Seoul National University Bundang Hospital's Electronic System for Total Care
- Affiliations
-
- 1Center for Medical Informatics, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. neuroandy@snubh.org
- 2Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 3Department of Psychiatry, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 4Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 6Department of Nursing, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 7Department of Plastic Surgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 8Department of Orthopedics, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 9ezCaretech Co., Itd., Seoul, Korea.
- 10Department of Ophthalmology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 11Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Seoul Metropolitan Government Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 12Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2045578
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2012.18.2.145
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, which is the first Stage 7 hospital outside of North America, has adopted and utilized an innovative and emerging information technology system to improve the efficiency and quality of patient care. The objective of this paper is to briefly introduce the major components of the SNUBH information system and to describe our progress toward a next-generation hospital information system (HIS).
METHODS
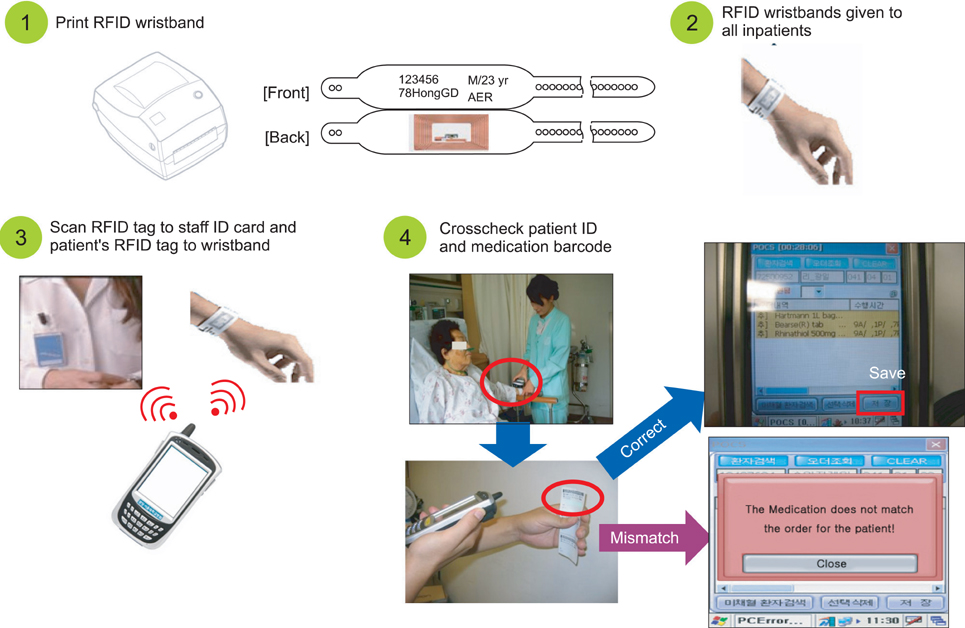
SNUBH opened in 2003 as a fully digital hospital by successfully launching a new HIS named BESTCare, "Bundang hospital Electronic System for Total Care". Subsequently, the system has been continuously improved with new applications, including close-loop medication administration (CLMA), clinical data warehouse (CDW), health information exchange (HIE), and disaster recovery (DR), which have resulted in the achievement of Stage 7 status.
RESULTS
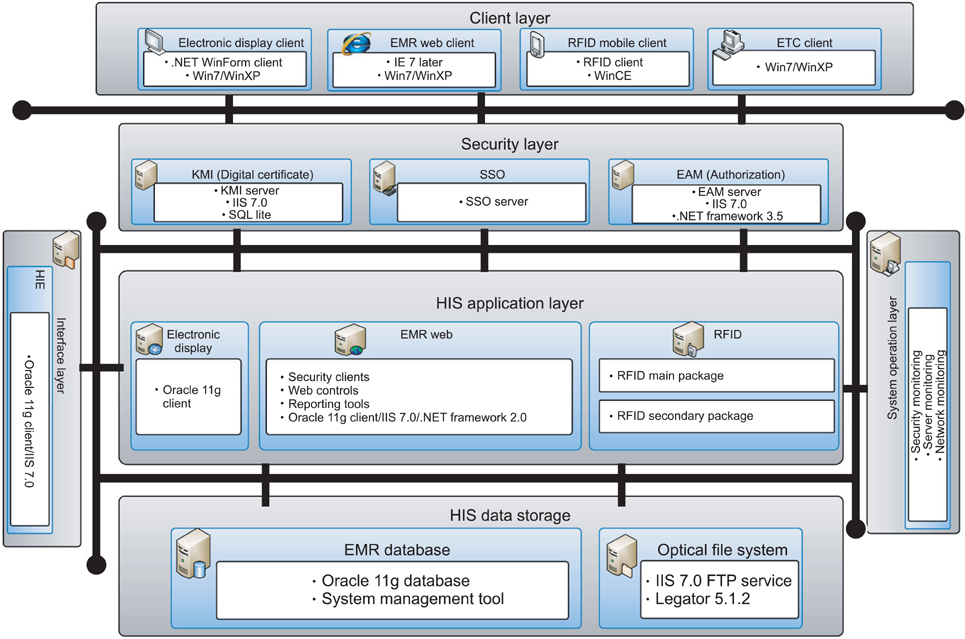
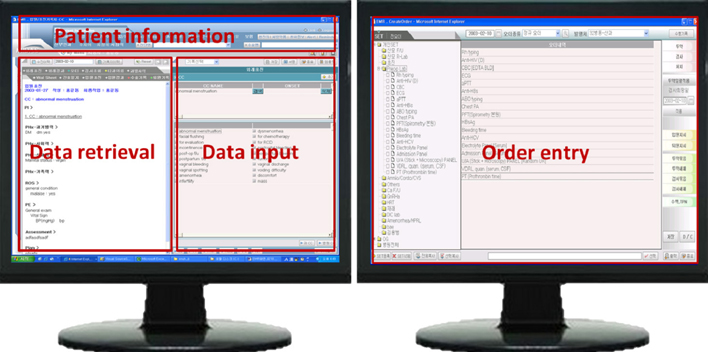
The BESTCare system is an integrated system for a university hospital setting. BESTCare is mainly composed of three application domains: the core applications, an information infrastructure, and channel domains. The most critical and unique applications of the system, such as the electronic medical record (EMR), computerized physician order entry (CPOE), clinical decision support system (CDSS), CLMA, CDW, HIE, and DR applications, are described in detail.
CONCLUSIONS
Beyond our achievement of Stage 7 hospital status, we are currently developing a next-generation HIS with new goals of implementing infrastructure that is flexible and innovative, implementing a patient-centered system, and strengthening the IT capability to maximize the hospital value.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Oral Allergy Syndrome in Birch Pollen-Sensitized Patients from a Korean University Hospital
Jung-Hyun Kim, Sae-Hoon Kim, Heung-Woo Park, Sang-Heon Cho, Yoon-Seok Chang
J Korean Med Sci. 2018;33(33):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2018.33.e218.Monitor Preference for Electronic Medical Record in Outpatient Clinic
Kee-Hyuck Lee, Woo Kyung Bae, Jong Soo Han, Sooyoung Yoo, Jon Soo Kim, Jonghoar Yun, Hyun Young Baek, Rong-Min Baek, Hee Hwang
Healthc Inform Res. 2012;18(4):266-271. doi: 10.4258/hir.2012.18.4.266.Factors Affecting Electronic Medical Record System Adoption in Small Korean Hospitals
Young-Taek Park, Jinhyung Lee
Healthc Inform Res. 2014;20(3):183-190. doi: 10.4258/hir.2014.20.3.183.Impacts of Financial Coverage on Long-Term Outcome of Intensive Care Unit Survivors in South Korea
Jun Kwon Cha, Tak Kyu Oh, In-Ae Song
Yonsei Med J. 2019;60(10):976-983. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2019.60.10.976.
Reference
-
1. Palacio C, Harrison JP, Garets D. Benchmarking electronic medical records initiatives in the US: a conceptual model. J Med Syst. 2010. 34:273–279.
Article2. Hillestad R, Bigelow J, Bower A, Girosi F, Meili R, Scoville R, Taylor R. Can electronic medical record systems transform health care? Potential health benefits, savings, and costs. Health Aff (Millwood). 2005. 24:1103–1117.
Article3. Gartee R. Essentials of electronic health records. 2012. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.4. Choi J, Kim JW, Seo JW, Chung CK, Kim KH, Kim JH, Kim JH, Chie EK, Cho HJ, Goo JM, Lee HJ, Wee WR, Nam SM, Lim MS, Kim YA, Yang SH, Jo EM, Hwang MA, Kim WS, Lee EH, Choi SH. Implementation of Consolidated HIS: Improving Quality and Efficiency of Healthcare. Healthc Inform Res. 2010. 16:299–304.
Article5. Healthcare Information and Management System Society (HIMSS) Analytics. Stage 7 hospitals [Internet]. 2012. cited at 2012 May 21. Chicago, IL: HIMSS;Available from: http://www.himssanalyticsasia.org/emradoptionmodel-stage7hospitals.asp.6. Richter-Ehrenstein C, Heymann S, Schneider A, Vargas Hein O. Effects of a clinical pathway 3 years after implementation in breast surgery. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2012. 285:515–520.
Article7. Han SH, Lee MH, Kim SG, Jeong JY, Lee BN, Choi MS, Kim IK, Park WS, Ha K, Cho E, Kim Y, Bae JB. Implementation of Medical Information Exchange System Based on EHR Standard. Healthc Inform Res. 2010. 16:281–289.
Article8. Franklin BD, O'Grady K, Donyai P, Jacklin A, Barber N. The impact of a closed-loop electronic prescribing and administration system on prescribing errors, administration errors and staff time: a before-and-after study. Qual Saf Health Care. 2007. 16:279–284.
Article9. Poon EG, Keohane CA, Yoon CS, Ditmore M, Bane A, Levtzion-Korach O, Moniz T, Rothschild JM, Kachalia AB, Hayes J, Churchill WW, Lipsitz S, Whittemore AD, Bates DW, Gandhi TK. Effect of bar-code technology on the safety of medication administration. N Engl J Med. 2010. 362:1698–1707.
Article10. Paoletti RD, Suess TM, Lesko MG, Feroli AA, Kennel JA, Mahler JM, Sauders T. Using bar-code technology and medication observation methodology for safer medication administration. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2007. 64:536–543.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Electronic Medical Records in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
- User's Satisfaction on the Electronic Medical Record System in Seoul National University Bundang Hospital
- Implementation of a Next-Generation Electronic Nursing Records System Based on Detailed Clinical Models and Integration of Clinical Practice Guidelines
- Formative Evaluation of Standard Terminology-based Electronic Nursing Record System in Clinical Setting
- Availability of nursing data in an electronic nursing record system for a development of a risk assessment tool for pressure ulcers