Lab Med Online.
2013 Jul;3(3):145-154. 10.3343/lmo.2013.3.3.145.
Comparison between V-Tubes and BD Vacutainer Tubes for Use in Laboratory Tests
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. mgshin@chonnam.ac.kr
- 2School of Electronics and Computer Engineering, College of Engineering, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 2053549
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/lmo.2013.3.3.145
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Vacuum tubes are widely used in clinical laboratories for routine tests. We compared a newly developed V-tube (AB Medical, Korea) and BD tubes (BD, USA) in common clinical assays, i.e., hematological, chemical, and immunological tests.
METHODS
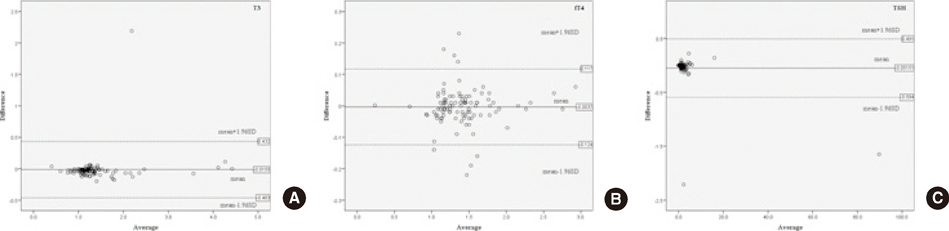
In total, 100 volunteers comprising 79 patients and 21 healthy volunteers were recruited and peripheral blood samples were collected with 2 brands of EDTA tubes and serum-separating tubes (SSTs). EDTA-tube samples were evaluated using 16 routine hematological tests. The SST samples were analyzed for 32 routine chemical parameters and 3 thyroid hormones. The results were statistically analyzed using the paired t-test and Bland-Altman plot. In addition, the stability of each analyte in 2 brands of vacutainers was evaluated. The results of the hematological tests at t=0 hr were compared with those at t=72+/-2 hr, and the results of the chemical parameters and thyroid hormones at t=0 hr were compared with those at t=72+/-2 hr and t=168+/-2 hr for each tube.
RESULTS
Paired t-test analysis revealed that the test results of 16 routine hematological parameters, 32 routine chemical parameters, and 3 thyroid hormones showed clinically allowable differences between the 2 brands of vacuum tubes (t=0 hr). The results obtained when using V-tubes showed a statistically significant correlation with those obtained when using BD tubes. The stability of each analyte was similar in both vacuum tubes. Except for 10 parameters (white blood cell count, mean corpuscular volume, basophils [%], mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration, monocytes [%], phospholipid, sodium, potassium, chloride, and free T4), all parameters showed significant but clinically allowable differences with regard to storage duration.
CONCLUSIONS
The newly developed V-tube vacutainers provide a suitable alternative to BD tubes in common clinical laboratories.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
A Comparison of the Performance of Soyagreentec Ampulab EDTA and Sodium Citrate Tubes with That of BD Vacutainer Tubes
Jun Hyung Lee, Young Joo Cha, Dong Soon Lee, Seon Young Kim
Lab Med Online. 2015;5(2):92-100. doi: 10.3343/lmo.2015.5.2.92.Comparison between Medion Vacuon Tube and BD Vacutainer Tube for Clinical Laboratory Practice
Jinho Jhang, Ju Young Cho, Jong-Han Lee, Juwon Kim
Lab Med Online. 2019;9(2):77-83. doi: 10.3343/lmo.2019.9.2.77.
Reference
-
1. Kim JY, Nam DH, Kim SH, Yang JH, Yoon SY, Lim CS, et al. Evaluation of green Vac-Tube in clinical laboratory Tests. J Lab Med Qual Assur. 2008; 30:307–314.2. Reinartz JJ, Ramey ML, Fowler MC, Killeen AA. Plastic vs glass SST evacuated serum-separator blood-drawing tubes for endocrinologic analytes. Clin Chem. 1993; 39:2535–2536.
Article3. Oh SH. Comparison of two new plastic tubes (Sekisui INSEPACK and Green Cross Green Vac-Tube) with BD Vacutainer tubes for 49 analytes. Korean J Lab Med. 2007; 27:69–75.
Article4. Bowen RA, Hortin GL, Csako G, Otañez OH, Remaley AT. Impact of blood collection devices on clinical chemistry assays. Clin Biochem. 2010; 43:4–25.
Article5. Dewitte K, Fierens C, Stöckl D, Thienpont LM. Application of the Bland-Altman plot for interpretation of method-comparison studies: a critical investigation of its practice. Clin Chem. 2002; 48:799–801.
Article6. Medicare, Medicaid and CLIA programs; regulations implementing the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments of 1988 (CLIA)-HCFA. Final rule with comment period. Fed Regist. 1992; 57:7002–7186.7. Tanner M, Kent N, Smith B, Fletcher S, Lewer M. Stability of common biochemical analytes in serum gel tubes subjected to various storage temperatures and times pre-centrifugation. Ann Clin Biochem. 2008; 45:375–379.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Two New Plastic Tubes (Sekisui INSEPACK and Green Cross Green Vac-Tube) with BD Vacutainer Tubes for 49 Analytes
- Comparison of Sekisui Trank Insepack and BD Vacutainer Plastic Citrate Tubes for Routine Coagulation Assays
- A Comparison of the Performance of Soyagreentec Ampulab EDTA and Sodium Citrate Tubes with That of BD Vacutainer Tubes
- Comparison between Medion Vacuon Tube and BD Vacutainer Tube for Clinical Laboratory Practice
- Comparison of Three Plastic Tubes (Two Gongdong Vacuum Blood Tubes and Improve Vacuum Blood Collection Tube) with BD Vacutainer Tube for 37 Laboratory Tests