Anat Cell Biol.
2012 Jun;45(2):136-139. 10.5115/acb.2012.45.2.136.
Four-headed biceps brachii, three-headed coracobrachialis muscles associated with arterial and nervous anomalies in the upper limb
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Akdeniz University, Antalya, Turkey. levent@akdeniz.edu.tr
- KMID: 2005877
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.2012.45.2.136
Abstract
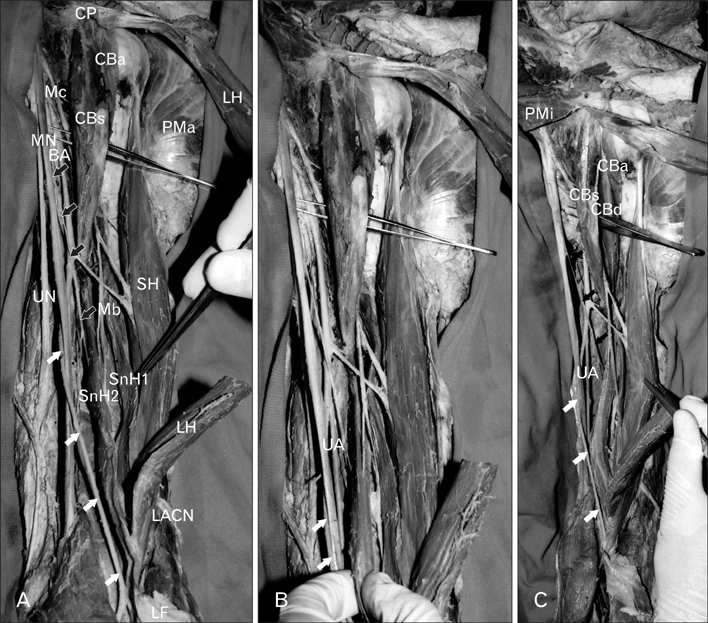
- A four-headed biceps brachii muscle and three-headed coracobrachialis muscle, high-originated radial artery and communication between the median and musculocutaneous nerves have been well documented in the available literature. However co-existence of these variations is rare. In this study we aimed to describe multiple variations in the upper limb and discuss their co-existence from clinical and embryological points of view.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Superficial brachioulnar artery and its clinical significance
Jacob Sieger, Lajja Patel, Kabir Sheikh, Emily Parker, Max Sheng, Sumathilatha Sakthi-Velavan
Anat Cell Biol. 2019;52(3):333-336. doi: 10.5115/acb.19.008.
Reference
-
1. Bergman RA, Thompson SA, Afifi AK. Catalog of human variation. 1985. Baltimore: Urban and Schwarzenberg;108–114.2. Kopuz C, Sancak B, Ozbenli S. On the incidence of third head of biceps brachii in Turkish neonates and adults. Kaibogaku Zasshi. 1999. 74:301–305.3. Rodríguez-Niedenführ M, Vázquez T, Choi D, Parkin I, Sañudo JR. Supernumerary humeral heads of the biceps brachii muscle revisited. Clin Anat. 2003. 16:197–203.4. Abu-Hijleh MF. Three-headed biceps brachii muscle associated with duplicated musculocutaneous nerve. Clin Anat. 2005. 18:376–379.5. Lee SE, Jung C, Ahn KY, Nam KI. Bilateral asymmetric supernumerary heads of biceps brachii. Anat Cell Biol. 2011. 44:238–240.6. Nakatani T, Tanaka S, Mizukami S. Bilateral four-headed biceps brachii muscles: the median nerve and brachial artery passing through a tunnel formed by a muscle slip from the accessory head. Clin Anat. 1998. 11:209–212.7. Khaledpour C. Anomalies of the biceps muscle of the arm. Anat Anz. 1985. 158:79–85.8. de Burlet HM, Correljé J. Über variationen des menschlichen musculus biceps brachii. Gegenbaurs Morphol Jahrb. 1919. 50:403–416.9. Vollala VR, Nagabhooshana S, Bhat SM, Potu BK, Rodrigues V, Pamidi N. Multiple arterial, neural and muscular variations in upper limb of a single cadaver. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2009. 50:129–135.10. Sargon MF, Tuncali D, Celik HH. An unusual origin for the accessory head of biceps brachii muscle. Clin Anat. 1996. 9:160–162.11. Kosugi K, Shibata S, Yamashita H. Supernumerary head of biceps brachii and branching pattern of the musculocutaneus nerve in Japanese. Surg Radiol Anat. 1992. 14:175–185.12. El-Naggar MM, Zahir FI. Two bellies of the coracobrachialis muscle associated with a third head of the biceps brachii muscle. Clin Anat. 2001. 14:379–382.13. Beattie PH. Description of bilateral coraco-brachialis brevis muscle, with a note on its significance. Anat Rec. 1947. 97:123–126.14. Vollala VR, Nagabhooshana S, Bhat SM, Potu BK, Rakesh V. Multiple accessory structures in the upper limb of a single cadaver. Singapore Med J. 2008. 49:e254–e258.15. Grim M. Ultrastructure of the ulnar portion of the contrahent muscle layer in the embryonic human hand. Folia Morphol (Praha). 1972. 20:113–115.16. Kyou-Jouffroy MK, Lessertisseur J, Saban R, Souteyrand-Boulenger JD. Grassé PP, editor. Musculature des membres, membre pectoral, groupe branchial ventral. Traité de Zoologie. Mammiféres: Anatomie et Reproduction. 1971. Paris: Masson;96–98.17. Mori M. Statistics on the musculature of the Japanese. Okajimas Folia Anat Jpn. 1964. 40:195–300.18. Testut L. Mémoire sur la portion brachiale du nerf musculocutané. Int Monatsschr Anat Physiol. 1884. 1:305–341.19. Monden M. Anastomosis between the median and musculocutaneous nerves in the upper arm. Juzen Ishi. 1942. 47:2045–2055.20. Choi D, Rodríguez-Niedenführ M, Vázquez T, Parkin I, Sañudo JR. Patterns of connections between the musculocutaneous and median nerves in the axilla and arm. Clin Anat. 2002. 15:11–17.21. Kosugi K, Morita T, Koda M, Yamashita H. Branching pattern of musculocutaneous nerve. 2. Cases possessing supernumerary head of bicipital brachial muscle. Jikeikai Med J. 1986. 33:195–208.22. Venieratos D, Anagnostopoulou S. Classification of communications between the musculocutaneous and median nerves. Clin Anat. 1998. 11:327–331.23. Flatow EL, Bigliani LU, April EW. An anatomic study of the musculocutaneous nerve and its relationship to the coracoid process. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989. (244):166–171.24. Sonck WA, Francx MM, Engels HL. Innervation anomalies in upper and lower extremities: potential clinical implications. How to identify with electrophysiologic techniques. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1991. 31:67–80.25. Sunderland S. Nerves and nerve injuries. 1978. Edinburgh, London, NewYork: Churchill Livingstone.26. Sarikcioglu L, Yildirim FB. High origin of the radial artery accompanied by muscular and neural anomalies. Ann Anat. 2003. 185:179–182.27. Kopuz C, Fidan B, Islam A. An unusually distal and complete additional flexor profundus muscle to the index finger. J Anat. 1997. 191(Pt 3):465–467.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Bilateral asymmetric supernumerary heads of biceps brachii
- The Third Head of Biceps Brachii Muscle in Korean: Anatomical Study
- Morphological classification, anatomical variations, innervation patterns, musculocutaneous nerve relation of the coracobrachialis muscle: anatomical study and clinical significance
- Anatomical Locations of the Motor Points of the Biceps Brachii and Brachialis Muscles
- An Isolated Musculocutaneous Nerve Palsy