J Korean Fract Soc.
2012 Apr;25(2):110-116. 10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.2.110.
Treatment of Tibial Plateau Fractures Using a Locking Plate and Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Osteosynthesis Technique
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Dankook University Medical College, Cheonan, Korea. osdku@dankook.ac.kr
- KMID: 2015453
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.2.110
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To acknowledge the importance of precise reduction of articular surface of tibial plateau fractures and to make a guideline of treatment by evaluating outcomes and effectiveness of using locking plate and minimally invasive percutaneous osteosynthesis technique.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
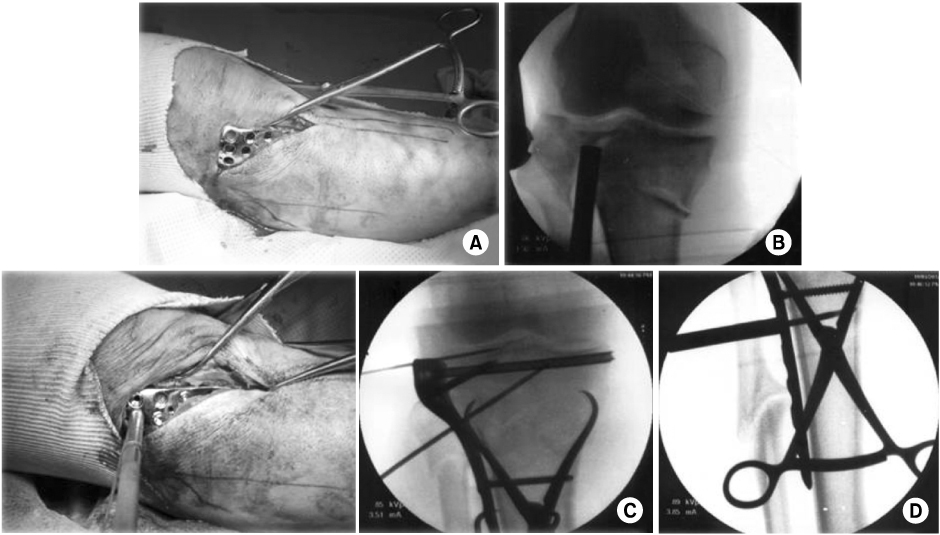
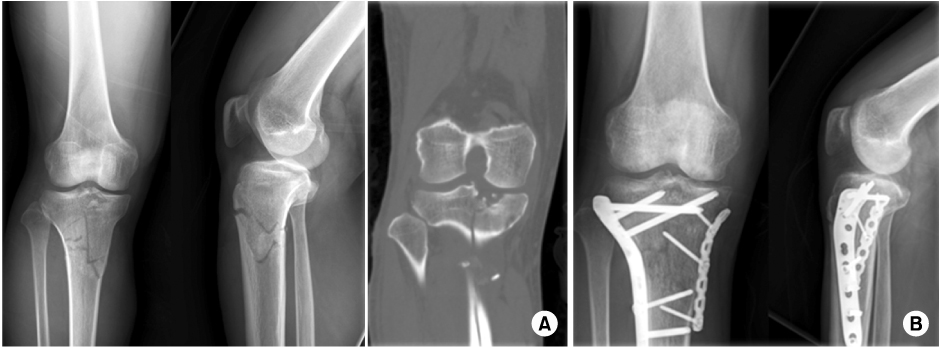
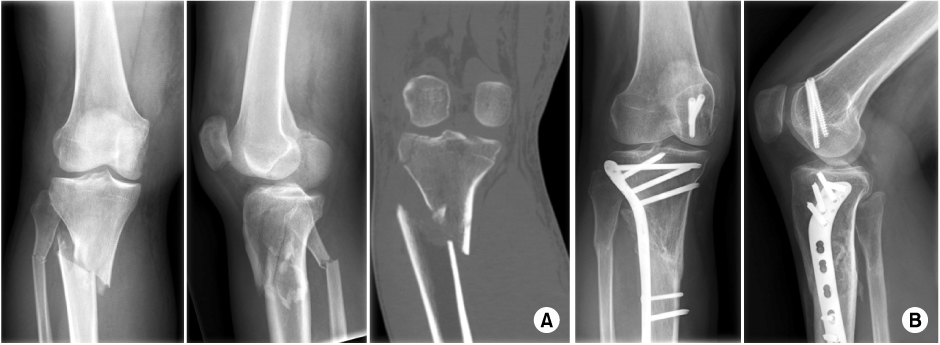
Twenty-nine patients who underwent surgery for tibial plateau fracture from November 2005 to March 2010 were enrolled with 12 months follow-up in a retrograde manner. The Shatzker classification was used to classify fractures, and we used lateral submeniscal approach to make a precise reduction of articular surface. Radiologic evaluation was determined by presence of bone union, malalignment, and reduction loss or joint depression of articular surface. Post-operative infection, time of active movement of the knee joint, time of partial weight loading, and range of motion (ROM) of knee joint were evaluated. Lysholm Knee Score was used for functional evaluation.
RESULTS
Bone union took place in all but one case that developed osteomyelitis. Angulation deformity of more than 10degrees and reduction loss or joint depression of more than 5 mm were not observed. There was one case of osteomyelitis and one case of superficial surgical site infection. There were satisfactory clinical results, with an average time of active knee joint movement and weight loading of 6 weeks. The average ROM of knee joint was 125degrees in the last follow up. As for functional evaluation using Lysholm Knee Score, cases showed an average Lysholm Knee Score of 94 which was a satisfactory result.
CONCLUSION
In cases of tibial plateau fractures, if a surgeon accurately reduces the articular surface of joint and use minimally invasive locking plate it will help in bone union biologically, reducing the incidence of soft tissue injuries, and biomechanically maintaining the articular surface of the joint, proving itself to be a useful method of treatment.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cullen AB, Curtiss S, Lee MA. Biomechanical comparison of polyaxial and uniaxial locking plate fixation in a proximal tibial gap model. J Orthop Trauma. 2009. 23:507–513.
Article2. Ali AM, Burton M, Hashmi M, Saleh M. Outcome of complex fractures of the tibial plateau treated with a beam-loading ring fixation system. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003. 85:691–699.
Article3. Ballmer FT, Hertel R, Nötzli HP. Treatment of tibial plateau fractures with small fragment internal fixation: a preliminary report. J Orthop Trauma. 2000. 14:467–474.
Article4. Bansal MR, Bhagat SB, Shukla DD. Bovine cancellous xenograft in the treatment of tibial plateau fractures in elderly patients. Int Orthop. 2009. 33:779–784.
Article5. Baumgaertel F, Buhl M, Rahn BA. Fracture healing in biological plate osteosynthesis. Injury. 1998. 29:Suppl 3. C3–C6.
Article6. Benirschke SK, Agnew SG, Mayo KA, Santoro VM, Henley MB. Immediate internal fixation of open, complex tibial plateau fractures: treatment by a standard protocol. J Orthop Trauma. 1992. 6:78–86.7. Cole PA, Zlowodzki M, Kregor PJ. Less Invasive Stabilization System (LISS) for fractures of the proximal tibia: indications, surgical technique and preliminary results of the UMC Clinical Trial. Injury. 2003. 34:Suppl 1. A16–A29.
Article8. Barei DP, Nork SE, Mills WJ, Coles CP, Henley MB, Benirschke SK. Functional outcomes of severe bicondylar tibial plateau fractures treated with dual incisions and medial and lateral plates. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006. 88:1713–1721.
Article9. Dendrinos GK, Kontos S, Katsenis D, Dalas A. Treatment of high-energy tibial plateau fractures by the Ilizarov circular fixator. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1996. 78:710–717.
Article10. Egol KA, Su E, Tejwani NC, Sims SH, Kummer FJ, Koval KJ. Treatment of complex tibial plateau fractures using the less invasive stabilization system plate: clinical experience and a laboratory comparison with double plating. J Trauma. 2004. 57:340–346.
Article11. Gosling T, Schandelmaier P, Muller M, Hankemeier S, Wagner M, Krettek C. Single lateral locked screw plating of bicondylar tibial plateau fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005. 439:207–214.
Article12. Kim YJ, Chae SU, Yang JH, Lee JW, Wi DH, Choi DH. The use of fresh frozen allogenic bone graft in the impacted tibial plateau fractures. J Korean Fract Soc. 2010. 23:26–33.
Article13. Mallik AR, Covall DJ, Whitelaw GP. Internal versus external fixation of bicondylar tibial plateau fractures. Orthop Rev. 1992. 21:1433–1436.14. Muggler E, Huber D, Burri C. Results of surgical treatment of 225 tibial-head fractures. Chirurg. 1975. 46:348–352.15. Nikolaou VS, Tan HB, Haidukewych G, Kanakaris N, Giannoudis PV. Proximal tibial fractures: early experience using polyaxial locking-plate technology. Int Orthop. 2011. 35:1215–1221.
Article16. Phisitkul P, McKinley TO, Nepola JV, Marsh JL. Complications of locking plate fixation in complex proximal tibia injuries. J Orthop Trauma. 2007. 21:83–91.
Article17. Pogliacomi F, Verdano MA, Frattini M, Costantino C, Vaienti E, Soncini G. Combined arthroscopic and radioscopic management of tibial plateau fractures: report of 18 clinical cases. Acta Biomed. 2005. 76:107–114.18. Lachiewicz PF, Funcik T. Factors influencing the results of open reduction and internal fixation of tibial plateau fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990. (259):210–215.
Article19. Ratcliff JR, Werner FW, Green JK, Harley BJ. Medial buttress versus lateral locked plating in a cadaver medial tibial plateau fracture model. J Orthop Trauma. 2007. 21:444–448.
Article20. Schütz M, Südkamp NP. Revolution in plate osteosynthesis: new internal fixator systems. J Orthop Sci. 2003. 8:252–258.
Article21. Singh S, Patel PR, Joshi AK, Naik RN, Nagaraj C, Kumar S. Biological approach to treatment of intra-articular proximal tibial fractures with double osteosynthesis. Int Orthop. 2009. 33:271–274.
Article21. Stannard JP, Wilson TC, Volgas DA, Alonso JE. Fracture stabilization of proximal tibial fractures with the proximal tibial LISS: early experience in Birmingham, Alabama (USA). Injury. 2003. 34:Suppl 1. A36–A42.
Article23. Stannard JP, Wilson TC, Volgas DA, Alonso JE. The less invasive system for treatment of complex fractures of the proximal tibia. Presented at the annual meeting of the OTA. 2001. 10. 18. San Diego, CA:24. Tscherne H, Lobenhoffer P. Tibial plateau fractures. Management and expected results. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993. (292):87–100.25. Watson JT, Ripple S, Hoshaw SJ, Fyhrie D. Hybrid external fixation for tibial plateau fractures. Orthop Clin North Am. 2002. 33:199–209. ix
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Stabilization Using a Medial Locking Plate for Proximal Tibial Fractures: Technical Note
- Clinical Outcomes of Locking Compression Plate Fixation through Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis in the Treatment of Distal Tibia Fracture
- Comparison of Results of Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis according to Types of Locking Plate in Distal Femoral Fractures
- Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis Using a Lateral Plate in Distal Tibial Fracture
- Anterolateral Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis of Distal Tibial Fractures Using an Anterolateral Locking Plate