Korean J Sports Med.
2011 Jun;29(1):64-67. 10.5763/kjsm.2011.29.1.64.
Calcific Tendinitis of the Common Extensor Tendon: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Chonbuk National University College of Medicine, Jeonju, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea. cbnuoskbs@naver.com
- KMID: 2054010
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5763/kjsm.2011.29.1.64
Abstract
- Calcific tendinitis is most common seen within the rotator cuff of the shoulder, although it may develop around the hip, wrist, elbow, knee, forefoot, and neck. However, there has been no report in the medical literature regarding calcific tendinitis of the common extensor tendon. We present a case of a 26-year-old woman who had calcific tendinitis of the common extensor tendon. Intraoperatively, partial rupture and calcific deposit at the insertion of the common extensor tendon were seen. We were removed calcific deposit and ruptured tissue of common extensor tendon, and then ruptured common extensor tendon was sutured. The patient showed excellent result two years postoperatively with return to range in a degree of activity levels.
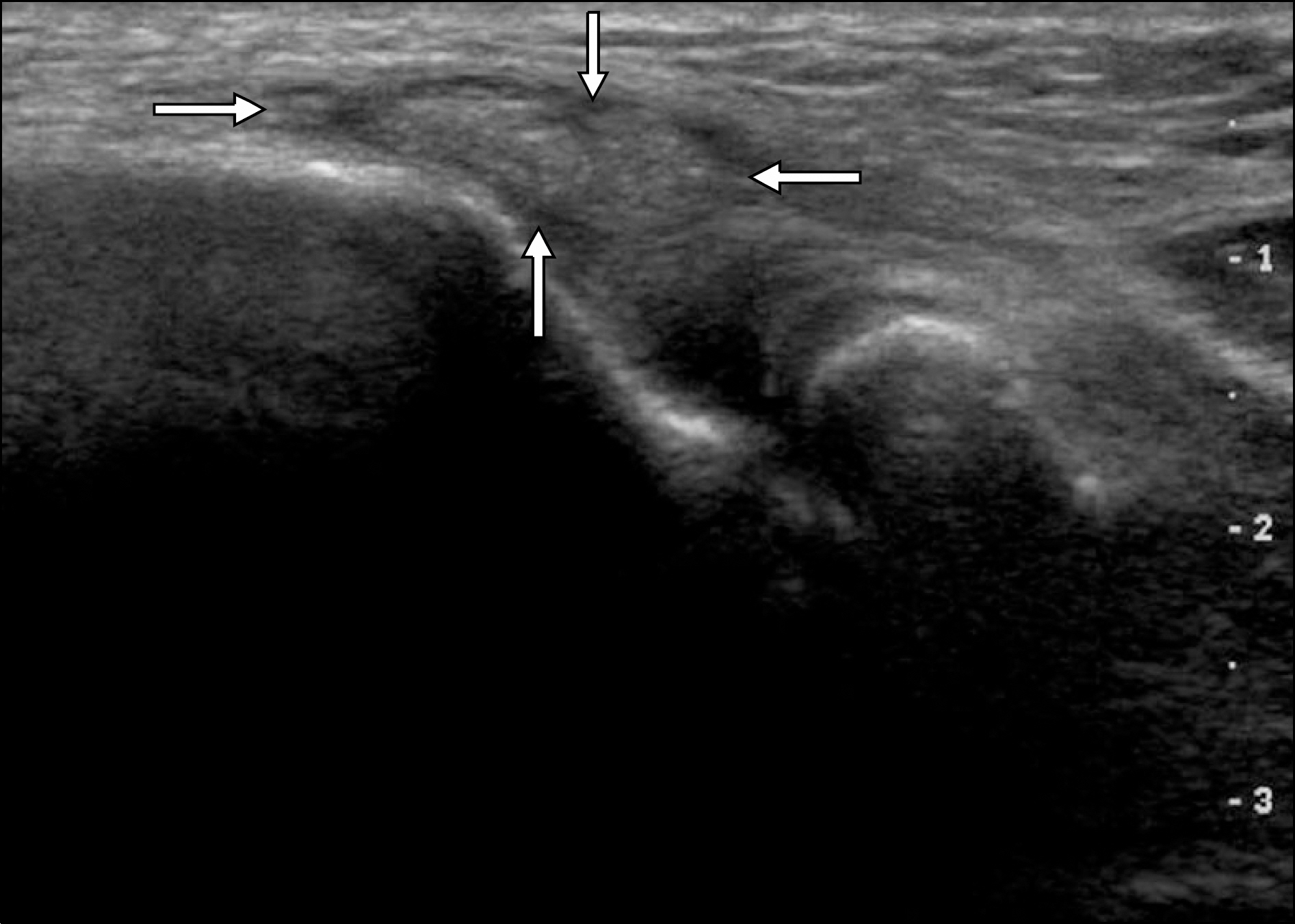
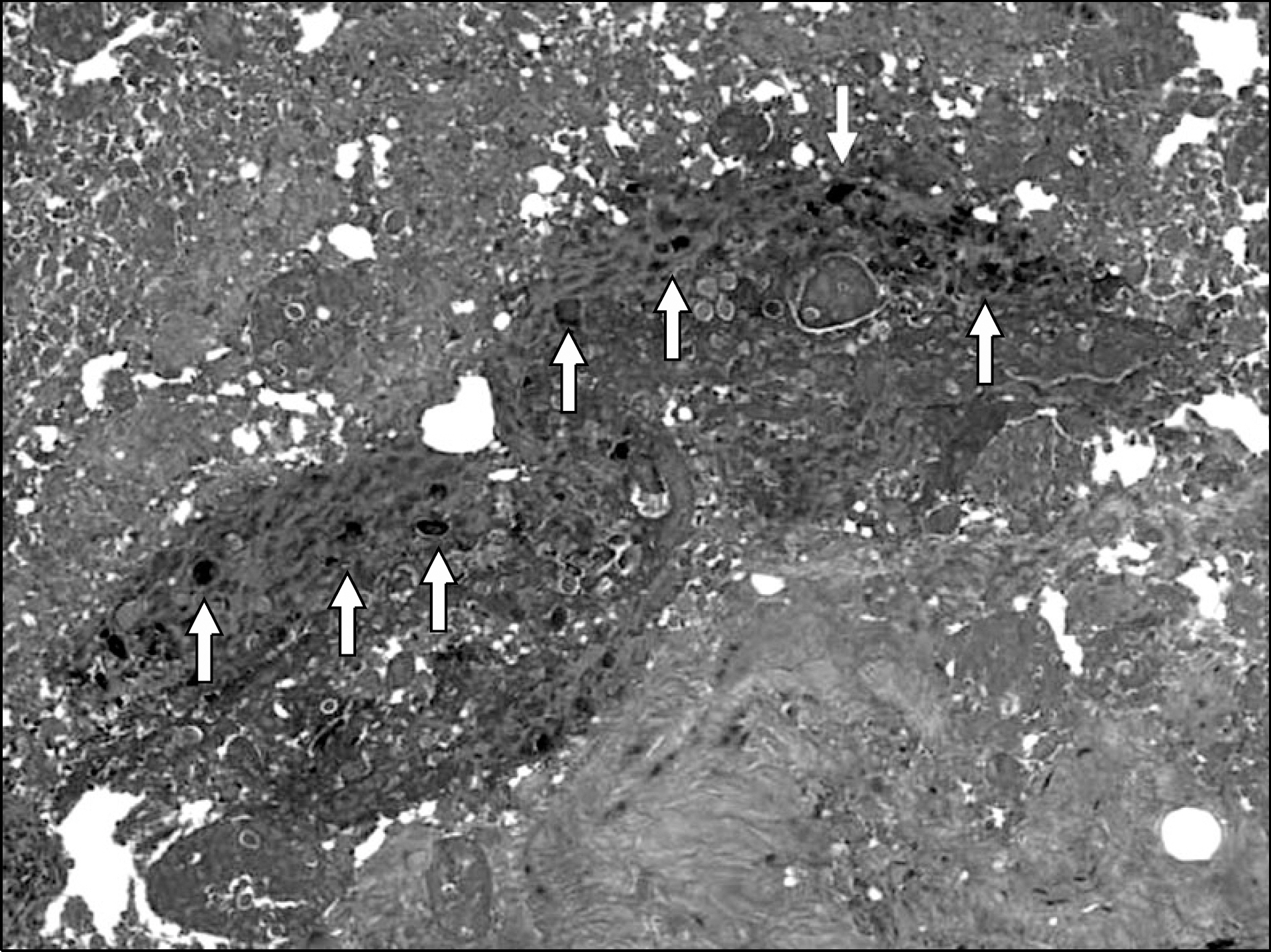
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Cox D, Paterson FW. Acute calcific tendinitis of peroneus longus. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991; 73:342.
Article2. Murase T, Tsuyuguchi Y, Hidaka N, Doi T. Calcific tendinitis at the biceps insertion causing rotatory limitation of the forearm: a case report. J Hand Surg Am. 1994; 19:266–8.
Article3. Kim JS, Yoo JH, Yoo SO. Arthroscopic treatment of chronic calcific tendinitis of the shoulder. J Korean Shoulder Elbow Soc. 1998; 1:6–11.4. Brinsden MD, Wilson JH. Acute calcific tendinitis of the peroneus longus tendon. Injury Extra. 2005; 36:426–7.
Article5. Uhthoff HK, Sarkar K, Maynard JA. Calcifying tendinitis: a new concept of its pathogenesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976; 118:164–8.6. Hamada J, Ono W, Tamai K, Saotome K, Hoshino T. Analy-sis of calcium deposits in calcific periarthritis. J Rheumatol. 2001; 28:809–13.7. Raghavendran RR, Peart F, Grindulis KA. Subcutaneous calcification following injection of triamcinolone hexacetonide for plantar fasciitis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008; 47:1838.
Article8. Uhthoff HK, Loehr JW. Calcific tendinopathy of the rotator cuff: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1997; 5:183–91.
Article9. Ark JW, Flock TJ, Flatow EL, Bigliani LU. Arthroscopic treatment of calcific tendinitis of the shoulder. Arthroscopy. 1992; 8:183–8.
Article10. Kim MK, Bae JH, Jeon YS. Conservative and early arthroscopic treatment of calcific tendinitis. J Korean Arthrosc Soc. 2009; 13:149–54.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Calcific Tendinitis of Peroneus Longus Tendon (A Case Report)
- Arthroscopic Treatment of Calcific Tendinitis of Subscapularis Tendon: A Case Report
- Arthroscopic treatment of chronic calcific tendinitis with intraosseous migration: a case report
- Calcific Tendinitis of the Supraspinatus Tendon in a 7-year-old Girl: A Case Report
- Calcific Tendinits at the Origin of Common Extensor Tendons of the Forearm: A Report of Two Cases