Clin Endosc.
2014 May;47(3):266-269. 10.5946/ce.2014.47.3.266.
Body Position Adjustment May Facilitate Capsule Endoscopic Real-Time Examination in Patients with a Large Amount of Food Retention in the Stomach
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastroenterology, First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China. zhbingqiang@163.com
- KMID: 2049025
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2014.47.3.266
Abstract
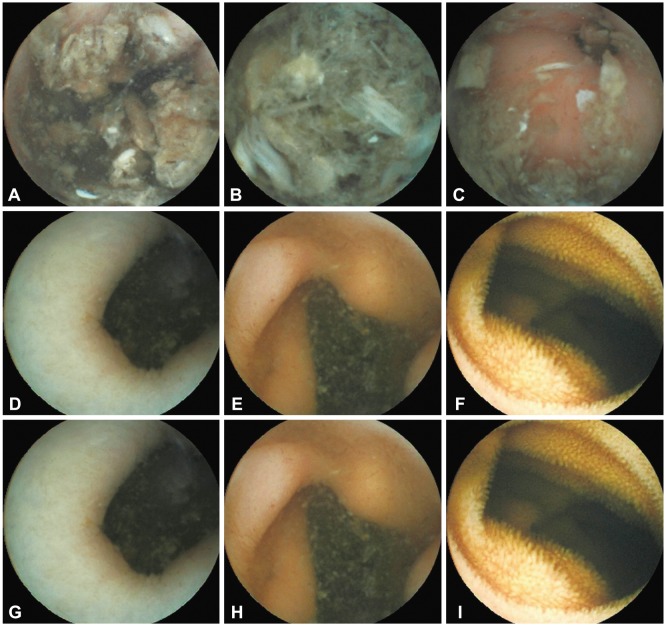
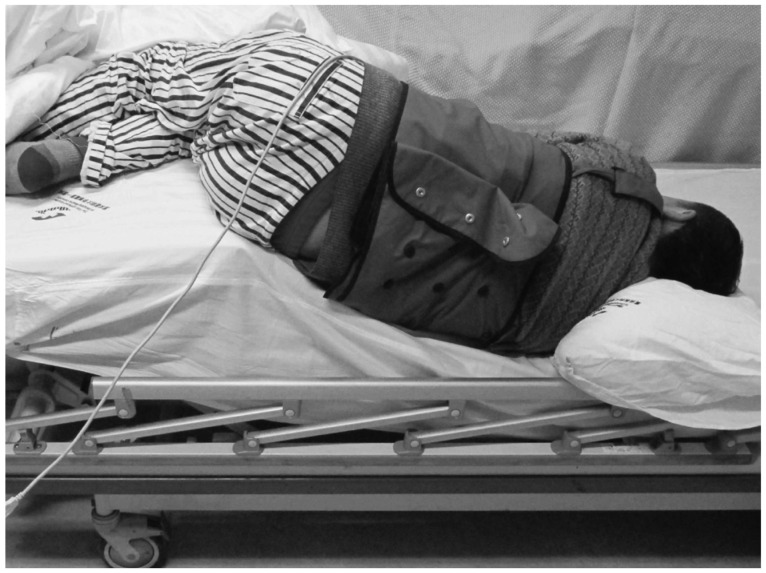
- A patient with acute obscure gastrointestinal bleeding was found to have a large amount of food retention in the stomach after fasting for >12 hours. We tried to adjust the patient's body position to facilitate capsule endoscopic examination. The patient laid on the bed on his right side, which is the position required for a normal procedure, and then his hip was raised while his upper body was lowered gradually until the pylorus appeared at the center of the screen of the real-time monitor. It took 15 minutes of body position adjustment to make the pylorus appear at the center of the monitor and another 5 minutes for the capsule endoscope to enter the duodenum. The lesion was ultimately found at the terminal small intestine.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bass LM, Misiewicz L. Use of a real-time viewer for endoscopic deployment of capsule endoscope in the pediatric population. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2012; 55:552–555. PMID: 22684350.
Article2. Orlando G, Luppino IM, Lerose MA, et al. Feasibility of capsule endoscopy in elderly patients with obscure gastrointestinal bleeding. An upto-date report. BMC Surg. 2012; 12(Suppl 1):S30. PMID: 23173943.
Article3. Höög CM, Bark LÅ, Arkani J, Gorsetman J, Broström O, Sjöqvist U. Capsule retentions and incomplete capsule endoscopy examinations: an analysis of 2300 examinations. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2012; 2012:518718. PMID: 21969823.
Article4. Shiotani A, Honda K, Kawakami M, et al. Use of an external real-time image viewer coupled with prespecified actions enhanced the complete examinations for capsule endoscopy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011; 26:1270–1274. PMID: 21443670.
Article5. Shim KN, Moon JS, Chang DK, et al. Guideline for capsule endoscopy: obscure gastrointestinal bleeding. Clin Endosc. 2013; 46:45–53. PMID: 23423225.
Article6. Eliakim R. Video capsule endoscopy of the small bowel. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2008; 24:159–163. PMID: 18301265.
Article7. Nakamura T, Terano A. Capsule endoscopy: past, present, and future. J Gastroenterol. 2008; 43:93–99. PMID: 18306982.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Role of Capsule Endoscopy in the Diagnosis of Crohn's Disease
- Small Bowel Obstruction and Capsule Retention by a Small Bowel Ulcer That Was Not Found on Capsule Endoscopy
- A Pilot Trial of Ambulatory Monitoring of Gastric Motility Using a Modified Magnetic Capsule Endoscope
- A study on the difference of gastrointestinal transit time with minimized capsule endoscope in dogs
- The Influence of Operative Approach on Food Retention after Open and Laparoscopy-Assisted Distal Gastrectomy (LADG) for Gastric Cancer