World J Mens Health.
2015 Aug;33(2):50-61. 10.5534/wjmh.2015.33.2.50.
Glans Penis Augmentation Using Hyaluronic Acid Gel as an Injectable Filler
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. dgmoon@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 2032824
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5534/wjmh.2015.33.2.50
Abstract
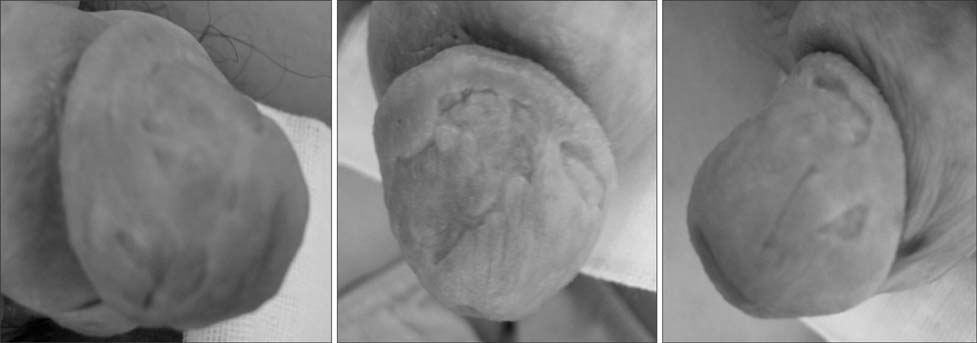
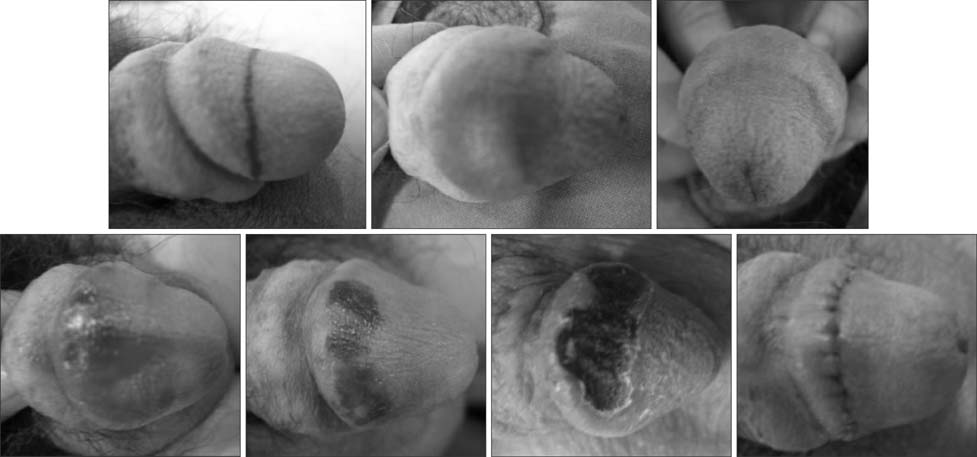
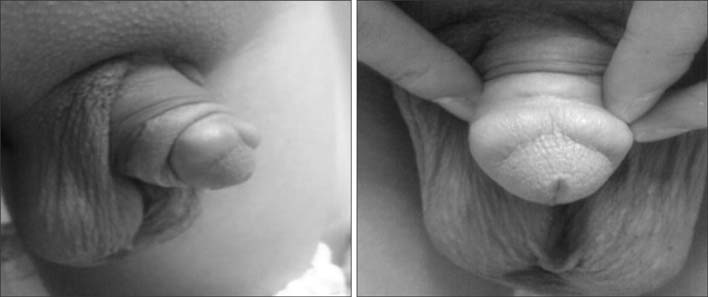
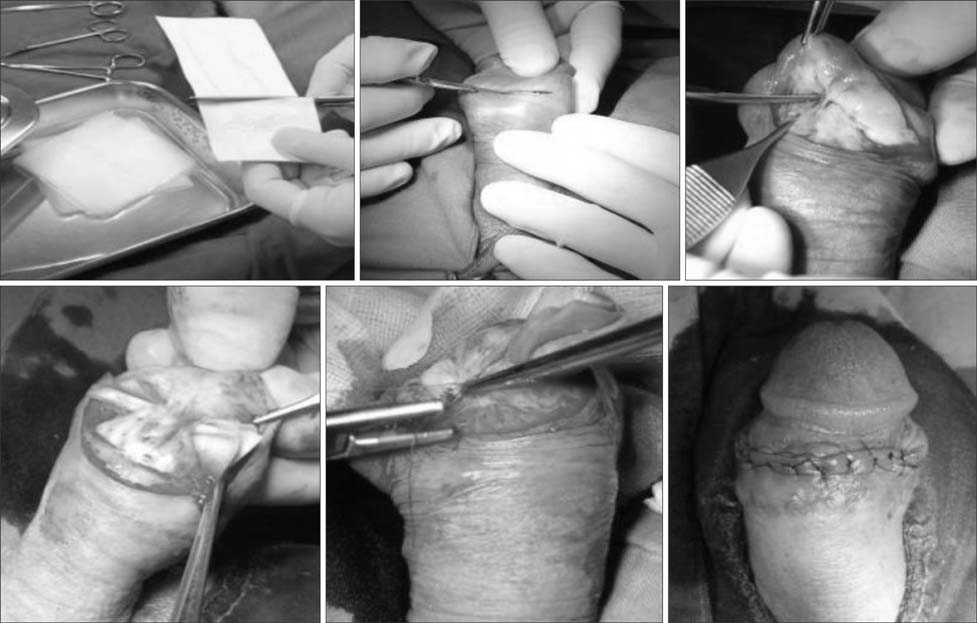
- Glans penis augmentation (GPA) has received little attention from experts despite the existence of a subset of patients who may be dissatisfied with a small glans or poor tumescence of the glans during erection. Recently, GPA using an injectable filler or implantation of a graft or filler has been developed. Despite a demanding injection technique and inevitable uneven undulation of the glandular surface, GPA using injectable hyaluronic acid (HA) gel is a novel and useful therapy and an effective and safe procedure for soft tissue enhancement. For long-term presence of implants, timed supplementation can be used similar to that for fascial plasty. In complications such as mucosal necrosis of the glans penis, most cases occur from the use of non-HA gel or an unpurified form and misunderstanding of the management protocol for immediate side effects. Currently, GPA using injectable HA gel is not recommended in the International Society for Sexual Medicine guideline due to possible sensory loss. In a 5-year long-term follow-up of GPA by subcutaneous injection of HA gel, the residual volume of implants decreased by 15% of the maximal glandular circumference, but was still effective for alleviating the hypersensitivity of the glans penis in premature ejaculation patients. For efficacy in premature ejaculation, selection of appropriate candidates is the most important factor for success. GPA does not harm erectile function and is less invasive and irreversible compared to dorsal neurectomy. To refine the procedure, more interest and well-designed studies are required for the establishment of the procedure.
MeSH Terms
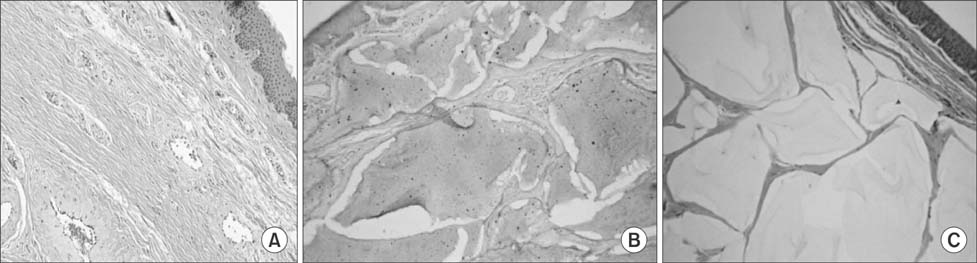
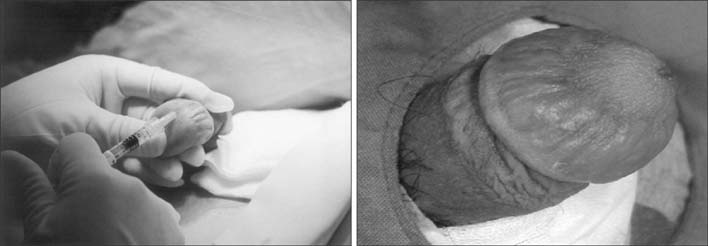
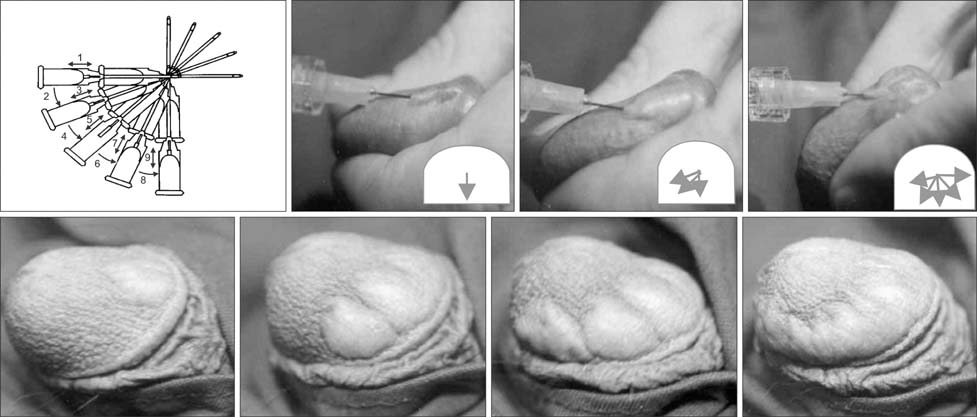
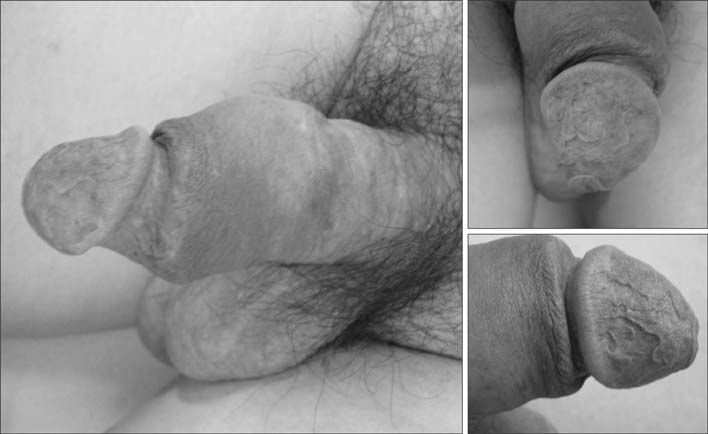
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Paraffin Granuloma Associated with Buried Glans Penis-Induced Sexual and Voiding Dysfunction
Wonhee Chon, Ja Yun Koo, Min Jung Park, Kyung-Un Choi, Hyun Jun Park, Nam Cheol Park
World J Mens Health. 2017;35(2):129-132. doi: 10.5534/wjmh.2017.35.2.129.
Reference
-
1. Ebbehøj J, Metz P. Lacking tumescence of glans during penile erection. J Urol. 1985; 134:1220.
Article2. Montague DK. Penile prosthesis implantation: size matters. Eur Urol. 2007; 51:887–888.
Article3. Chew KK, Stuckey BG. Use of transurethral alprostadil (MUSE) (prostaglandin E1) for glans tumescence in a patient with penile prosthesis. Int J Impot Res. 2000; 12:195–196.
Article4. Moon DG, Kwak TI, Cho HY, Bae JH, Park HS, Kim JJ. Augmentation of glans penis using injectable hyaluronic acid gel. Int J Impot Res. 2003; 15:456–460.
Article5. Kim JJ, Kwak TI, Jeon BG, Cheon J, Moon DG. Human glans penis augmentation using injectable hyaluronic acid gel. Int J Impot Res. 2003; 15:439–443.
Article6. Perovic S, Radojicic ZI, Djordjevic MLj, Vukadinovic VV. Enlargement and sculpturing of a small and deformed glans. J Urol. 2003; 170(4 Pt 2):1686–1690. discussion 1690
Article7. Shaeer O. Supersizing the penis following penile prosthesis implantation. J Sex Med. 2010; 7:2608–2616.
Article8. Kim JJ, Kwak TI, Jeon BG, Cheon J, Moon DG. Effects of glans penis augmentation using hyaluronic acid gel for premature ejaculation. Int J Impot Res. 2004; 16:547–551.
Article9. Kwak TI, Jin MH, Kim JJ, Moon DG. Long-term effects of glans penis augmentation using injectable hyaluronic acid gel for premature ejaculation. Int J Impot Res. 2008; 20:425–428.
Article10. Abdallah H, Abdelnasser T, Hosny H, Selim O, Al-Ahwany A, Shamloul R. Treatment of premature ejaculation by glans penis augmentation using hyaluronic acid gel: a pilot study. Andrologia. 2012; 44:Suppl 1. 650–653.
Article11. Elson ML. Soft tissue augmentation. A review. Dermatol Surg. 1995; 21:491–500.12. Pollack SV. Silicone, fibrel, and collagen implantation for facial lines and wrinkles. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1990; 16:957–961.
Article13. Olenius M. The first clinical study using a new biodegradable implant for the treatment of lips, wrinkles, and folds. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 1998; 22:97–101.
Article14. Duranti F, Salti G, Bovani B, Calandra M, Rosati ML. Injectable hyaluronic acid gel for soft tissue augmentation. A clinical and histological study. Dermatol Surg. 1998; 24:1317–1325.15. Goa KL, Benfield P. Hyaluronic acid. A review of its pharmacology and use as a surgical aid in ophthalmology, and its therapeutic potential in joint disease and wound healing. Drugs. 1994; 47:536–566.16. Larsen NE, Pollak CT, Reiner K, Leshchiner E, Balazs EA. Hylan gel biomaterial: dermal and immunologic compatibility. J Biomed Mater Res. 1993; 27:1129–1134.
Article17. Richter W. Non-immunogenicity of purified hyaluronic acid preparations tested by passive cutaneous anaphylaxis. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1974; 47:211–217.
Article18. Richter AW, Ryde EM, Zetterström EO. Non-immunogenicity of a purified sodium hyaluronate preparation in man. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1979; 59:45–48.
Article19. Gibbs DA, Merrill EW, Smith KA, Balazs EA. Rheology of hyaluronic acid. Biopolymers. 1968; 6:777–791.
Article20. Balazs EA. Intercellular matrix of connective tissue. In : Finch CE, Hayflick L, editors. Handbook of the biology of aging. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold;1977. p. 22–240.21. DeVore DP, Hughes E, Scott JB. Effectiveness of injectable filler materials for smoothing wrinkle lines and depressed scars. Med Prog Technol. 1994; 20:243–250.22. Läckgren G, Wåhlin N, Stenberg A. Endoscopic treatment of children with vesico-ureteric reflux. Acta Paediatr Suppl. 1999; 88:62–71.
Article23. Engelman DE, Bloom B, Goldberg DJ. Dermal fillers: complications and informed consent. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2005; 7:29–32.
Article24. Andre P, Lowe NJ, Parc A, Clerici TH, Zimmermann U. Adverse reactions to dermal fillers: a review of European experiences. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2005; 7:171–176.
Article25. Duffy DM. Complications of fillers: overview. Dermatol Surg. 2005; 31:1626–1633.
Article26. Bergeret-Galley C. Comparison of resorbable soft tissue fillers. Aesthet Surg J. 2004; 24:33–46.
Article27. Piacquadio D, Jarcho M, Goltz R. Evaluation of hylan b gel as a soft-tissue augmentation implant material. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997; 36:544–549.
Article28. Alijotas-Reig J, Garcia-Gimenez V. Delayed immune-mediated adverse effects related to hyaluronic acid and acrylic hydrogel dermal fillers: clinical findings, long-term follow-up and review of the literature. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2008; 22:150–161.
Article29. Xin ZC, Chung WS, Choi YD, Seong DH, Choi YJ, Choi HK. Penile sensitivity in patients with primary premature ejaculation. J Urol. 1996; 156:979–981.
Article30. Tullii RE, Guillaux CH, Vaccari R, Ferreira R. Premature ejaculation-selective neurectomy: A new therapeutic technique-base, indication and results. Int J Impot Res. 1994; 6:109–113.31. Yang CC, Bradley WE. Neuroanatomy of the penile portion of the human dorsal nerve of the penis. Br J Urol. 1998; 82:109–113.
Article32. Halata Z, Munger BL. The neuroanatomical basis for the protopathic sensibility of the human glans penis. Brain Res. 1986; 371:205–230.
Article33. Althof SE, Abdo CH, Dean J, Hackett G, McCabe M, McMahon CG, et al. International Society for Sexual Medicine. International Society for Sexual Medicine's guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of premature ejaculation. J Sex Med. 2010; 7:2947–2969.
Article34. de Bree R, Middelweerd MJ, van der Waal I. Severe granulomatous inflammatory response induced by injection of polyacrylamide gel into the facial tissue. Arch Facial Plast Surg. 2004; 6:204–206.
Article35. Kang SS, Zhang ZW, Chou HY, Zhai HF. Complication of polyacrylamide hydrogel injection for facial plasty. Zhonghua Zheng Xing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2003; 19:325–327.36. Liu Y, Cen Y, Xu XW, Duan WQ. Analysis of complications induced by polyacrylamide hydrogel injection for augmentation mammaplasty. Zhonghua Zheng Xing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2005; 21:464–466.37. Brody HJ. Use of hyaluronidase in the treatment of granulomatous hyaluronic acid reactions or unwanted hyaluronic acid misplacement. Dermatol Surg. 2005; 31:893–897.
Article38. Hirsch RJ, Cohen JL, Carruthers JD. Successful management of an unusual presentation of impending necrosis following a hyaluronic acid injection embolus and a proposed algorithm for management with hyaluronidase. Dermatol Surg. 2007; 33:357–360.
Article39. Hirsch RJ, Brody HJ, Carruthers JD. Hyaluronidase in the office: a necessity for every dermasurgeon that injects hyaluronic acid. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2007; 9:182–185.
Article40. Shaeer O. Shaeer's glans augmentation technique: a pilot study. J Sex Med. 2012; 9:3264–3269.
Article41. Perovic SV, Scepanovic DR, Vukadinovic VM, Djakovic NG, Djordjevic ML. Penile disassembly technique: a new approach in the surgical reconstruction of hypospadias. Prog Urol. 1999; 9:371–379.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Injectable Hyaluronic Acid Gel in Augmentation of Glans Penis
- Effects of Glans Penis Augmentation Using Hyaluronic Acid Gel for Premature Ejaculation
- The Stability of the ALSA Plasma Gel Filler and the Hyaluronic Acid Filler in Rabbits
- The Problems and Solutions of Filler Augmentation Rhinoplasty
- Hyaluronidase: An overview of its properties, applications, and side effects