Korean J Sports Med.
2015 Jun;33(1):19-28. 10.5763/kjsm.2015.33.1.19.
Effects of Auditory Information and Expertise on the Kinematic Variables of Lower Extremity during Golf Iron Swing
- Affiliations
-
- 1Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Daejeon, Korea. ksma@kaist.ac.kr
- KMID: 2054037
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5763/kjsm.2015.33.1.19
Abstract
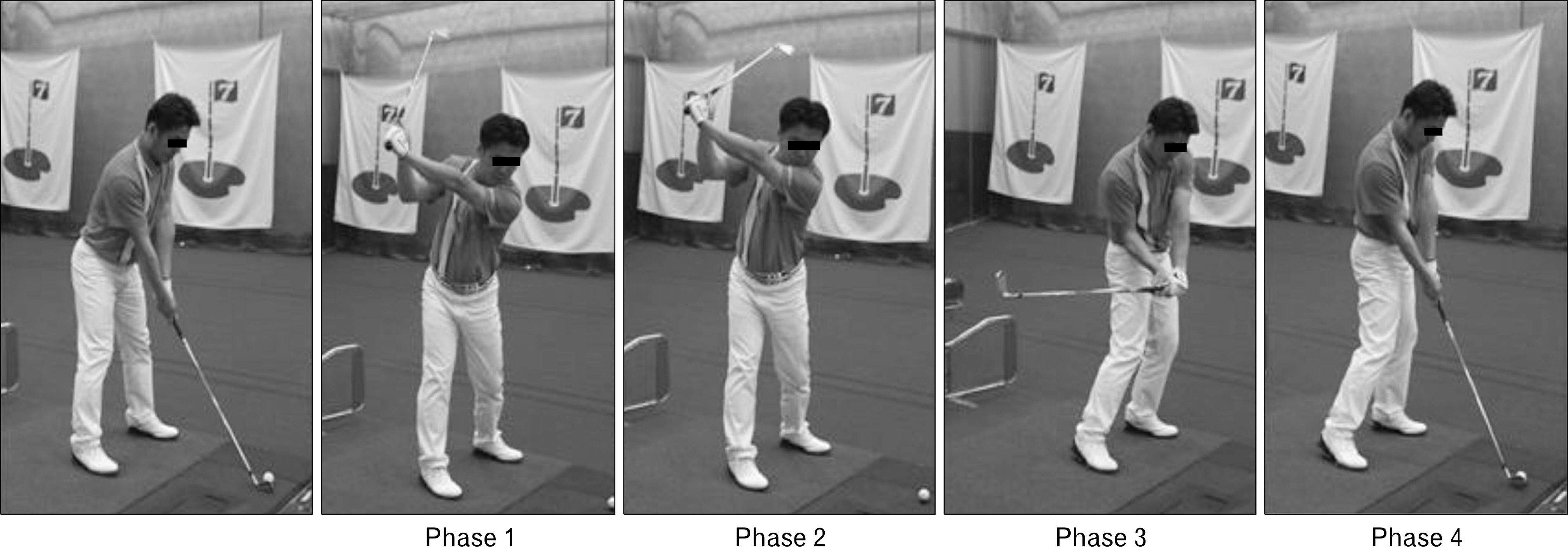
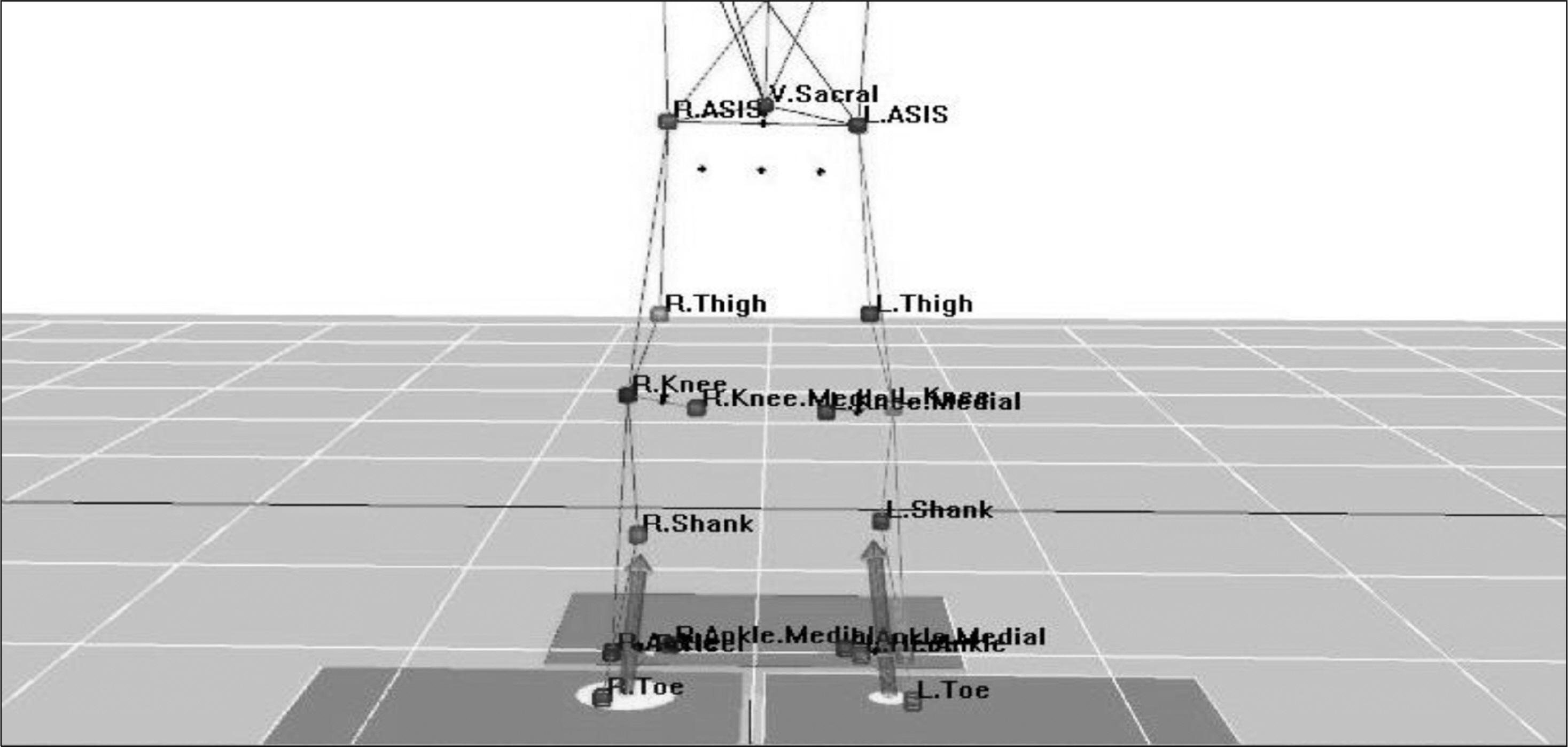
- The purpose of this study was to examine kinematic variables in golf swing depending on auditory information and expertise. The subjects were semi-professional 5 golfers and amateur 5 golfers. Data were analyzed with analysis of variance for repeated measures using SPSS program. The results were followed. The angular displacement of the shoulder joint's right was significant that skilled and unskilled group were according to the swing the most phase in the metronome. Unskilled group was significant difference to swing with the music performed in 4 phases. Angular displacement of the hip joint's right was significant difference that skilled group was to swing in all phases and unskilled group was showed significant differences in the 3 phase. Angular displacement of the hip joint's left was significant difference that skilled group in all phases except for two phase. Unskilled group was significant differences in all phases. The angular displacement of knee joint's right were significant difference that skilled group was to swing in all phases. Unskilled group was showed except for 1 phase a significant difference was found in all phases. The angular displacement of knee joint's left were significant difference that skilled group and unskilled group showed significant differences in all phases. The angular displacement of ankle joint's right and left ankle joint were significant differences, both skilled and unskilled group in all aspects. Consequently, efficient golf swing may affect that the accuracy considered over the regular rhythmic auditory training methods that provide auditory information.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1.Wulf G., Shea CH., Matschiner S. Frequent feedback enhances complex motor skill learning. J Mot Behav. 1998. 30:180–92.
Article2.Shea CH., Wright DL., Wulf G., Whitacre C. Physical and observational practice afford unique learning opportunities. J Mot Behav. 2000. 32:27–36.
Article3.Budney DR., Bellow DG. On the swing mechanics of a matched set of golf clubs. Res Q Exerc Sport. 1982. 53:185–92.
Article4.Park SS. Optimizing time of impact in golf swing. J Sport Sci Res. 1991. 10:51–69.5.Lee HY., Woo BH. Kinematical analysis of golf swing on rhythm. Korean J Golf Stud. 2008. 2:1–8.6.Nicklaus J., Bowden K. Golf my way. New York, NY: Fireside;1998.7.Geiberger Al. Tempo, golf's master key: how to find it, how to keep it. Norwalk: Distribution By Simon And Schuster;1980.8.Choi GJ. Effects of practice with music on golf swing learning [dissertation]. Seoul: Department of Physical Education Graduate School Seoul National University;2003.9.Neal RJ., Wilson BD. 3D kinematics and kinetics of the golf swing. J Appl Biomech. 1985. 1:221–32.
Article10.Merrins E. Is your timing in lune. Golf Mag. 1979. 36–9.11.Choi GJ. Effects of practice with music on rhythm of golf swing and distance. J Korean Physic Educ Assoc Girls Women. 2005. 19:55–65.12.Kim GB., Yoon GW. A review of timing control mechanism in human movement. J Sport Sci Res. 1991. 10:21–34.13.Lai Q., Shea CH., Bruechert L., Little M. Auditory model enhances relative-timing learning. J Mot Behav. 2002. 34:299–307.
Article14.Shea CH., Wulf G., Park JH., Gaunt B. Effects of an auditory model on the learning of relative and absolute timing. J Mot Behav. 2001. 33:127–38.
Article15.Park YM. Teaching method for enhancement of rhythmic sense based on Gordon's theory of music learning sequence [dissertation]. Seoul: Department of Physical Education Graduate School Yonsei University;2000.16.Strand BN., Wilson R. Assessing sport skills. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics Publishers;1993.17.Kim YR. Learning effect of visual and auditory feedback by motivation level in task participation of golf putting. Korea J Sports Sci. 2008. 17:405–17.18.Cochran AJ., Stobbs J. Golf Society of Great Britain. The search for the perfect swing. Philadelphia: Lippincott;1968.19.Crenshaw B. 8 ways to slow it down. Golf Mag. 1978. Oct:66–8.20.Geiberger Al. Dennis L. Tempo, golf's master key: how to find it, how to keep it. New York: Golf Digest, Distribution by Simon and Schuster;1980.21.Walton JN. The electromyogram in myopathy: analysis with the audio-frequency spectrometer. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1952. 15:219–26.
Article22.Redanty J. More distance for the older golfer. Golf Mag. 1975. Aug:40–1.23.Salthouse TA. Speed of behavior and it simplication for cognition. Birren JE, Schaie KW, editors. editors.Handbook of the psychology of aging. 2nd ed.NewYork: Van Nostrand Reinhold Co.;1985. p. 400–26.24.Stelmach GE., Nahom A. Cognitive-motor abilities of the elderly driver. Hum Factors. 1992. 34:53–65.
Article25.Ahn WS. Kinematical analysis of golf drive swing motion. Korea Sports Res. 2005. 16:57–66.26.Yoon GW. The effects of auditory information on learning of golf putting. J Korea Soc Study Physic Educ. 2004. 8:187–96.27.Mann R. Grand cypress academy of golf, grand cypress report. Orlando, FL: Grand cypress academy of golf;1987.28.Lim TS., Lee KS. A comparative study between kinematic variables of the driver and the Iron in golf swing. Korean J Sport Biomech. 1996. 6:35–51.29.Na SH. The kinematic analysis of the nether limbs during the golf driver swing. Korean J Sports Sci. 2012. 21:1295–306.30.Jagacinski RJ., Greenberg N., Liao MJ. Tempo, rhythm, and aging in golf. J Motor Behav. 1997. 29:159–73.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Golf-related Spine and Lower Extremity Injury
- Electromyographic Analysis of Left Leg Muscle Activity during Golf Driver Swing
- Golf-related Injury: Upper Extremity
- Effects of Stretching Exercise on the Head Speed of Golf Club and Driving Distance
- Characteristics of Pain in Professional Golfers Who Visited a Mobile Medical Clinic during the Season