J Korean Neurotraumatol Soc.
2011 Oct;7(2):63-67. 10.13004/jknts.2011.7.2.63.
Clinical and Radiological Outcome Analysis on Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Interbody Fusion Using Hydroxyapatite Block
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department Neurological Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. srjeon@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 2019915
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13004/jknts.2011.7.2.63
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Although use of autologous iliac bone graft in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF) for cervical degenerative diseases remain standard surgical procedure, donor site morbidity are still concerns. Several synthetic graft materials have been developed to prevent this complication. This is retrospective study of clinical and radiological outcomes of ACDF using synthetic hydroxyapatite (HA) block to evaluate the efficacy.
METHODS
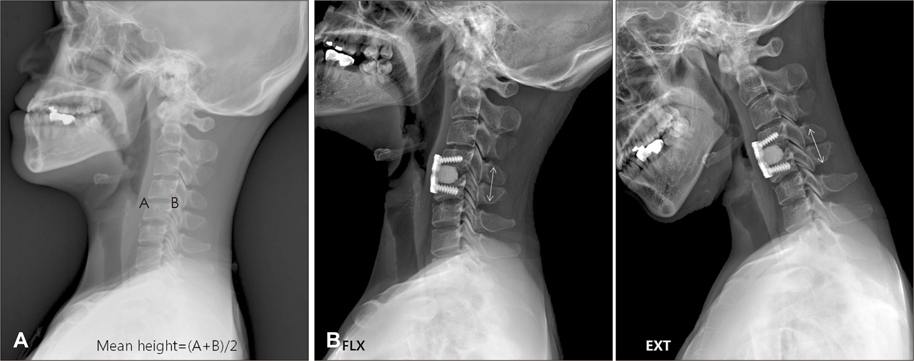
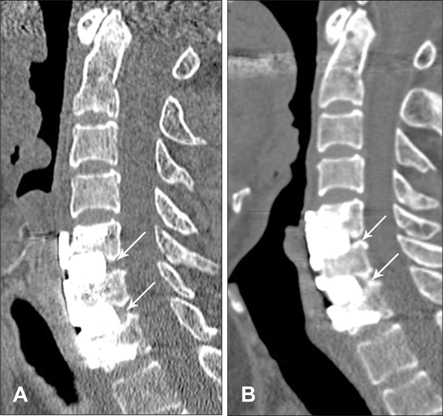
From May 2009 to June 2010, twenty-one patients (M 11 ; F 10) were enrolled in this study and 35 segments were involved. All patients were performed ACDF using HA block and plating system. Indications of surgery were radiculopathy caused by degenerative cervical spondylosis with or without myelopathy. The mean period of clinical follow-up was 6.6 months (range from 6 to 12 months). The change of Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) and Neck Disability Index (NDI) at 6 month were used for clinical outcome analysis. Cervical spine radiographs including dynamic views were obtained at postoperative 3 day, 1, 3, 6 months in all patients to measure the change of disc height, overall and segmental lordosis, segmental motion. Computed tomography was done at postoperative 6 month in all patients to confirm the radiological fusion.
RESULTS
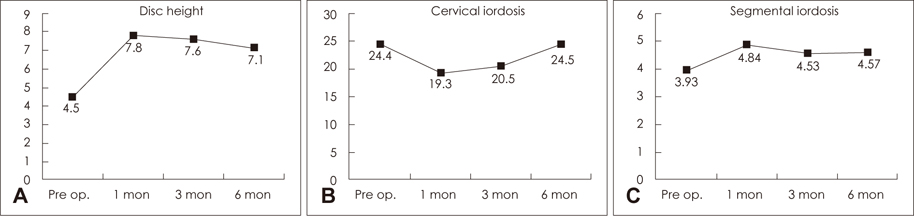
Mean VAS and NDI score changed from 8.2 to 2.7 and from 23.4 to 10.5, respectively. The mean disc height change was from 4.5 to 7.1. Cervical lordosis and segmental lordosis changes were from 24.4 to 24.5 and from 3.93 to 4.57, respectively. Complete interbody fusion was achieved in 95.2% of patients. There was one case of non-fusion patient.
CONCLUSION
HA block is very efficient graft material in achieving cervical fusion, maintaining intervertebral disc height for ACDF. Further follow up study should be needed to evaluate the efficacy of this material.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Preliminary Report of Combined Microscopic Fragmentectomy and Nucleoplasty for Sequestrated Lumbar Disc Herniation
Jae Ho Kim, Seok Won Kim
Korean J Neurotrauma. 2014;10(1):6-9. doi: 10.13004/kjnt.2014.10.1.6.
Reference
-
1. Alvarez JA, Hardy RW Jr. Anterior cervical discectomy for one- and two-level cervical disc disease: the controversy surrounding the question of whether to fuse, plate, or both. Crit Rev Neurosurg. 1999; 9:234–251.
Article2. Bärlocher CB, Barth A, Krauss JK, Binggeli R, Seiler RW. Comparative evaluation of microdiscectomy only, autograft fusion, polymethylmethacrylate interposition, and threaded titanium cage fusion for treatment of single-level cervical disc disease: a prospective randomized study in 125 patients. Neurosurg Focus. 2002; 12:E4.
Article3. Bohlman HH, Emery SE, Goodfellow DB, Jones PK. Robinson anterior cervical discectomy and arthrodesis for cervical radiculopathy. Long-term follow-up of one hundred and twenty-two patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993; 75:1298–1307.
Article4. Connolly PJ, Esses SI, Kostuik JP. Anterior cervical fusion: outcome analysis of patients fused with and without anterior cervical plates. J Spinal Disord. 1996; 9:202–206.5. Denissen HW, de Groot K. Immediate dental root implants from synthetic dense calcium hydroxylapatite. J Prosthet Dent. 1979; 42:551–556.
Article6. el Deeb M, Waite DE, Mainous EG. Correction of the deficient alveolar ridge. Clin Plast Surg. 1989; 16:733–748.7. Geer CP, Papadopoulos SM. The argument for single-level anterior cervical discectomy and fusion with anterior plate fixation. Clin Neurosurg. 1999; 45:25–29. discussion 21.8. Gercek E, Arlet V, Delisle J, Marchesi D. Subsidence of stand-alone cervical cages in anterior interbody fusion: warning. Eur Spine J. 2003; 12:513–516.
Article9. Hacker RJ. Threaded cages for degenerative cervical disease. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002; 39–46.
Article10. Hwang SL, Lin CL, Lieu AS, Lee KS, Kuo TH, Hwang YF, et al. Three-level and four-level anterior cervical discectomies and titanium cage-augmented fusion with and without plate fixation. J Neurosurg Spine. 2004; 1:160–167.
Article11. Madawi AA, Powell M, Crockard HA. Biocompatible osteoconductive polymer versus iliac graft. A prospective comparative study for the evaluation of fusion pattern after anterior cervical discectomy. . Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996; 21:2123–2129. discussion 2129-2130.12. Matge G. Anterior interbody fusion with the BAK-cage in cervical spondylosis. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1998; 140:1–8.
Article13. McConnell JR, Freeman BJ, Debnath UK, Grevitt MP, Prince HG, Webb JK. A prospective randomized comparison of coralline hydroxyapatite with autograft in cervical interbody fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003; 28:317–323.
Article14. Pintar FA, Maiman DJ, Hollowell JP, Yoganandan N, Droese KW, Reinartz JM, et al. Fusion rate and biomechanical stiffness of hydroxylapatite versus autogenous bone grafts for anterior discectomy. An in vivo animal study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994; 19:2524–2528.15. Schmieder K, Wolzik-Grossmann M, Pechlivanis I, Engelhardt M, Scholz M, Harders A. Subsidence of the wing titanium cage after anterior cervical interbody fusion: 2-year follow-up study. J Neurosurg Spine. 2006; 4:447–453.
Article16. Schneider JR, Bright RW. Anterior cervical fusion using preserved bone allografts. Transplant Proc. 1976; 8:73–76.17. Zdeblick TA, Cooke ME, Kunz DN, Wilson D, McCabe RP. Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion using a porous hydroxyapatite bone graft substitute. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994; 19:2348–2357.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Analysis of Noninstrumented Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Interbody Fusion in Degenerative Cervical Disease
- Results of Anterior Cervical Discectomy without Interbody Fusion
- Anterior Cervical Discectomy
- Anterior Interbody Fusion of the Cervical Spine: Clinical Study of 56 Cases
- Long-term Follow-up Results of Anterior Cervical Interbody Fusion with and without Cervical Plate