Lab Med Online.
2013 Jul;3(3):178-182. 10.3343/lmo.2013.3.3.178.
A Complex Chromosomal Rearrangement Involving 46,XX,t(1;7;16)(p32.1;q22;q13) in a Female with Recurrent Miscarriages After in vitro Fertilization
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea. juwon76@yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea.
- KMID: 2053554
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/lmo.2013.3.3.178
Abstract
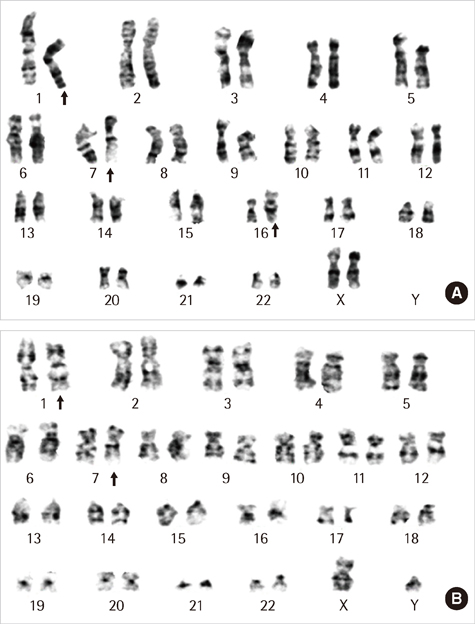
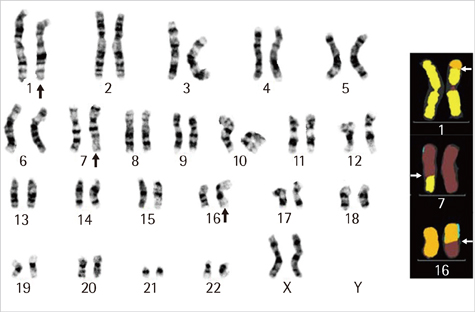
- Balanced complex chromosomal rearrangements involving three or more chromosomes are often detected in phenotypically normal female patients with an adverse obstetric history. Here, we report a 32-yr-old phenotypically normal female with a history of multiple in vitro fertilization (IVF) failures and carrying a balanced complex chromosomal rearrangement involving chromosomes 1, 7, and 16. Cytogenetic analysis revealed the following complex karyotype: 46,XX,t(1;7;16)(p32.1;q22;q13). The patient achieved a twin pregnancy after IVF, although no heartbeat was detected during the sixth gestational week checkup. Tissues from intrauterine fetal demise were tested for chromosomal analysis and revealed 46,XX,t(1;7;16)(p32.1;q22;q13)mat and 46,XY,der(1)t(1;16)(p32.1;q13),der(7)t(1;7) (p32.1;q22)mat. This case illustrates the importance of chromosomal analysis in infertile females or infertile females with multiple IVF failures. Therefore, it would be beneficial for patients visiting infertility clinics to undergo cytogenetic screening for complex chromosome rearrangements before further counseling and prenatal investigations.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Pellestor F, Anahory T, Lefort G, Puechberty J, Liehr T, Hédon B, et al. Complex chromosomal rearrangements: origin and meiotic behavior. Hum Reprod Update. 2011; 17:476–494.
Article2. Batista DA, Pai GS, Stetten G. Molecular analysis of a complex chromosomal rearrangement and a review of familial cases. Am J Med Genet. 1994; 53:255–263.
Article3. Gorski JL, Kistenmacher ML, Punnett HH, Zackai EH, Emanuel BS. Reproductive risks for carriers of complex chromosome rearrangements: analysis of 25 families. Am J Med Genet. 1988; 29:247–261.
Article4. Iyer PA, Vyas JC, Ranjan P, Saranath D. A de novo complex chromosomal rearrangement of 46,XX,t(7;15;13)(p15;q21;q31) in female with an adverse obstetric History. Int J Hum Genet. 2009; 9:139–143.
Article5. Patsalis PC, Evangelidou P, Charalambous S, Sismani C. Fluorescence in situ hybridization characterization of apparently balanced translocation reveals cryptic complex chromosomal rearrangements with unexpected level of complexity. Eur J Hum Genet. 2004; 12:647–653.
Article6. Rodriguez MT, Martin MJ, Abrisqueta JA. A complex balanced rearrangement involving four chromosomes in an azoospermic man. J Med Genet. 1985; 22:66–67.
Article7. Batanian JR, Eswara MS. De novo apparently balanced complex chromosome rearrangement (CCR) involving chromosomes 4, 18, and 21 in a girl with mental retardation: report and review. Am J Med Genet. 1998; 78:44–51.
Article8. De Gregori M, Ciccone R, Magini P, Pramparo T, Gimelli S, Messa J, et al. Cryptic deletions are a common finding in "balanced" reciprocal and complex chromosome rearrangements: a study of 59 patients. J Med Genet. 2007; 44:750–762.
Article9. Madan K, Nieuwint AW, van Bever Y. Recombination in a balanced complex translocation of a mother leading to a balanced reciprocal translocation in the child. Review of 60 cases of balanced complex translocations. Hum Genet. 1997; 99:806–815.
Article10. Kleczkowska A, Fryns JP, Van den Berghe H. Complex chromosomal rearrangements (CCR) and their genetic consequences. J Genet Hum. 1982; 30:199–214.11. Templado C, Bosch M, Benet J. Frequency and distribution of chromosome abnormalities in human spermatozoa. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2005; 111:199–205.
Article12. Mau-Holzmann UA. Somatic chromosomal abnormalities in infertile men and women. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2005; 111:317–336.
Article13. Oliver-Bonet M, Ko E, Martin RH. Male infertility in reciprocal translocation carriers: the sex body affair. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2005; 111:343–346.
Article14. Giardino D, Corti C, Ballarati L, Colombo D, Sala E, Villa N, et al. De novo balanced chromosome rearrangements in prenatal diagnosis. Prenat Diagn. 2009; 29:257–265.
Article15. Kousseff BG, Papenhausen P, Essig YP, Torres MP. Complex chromosome rearrangement with ankyloblepharon filiforme adnatum. J Med Genet. 1993; 30:167–170.
Article16. Kausch K, Haaf T, Köhler J, Schmid M. Complex chromosomal rearrangement in a woman with multiple miscarriages. Am J Med Genet. 1988; 31:415–420.
Article17. Johannisson R, Löhrs U, Passarge E. Pachytene analysis in males heterozygous for a familial translocation (9;12;13) (q22; q22; q32) ascertained through a child with partial trisomy 9. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1988; 47:160–166.
Article18. Kovács A, Villagómez DA, Gustavsson I, Lindblad K, Foote RH, Howard TH. Synaptonemal complex analysis of a three-breakpoint translocation in a subfertile bull. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1992; 61:195–201.
Article19. Saadallah N, Hulten M. A complex three breakpoint translocation involving chromosomes 2, 4, and 9 identified by meiotic investigations of a human male ascertained for subfertility. Hum Genet. 1985; 71:312–320.
Article20. Loup V, Bernicot I, Janssens P, Hedon B, Hamamah S, Pellestor F, et al. Combined FISH and PRINS sperm analysis of complex chromosome rearrangement t(1;19;13): an approach facilitating PGD. Mol Hum Reprod. 2010; 16:111–116.
Article21. Hecht F, Kaiser-McCaw B, Patil S, Wyandt HE. Are balanced translocations really balanced? Preliminary cytogenetic evidence for position effect in man. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1978; 14:281–286.22. Sismani C, Kitsiou-Tzeli S, Ioannides M, Christodoulou C, Anastasiadou V, Stylianidou G, et al. Cryptic genomic imbalances in patients with de novo or familial apparently balanced translocations and abnormal phenotype. Mol Cytogenet. 2008; 1:15.
Article23. Escudero T, Estop A, Fischer J, Munne S. Preimplantation genetic diagnosis for complex chromosome rearrangements. Am J Med Genet A. 2008; 146A:1662–1669.
Article24. Lim CK, Cho JW, Kim JY, Kang IS, Shim SH, Jun JH. A healthy live birth after successful preimplantation genetic diagnosis for carriers of complex chromosome rearrangements. Fertil Steril. 2008; 90:1680–1684.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Rarely Observed Jumping Translocation in Spontaneous Abortion
- A Case of 46 XX Male Syndrome
- A Case with Balanced Chromosome Rearrangement Involving Chromosomes 9, 14, and 13 in a Woman with Recurrent Abortion
- Cytogenetic Study for Reciprocal and Robertsonian Translocation
- A Case of Synophthalmia with Chromosomal Anomaly: 46, XX, -15, t (15q, 21q)