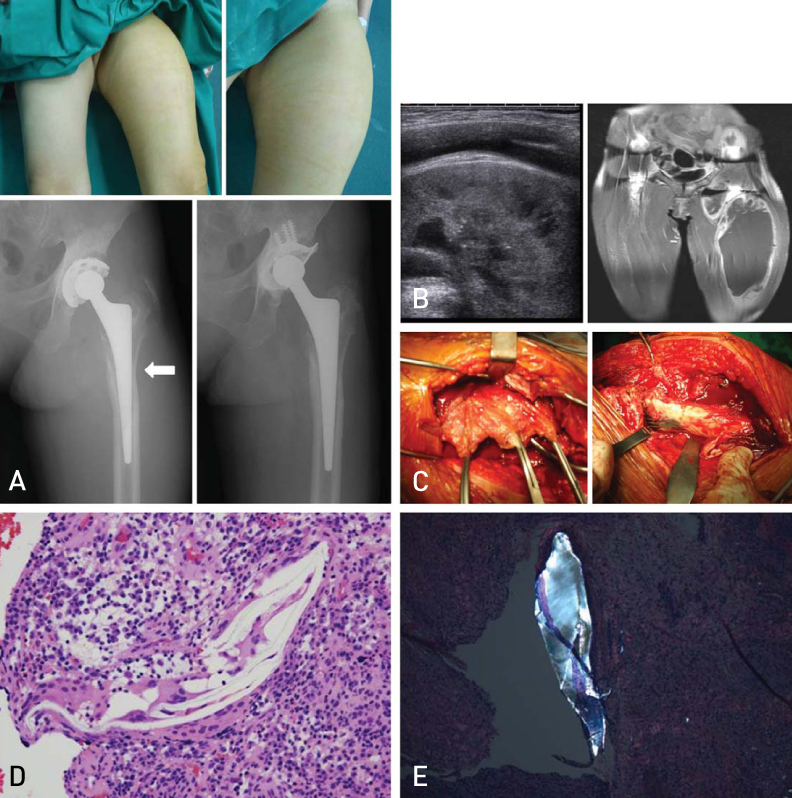
Hip Pelvis.
2012 Sep;24(3):206-212. 10.5371/hp.2012.24.3.206.
Periprosthetic Mass after Total Hip Replacement
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Research Institute for Medical Science, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. dshwang@cnu.ac.kr
- 2On Orthopedic Clinic, Suwon, Korea.
- KMID: 2054134
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5371/hp.2012.24.3.206
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To analyze the characteristics and causes of periprosthetic huge mass which occur after treatment by total hip arthroplasty.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Of the patients who had undergone total hip arthroplasty from January 2000 to October 2007, we retrospectively evaluated the 10 patients who suffered huge soft tissue mass. Five of these patients had received metal-on-metal bearing (group 1) prostheses, and the other 5 had received metal-on-polyethylene bearings (group 2). We evaluated the size and location of the mass, the extent of osteolysis, and the hematologic and pathologic examination results.
RESULTS
Roentgenographically, the location of the masses varied from the acetabular area to the distal femoral stem. The mean mass diameter of all 10 patients was 14.6 cm(7-21 cm)x6.2 cm(3-9 cm)x7.2 cm(4-12 cm). Osteolytic lesions were found in 3 group 1 patients and 3 patients in group 2. High counts of lymphocytes and eosinophils were present in group 1. High counts of macrophages were present in group 2.
CONCLUSION
The occurrence of osteolysis and huge soft mass after total hip arthroplasty is thought to be related to foreign body reaction by polyethylene wear particles and metal hypersensitivity. Outside-in patterned cortical thinning was considered to be indicative of a long standing periprosthetic soft tissue mass effect.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Archibeck MJ, Jacobs JJ, Roebuck KA, Glant TT. The basic science of periprosthetic osteolysis. Instr Course Lect. 2001. 50:185–195.
Article2. Butler RA, Barrack RL. Total hip wear debris presenting as lower extremity swelling. A report of two cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004. 86-A:142–145.3. Gruber FW, Böck A, Trattnig S, Lintner F, Ritschl P. Cystic lesion of the groin due to metallosis: a rare long-term complication of metal-on-metal total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2007. 22:923–927.
Article4. Hananouchi T, Saito M, Nakamura N, Yamamoto T, Yonenobu K. Huge pelvic mass secondary to wear debris causing ureteral obstruction. J Arthroplasty. 2005. 20:946–949.
Article5. Korkala O, Syrjänen KJ. Intrapelvic cyst formation after hip arthroplasty with a carbon fibre-reinforced polyethylene socket. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1998. 118:113–115.
Article6. Mak KH, Wong TK, Poddar NC. Wear debris from total hip arthroplasty presenting as an intrapelvic mass. J Arthroplasty. 2001. 16:674–676.
Article7. Park YS, Moon YW, Lim SJ, Yang JM, Ahn G, Choi YL. Early osteolysis following second-generation metal-on-metal hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005. 87:1515–1521.
Article8. Sieber HP, Rieker CB, Köttig P. Analysis of 118 second-generation metal-on-metal retrieved hip implants. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1999. 81:46–50.
Article9. Lee JM, Salvati EA, Betts F, DiCarlo EF, Doty SB, Bullough PG. Size of metallic and polyethylene debris particles in failed cemented total hip replacements. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1992. 74:380–384.
Article10. Boardman DR, Middleton FR, Kavanagh TG. A benign psoas mass following metal-on-metal resurfacing of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006. 88:402–404.
Article11. Brown GC, Lockshin MD, Salvati EA, Bullough PG. Sensitivity to metal as a possible cause of sterile loosening after cobalt-chromium total hip-replacement arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1977. 59:164–168.
Article12. Svensson O, Mathiesen EB, Reinholt FP, Blomgren G. Formation of a fulminant soft-tissue pseudotumor after uncemented hip arthroplasty. A case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1988. 70:1238–1242.
Article13. Pandit H, Glyn-Jones S, McLardy-Smith P, et al. Pseudotumors associated with metal-on-metal hip resurfacings. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008. 90:847–851.14. Jacobs JJ, Hallab NJ. Loosening and osteolysis associated with metal-on-metal bearings: A local effect of metal hypersensitivity? J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006. 88:1171–1172.15. Mikhael MM, Hanssen AD, Sierra RJ. Failure of metal-on-metal total hip arthropalsty mimicking hip infection. A report of two cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009. 91:443–446.16. Deutman R, Mulder TJ, Brian R, Nater JP. Metal sensitivity before and after total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1977. 59:862–865.
Article17. Milavec-Puretić V, Orlić D, Marusić A. Sensitivity to metals in 40 patients with failed hip endoprosthesis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1998. 117:383–386.
Article18. Brodner W, Bitzan P, Meisinger V, Kaider A, Gottsauner-Wolf F, Kotz R. Elevated serum cobalt with metal-on-metal articulating surfaces. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1997. 79:316–321.
Article19. Brodner W, Bitzan P, Meisinger V, Kaider A, Gottsauner-Wolf F, Kotz R. Serum cobalt levels after metal-on-metal total hip arthropalsty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003. 85-A:2168–2173.20. Brodner W, Grübl A, Jankovsky R, Meisinger V, Lehr S, Gottsauner-Wolf F. Cup inclination and serum concentration of cobalt and chromium after metal-onmetal total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2004. 19:66–70.
Article21. Savarino L, Granchi D, Ciapetti G, et al. Ion release in stable hip arthroplasties using metal-on-metal articulating surfaces: a comparison between short- and medium-term results. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2003. 66:450–456.
Article22. Hallab N, Merritt K, Jacobs JJ. Metal sensitivity in patients with orthopaedic implants. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001. 83-A:428–436.
Article23. Skinner J, Gie G, Kay P. Metal on metal hip replacement and hip resurfacing arthroplasty: What does the MHRA medical device alert mean?-letter from John Skinner, Graham Gie and Peter Kay. British Hip Society Newsletter. 2010. 07. London: British Hip Society;19–20.24. Cho MR, Lee SW. A giant mass mimicking malignancy developed in the proximal thigh after hip arthroplasty: A case report. J Korean Hip Soc. 2006. 18:132–137.
Article25. Lachiewicz PF. Case report: a thigh mass resulting from polyethylene wear of a revision total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007. 455:274–276.
Article26. Suh KT, Lee CK, Lee JS. An inguinal mass associated with polyethylene wear debris after a total hip arthroplasty: A case report. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2005. 40:365–368.
Article27. Jacobs JJ, Shanbhag A, Glant TT, Black J, Galante JO. Wear debris in total joint replacements. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1994. 2:212–220.
Article28. Santavirta S, Konttinen YT, Bergroth V, Eskola A, Tallroth K, Lindholm TS. Aggressive granulomatous lesions associated with hip arthroplasty. Immunopathological studies. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1990. 72:252–258.
Article29. Hallab NJ, Anderson S, Stafford T, Glant T, Jacobs JJ. Lymphocyte responses in patients with total hip arthroplasty. J Orthop Res. 2005. 23:384–391.
Article30. Hanna MW, Thornhill TS. Thigh mass and lytic diaphyseal femoral lesion associated with polyethylene wear after hybrid total knee arthroplasty. A case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006. 88:2473–2478.
Article31. Zicat B, Engh CA, Gokcen E. Patterns of osteolysis around total hip components inserted with and without cement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995. 77:432–439.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment of Periprosthetic Tuberculous Infection of Total Hip Arthroplasty with Long Term Medication without Implant Removal
- Periprosthetic Femoral Fractures after Hip Arthroplasty
- Three Concurrent Periprosthetic Joint Infections: A Case Report and Literature Review
- Atypical Vancouver B1 periprosthetic fracture of the proximal femur in the United Kingdom: a case report challenged by myeloma, osteoporosis, infection, and recurrent implant failures
- A Case of Periprosthetic Fracture of Acetabulum Associated with Osteolysis