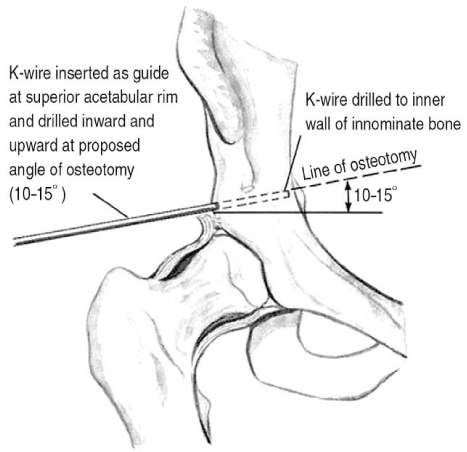
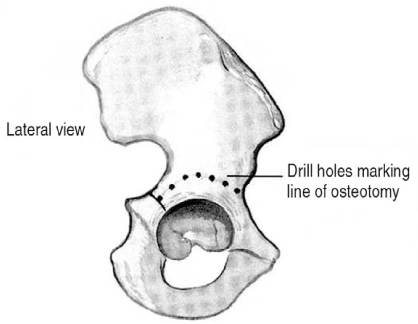
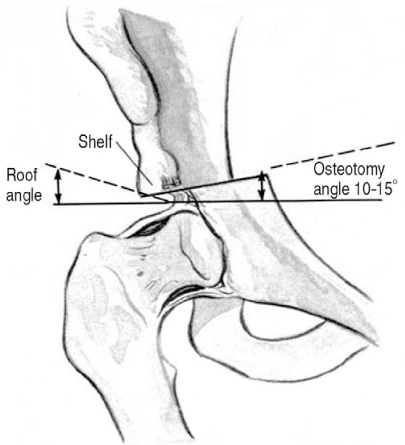
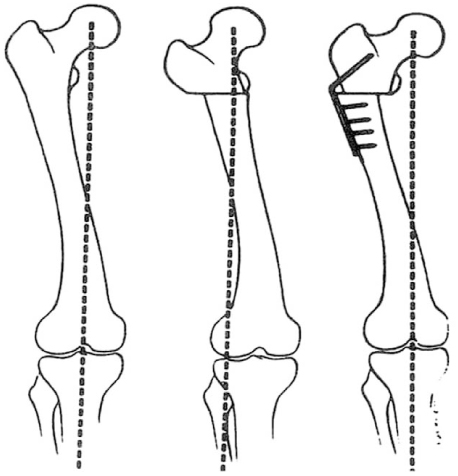
J Korean Hip Soc.
2012 Mar;24(1):2-17. 10.5371/jkhs.2012.24.1.2.
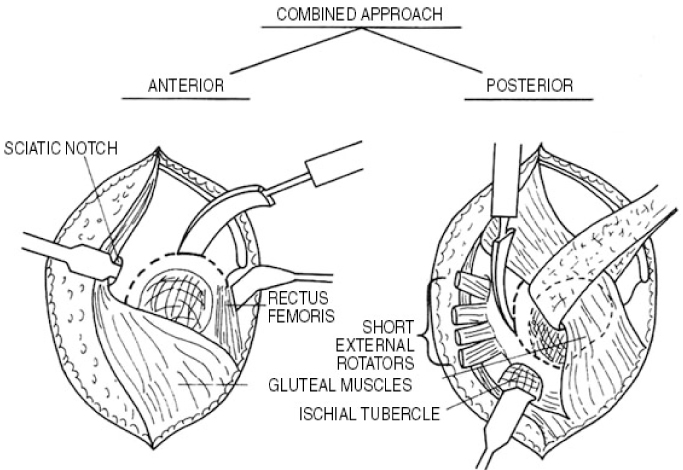
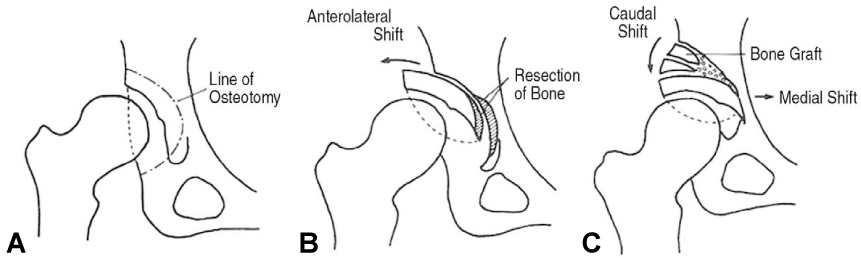
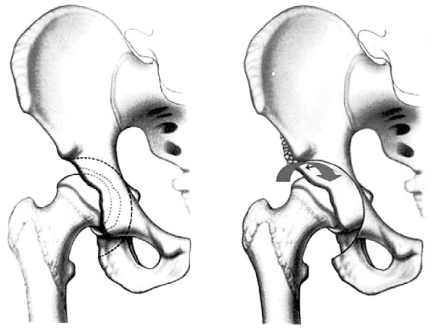
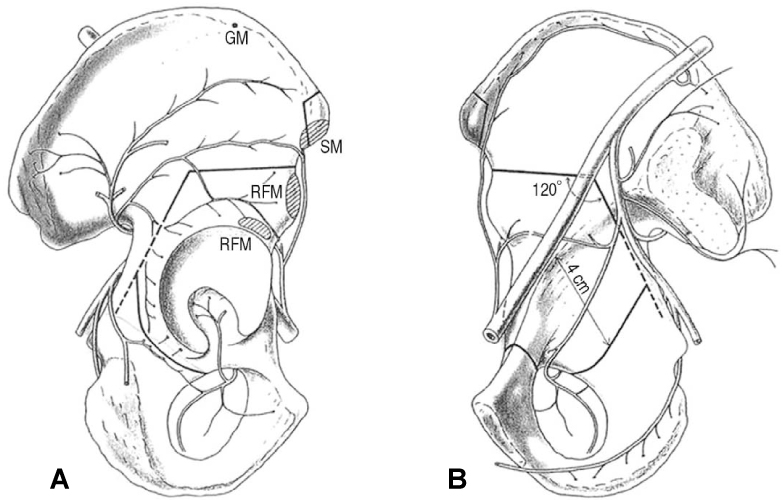
Osteotomy around the Hip Joint
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, School of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. yjcho@khmc.or.kr
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Daerim St. Mary's Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2014892
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5371/jkhs.2012.24.1.2
Abstract
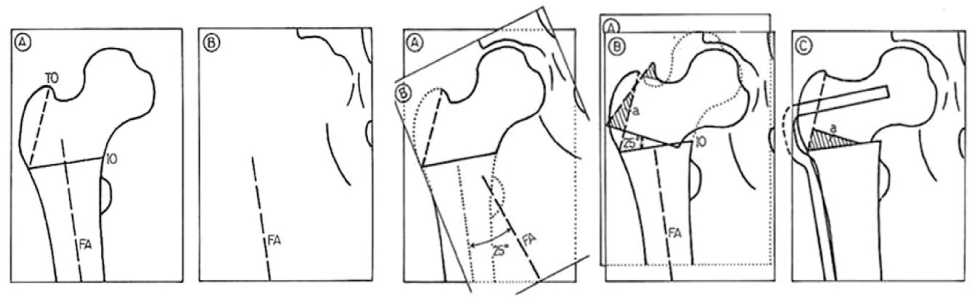
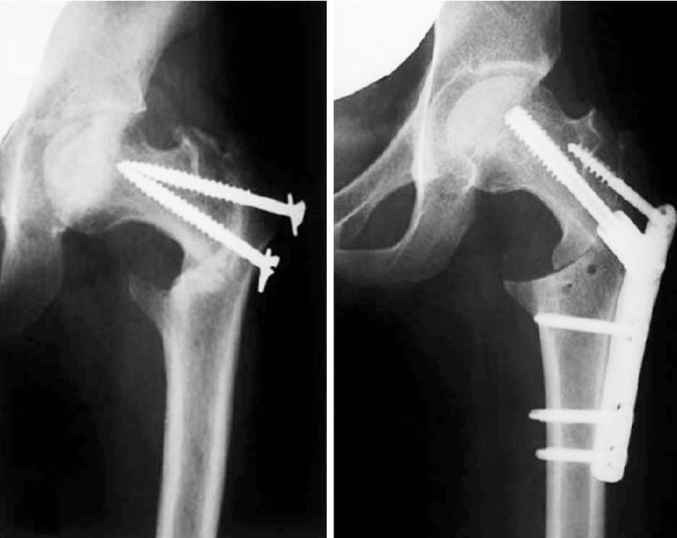
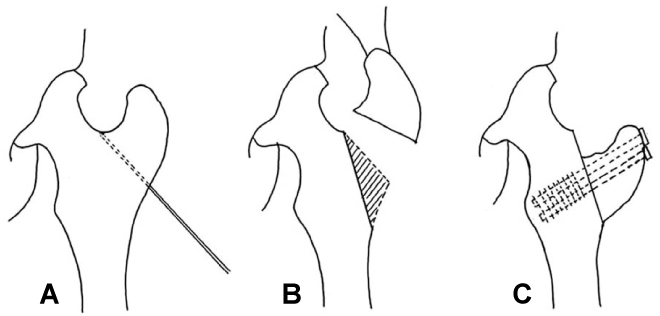
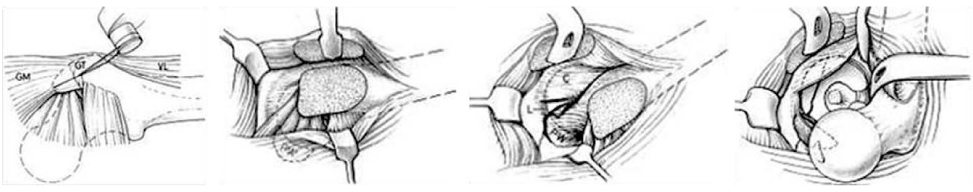
- Hip joint preserving osteotomy surgery is the treatment of choice for young patients with early symptomatic structural abnormalities of the acetabulum and proximal femur. This is true even in the absence of severe secondary degenerative changes. These disorders can include hip instability from classic developmental dysplasia, post-traumatic acetabular dysplasia, hip impingement from retrotorsional acetabular deformities, or, rarely, post-traumatic problems. During the past 20 years, various techniques of acetabular and proximal femoral reorientation have evolved, making the procedure reliable, reproducible, and durable. In this report, the current indications and results of acetabular and proximal femoral osteotomies in patients with symptomatic acetabular structural problems will be discussed.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Aronson J. Osteoarthritis of the young adult hip: etiology and treatment. Instr Course Lect. 1986. 35:119–128.2. Buckwalter JA, Lohmander S. Operative treatment of osteoarthrosis. Current practice and future development. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994. 76:1405–1418.
Article3. Millis MB, Murphy SB, Poss R. Osteotomies about the hip for the prevention and treatment of osteoarthrosis. Instr Course Lect. 1996. 45:209–226.
Article4. Pauwels F. Biomechanics of the normal and diseased hip: Theoretical foundation, technique and results of treatment: an atlas. 1976. New York: Springer;106–115.5. Ewald FC, Poss R, Pugh J, Schiller AL, Sledge CB. Hip cartilage supported by methacrylate in canine arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1982. 171:273–279.
Article6. Solomon L, Schnitzler CM. Pathogenetic types of coxarthrosis and implications for treatment. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1983. 101:259–261.
Article7. Stulberg SD, Cordell LD, Harris WH, Ramsey PL, MacEwen GD. Unrecognized childhood hip disease: a major cause of idiopathic osteoarthritis of the hip. The hip: Proceedings of the third open scientific meeting of the hip society. 1975. St. Louis: Mosby;212–228.8. Cooperman DR, Wallensten R, Stulberg SD. Post-reduction avascular necrosis in congenital dislocation of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1980. 62:247–258.
Article9. Cooperman DR, Wallensten R, Stulberg SD. Acetabular dysplasia in the adult. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983. 175:79–85.
Article10. Klaue K, Durnin CW, Ganz R. The acetabular rim syndrome. A clinical presentation of dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991. 73:423–429.
Article11. Dorrell JH, Catterall A. The torn acetabular labrum. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1986. 68:400–403.
Article12. Harris WH. Etiology of osteoarthritis of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986. 213:20–33.
Article13. Ninomiya S, Tagawa H. Rotational acetabular osteotomy for the dysplasitc hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984. 66:430–436.14. Hasegawa Y, Iwase T, Kitamura S, Yamauchi Ki K, Sakano S, Iwata H. Eccentric rotational acetabular osteotomy for acetabular dysplasia: follow-up of one hundred and thirty-two hips for five to ten years. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002. 84-A:404–410.15. Kim HJ, Kim JW. Acetabular osteotomy. J Korean Hip Soc. 2004. 16:254–260.16. Ko JY, Wang CJ, Lin CF, Shih CH. Periacetabular osteotomy through a modified ollier transtrochanteric approach for treatment of painful dysplastic hips. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002. 84-A:1594–1604.
Article17. Nakamura S, Ninomiya S, Takatori Y, Moritomo S, Umeyama T. Long-term outcome of rotational acetabular osteotomy:145 hips followed for 10-23 years. Acta Orthop Scand. 1998. 69:259–265.
Article18. Yasunaga Y, Ochi M, Terayama H, Tanaka R, Yamasaki T, Ishii Y. Rotational acetabular osteotomy for advanced osteoarhtritis secondary to dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006. 88:1915–1919.
Article19. Kang CS. Rotational acetabular osteotomy in acetabular dysplasia. J Korean Hip Soc. 2001. 13:208–213.
Article20. Kang CS, Shon SW, Kim SY. Rotational acetabular osteotomy for the dysplastic acetabulum. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1986. 21:791–798.
Article21. Min BW, Bae KC, Kang CH, Song KS, Sohn SW. Rotational acetabular osteotomy for the dysplastic hip: A follow-up for 5 to 18 years. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2005. 40:717–722.
Article22. Yoo MC, Cho YJ, Kim KI, Park HC, Chung CJ. Periacetabular rotational osteotomy in hip dysplasia:short term follow up result. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2005. 40:434–441.
Article23. Yasunaga Y, Takahashi K, Ochi M, et al. Rotational acetabular osteotomy in patients forty-six years of age or older: comparison with younger patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003. 85-A:266–272.24. Chang JS, Park JH, Park HG, Lee SH, Kim KY. Bernese periacetabular osteotomy for hip dysplasia. J Korean Hip Soc. 1998. 10:141–148.25. Chang JS, Kwon KD, Shon HC. Bernese periacetbular osteotomy using dual approachs for hip dysplasia. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2002. 37:226–232.
Article26. Hussell JG, Rodriguez JA, Ganz R. Technical complications of the Bernese periacetabular osteotomy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999. 363:81–92.
Article27. Myers SR, Eijer H, Ganz R. Anterior femoroacetabular impingement after periacetabular osteotomy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999. 363:93–99.
Article28. Siebenrock KA, Schöll E, Lottenbach M, Ganz R. Bernese periacetabular osteotomy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999. 363:9–20.
Article29. Chiari K. Results of pelvic osteotomy as of the shelf method acetabular roof plastic. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb. 1955. 87:14–26.30. White RE Jr, Sherman FC. The hip-shelf procedure. A long-term evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1980. 62:928–932.
Article31. Park YS. Chiari pelvic osteotomy. J Korean Hip Soc. 2001. 13:214–216.32. Graham S, Westin GW, Dawson E, Oppenheim WL. The Chiari osteotomy. A review of 58 cases. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986. 208:249–258.33. Kawamura B, Hosono S, Yokogushi K. Tachdjian MO, editor. Dome osteotomy of the pelvis. 1982. New York: Churchill-Livingstone;609–623.34. Matsuno T, Ichioka Y, Kaneda K. Modified Chiari pelvic osteotomy: a long-term follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1992. 74:470–478.35. Chiari K. Medial displacement osteotomy of the pelvis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1974. 98:55–71.
Article36. Anwar MM, Sugano N, Matsui M, Takaoka K, Ono K. Dome osteotomy of the pelvis for osteoarthritis secondary to hip dysplasia. An over five-year follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1993. 75:222–227.
Article37. Nakata K, Masuhara K, Sugano N, Sakai T, Haraguchi K, Ohzono K. Dome (modified Chiari) pelvic osteotomy: 10- to 18-year followup study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001. 389:102–112.38. Marti RK, Schüller HM, Raaymakers EL. Intertrochanteric osteotomy for non-union of the femoral neck. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1989. 71:782–787.
Article39. Maguet PG. Biomechanics of the hip. 1985. New York: Springer-Verlag.40. Miegel RE, Harris WH. Medial-displacement intertrochanteric osteotomy in the treatment of osteoarthritis of the hip. A long-term follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984. 66:878–887.
Article41. Maistrelli GL, Gerundini M, Fusco U, Bombelli R, Avai A. Valgus-extension osteotomy for osteoarthritis of the hip. Indications and long-term results. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1990. 72:653–657.
Article42. Santore RF, Bombelli R. Long-term follow-up of the Bombelli experience with osteotomy for osteoarthritis: results at 11 years. Hip. 1983. 106–128.43. Leunig M, Slongo T, Kleinschmidt M, Ganz R. Subcapital correction osteotomy in slipped capital femoral epiphysis by means of surgical hip dislocation. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2007. 19:389–410.44. Sugioka Y. Orthopedists should never forget the utility of osteotomy as an option for regenerative medicine: the importance of joint preservation surgery and its dissemination. J Orthop Sci. 2007. 12:1–3.
Article45. Sugioka Y, Yamamoto T. Transtrochanteric posterior rotational osteotomy for osteonecrosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008. 466:1104–1109.
Article46. Atsumi T, Kajiwara T, Hiranuma Y, Tamaoki S, Asakura Y. Posterior rotational osteotomy for nontraumatic osteonecrosis with extensive collapsed lesions in young patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006. 88:Suppl 3. 42–47.
Article47. Kim HT, Wegner DR. "Functional retroversion" of the femoral head in Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease and epiphyseal dysplasia:analysis of head-neck deformity and its effect on limb position using three-dimentional computed tomography. J Pediatr Orthop. 1997. 17:240–246.
Article48. Kim HT, Wegner DR. Surgical correction of "functional retroversion" and "functional coxa vara" in late Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease and epiphyseal dysplasia: correction of deformity defined by new imaging modalities. J Pediatr Orthop. 1997. 17:247–254.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Osteotomies Around the Hip Joint
- Pelvic Osteotomy in Adults
- Femoral Osteotomy for Residual Subluxation of Hip after Reduction of Congenital Dislocation
- Hip Joint Surgery without Transfusion in Patients Who Were Jehovah's Witnesses: A Report of Two Cases
- Challenges in Total Hip Replacement after McMurray’s Osteotomy: A Report of 3 Cases and Review of Literature