J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2003 Jun;10(2):82-89. 10.4184/jkss.2003.10.2.82.
Outcome of Different Grafted Bone in Lumbar Posterolateral Fusion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, College of medicine, Dong-A University, Busan, Korea. gylee@mail.donga.ac.kr
- KMID: 2003204
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2003.10.2.82
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Using a retrospective analysis on the fusion rate and the postoperative improvement in symptoms, this study evaluated the clinical feasibility of a bone graft in lumbar fusion surgery in the following cases: (1) Group I: local autograft, (2) Group II: local autograft and iliac crest autograft, and (3) Group III: local autograft and customized heterograft.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
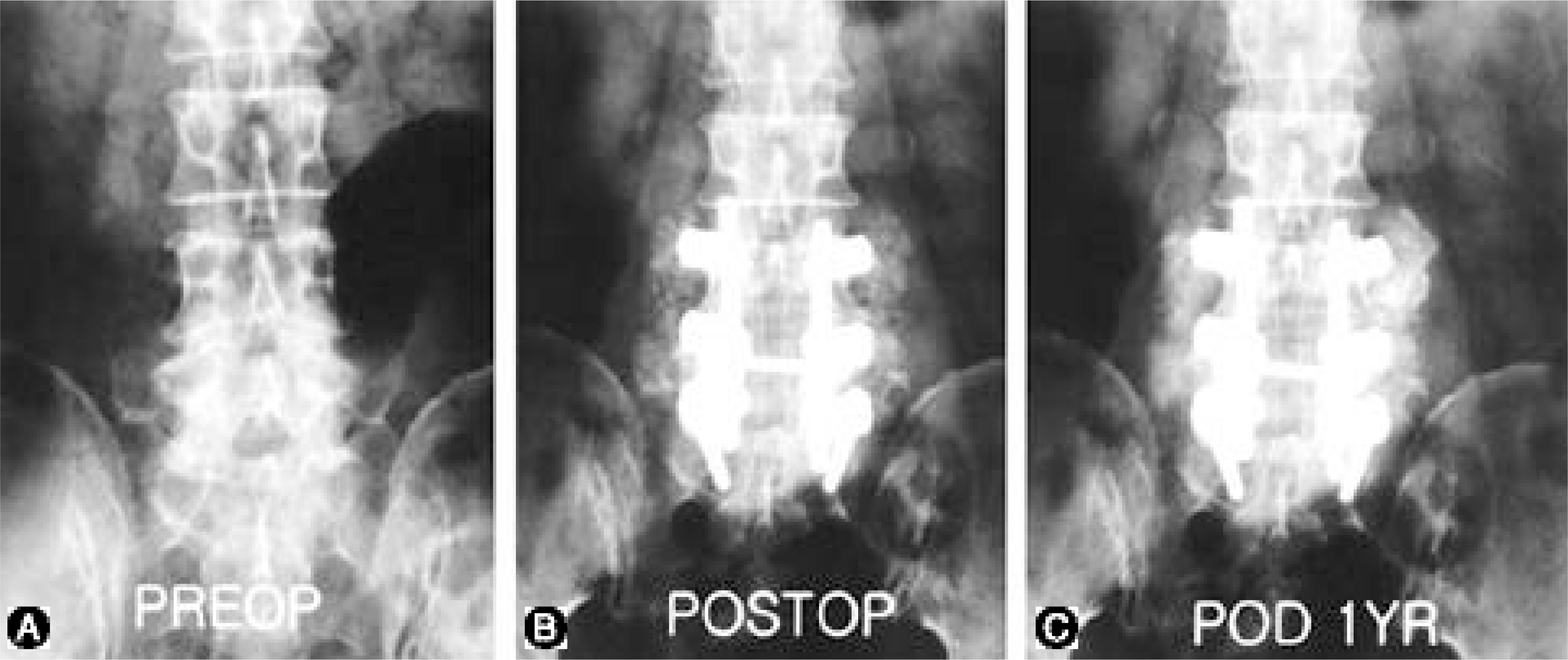
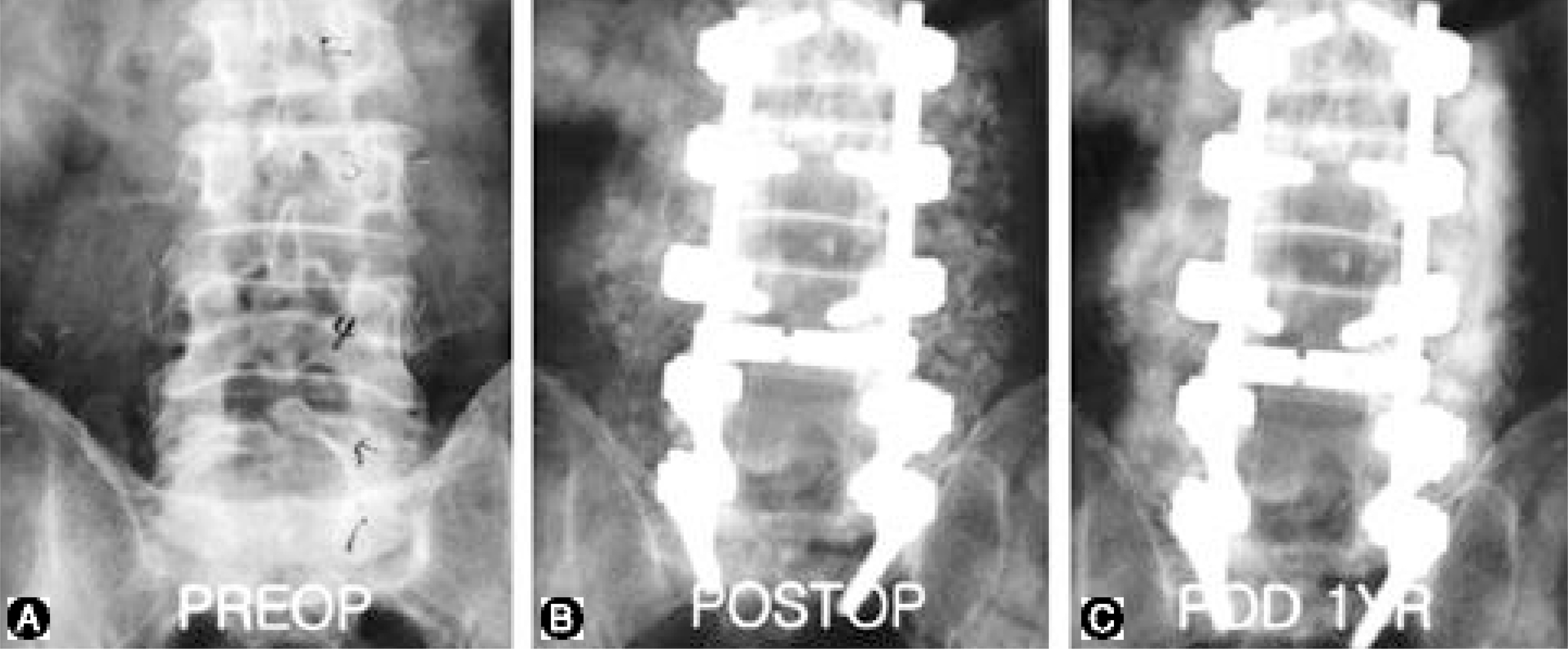
Among the patients who had undergone a decompression and lumbar posterolateral fusion for various lumbar diseases, between January 1997 and December 1999, 178, in who 2 year follow-up observations had been possible, were selected for this study. The patients were allocated to 1 of 3 groups, Group I (47 patients), Group II (57 patients) and Group III (74 patients). For each group, the mean patient ages were 58.3, 49 and 62.4 years old, respectively, with male to female ratios of 24:23, 23:24 and 36:38. Postoperative radiographs were taken at 2 weeks, 3 months and 1 year, and further follow-up observations were conducted at 1-year intervals. The bone fusions was determined, along with the fusion rates, based on Lenke's criteria, and the post-operative clinical outcomes were evaluated as excellent, good, normal and poor, using Kim's method. A statistical analysis was performed with Chi-square tests.
RESULTS
From the follow-up observations for over a year, the radiographic evaluations showed that the fusion rates of Groups I and II, over B: 86.6 and over B: 88.9%, were superior to the over B: 80.1% of Group III, but with no statistical significance. For the clinical outcomes, the 78.1 88% over good results were superior to the 69.4% of Group III, which also showed statistical significance.
CONCLUSIONS
The selective use of customized heterograft was assumed to be effective in an insufficient autogenous bone or a difficult autogenous bone collection even though it causes significantly lower improvement in the symptoms.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Ahn M H. Bone graft of autograft mixed with Lubboc in posterolateral fusion of thoracolumbar compression fracture, Journal of Korean Society of Spine Surgery. 34:273–279. 1999.2). Bonefiglio M., Fetter WS. Immunological responses to bone. Clin Orthop,. 87:19–27. 1972.3). Bos GD., Goldberg VM., Gordon NH. The long term fate of fresh and frozen orthotopic bone allografts in genetically defined rats. Clin Orthop,. 197:245–254. 1985.4). Bos GD., Glodberg VM., Heiple CH., Zika JM., an Powel AE. Immune responses of rats to frozen bone allografts. J Bone Joint Surg(Am),. 65:239. 1983.
Article5). Bos GD., Goldberg VM., Powel AE., Heiple KG., and Zika JM. The effect of histocompatibility matching on canine frozen bone allografts. J Bone Joint Surg(Am),. 65:89. 1983.
Article6). Chappard ., Zhioua A., Reb A. Biomaterials for bone Filling Comparison Bull Assoc Anaf,. 77:59–65. 1993.7). Cho TJ., Choi IH., and Park SS. The use of xenogrft (Lubboc) for pelvic osteotomy in children. J of Korean Orthop Surg,. 33:550–556. 1998.8). Crenshaw AH. Campbe ll' s Operative orthopaedic. 8th eD.Mosby-Year Book lne;p. 12–20. 1992.9). Elves MV., Pratt LM. The pattern of new bone formation in isografts of bone. Acta Orthop Scand,. 46:549–560. 1975.
Article10). Fischgrund JS., Mackay M. Degenerative lumbar spondylolithesis with spinal stenosis, Spine,. 22:2807–2812. 1997.11). Grahan CE. Further experience with fracture using xenograft mixed with autologous red marrow. In proceeding of the Australian Orthopedic Association. J Bone Joint Surg,. 64-B:123. 1982.12). Joo H S. The effect of Xenograft of Rat J of Korean Orthop Assoc. Vol 32(2):April 1997.13). Kim Nam hyun., Lee H. M. Usefulness of Posterolateral Fusion of Lumbar Spine with Allograft Bone (Tubo-plast), Journal of Korean Society of Spine Surgery. 5:198–204. 1998.14). Knapp DR., Jones ET. Use of cortical cancellous allograft for posterior spinal fusion. Clin Orthop,. 229:99–106. 1988.
Article15). Lane JM., Sandnu HS. Current approaches to experi -mental bone grafting. Orthop Clin North Am,. 18:213–225. 1987.16). Laurie SWS., Kaban LB., Mulliken JB., Murray JE. Donor site morbidity after harvesting rib and iliac bone. Plast Reconstr Surg,. 73(6):933. 1984.17). Lenke LG., Bridgwell KH., Baldus C., Blanke K. Cotrel-Dubousset instrumentation for adolescent idiopathic scol -iosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1992. 74:1056–1069.18). Lexer E. The History of Bone Graft. Clin Orthop. 226:292–298. 1998.19). Mizutani H., Urist MR. The nature of bone Mor -phogenic protein (BMP) reactions derived from bovine bone matrix gelatine. Clin Orthop,. 171:213–223. 1982.20). Morax S., Hubli T., Smida R. Bovine Heterogenous bone graft in orbital surgery. Ann Chir Plast Esthet,. 38:445–450. 1993.21). Parrish FF. Allograft replacement of all or part of the end of a long bone following excision of a tumor. J Bone Joint Surg(Am),. 55:1–22. 1973.
Article22). Poumark G., squire P. Compression of mechanism properties of human. Biomechanics. 14:337–340. 1993.23). Ramani PS., Kalbag RM., and Sengupta RP. C ervical spinal interbody fusion with Kiel bone. Br J Surg,. 62:147–150. 1975.24). Salama R. Xenogeneic bone grafting in humans. Clin Orthop,. 174:113–121. 1983.
Article25). Saito K., Urist MR. Induced regeneration of calvaria by bone morphogenic protein (BMP) in dogs. Clin Orthop,. 197:301–311. 1985.26). Spring field DS. Massure artopenous bone Graft Orthop Clin N AM. 249–256. 1987.27). Urist MR., Mikulske A., Boyd SD. A chemo-sterilized antigen-extracted autodigested allo-implant for bone banks. ArchSurg,. 110:416. 1975.
Article28). Younger EX., Chapman MW. Morbidity at bone graft donor sites (abstract). Orthop Trans,. 10(3):494. 1986.29). Zdeblick TA. A prospective randomized study of lumbar fusion: preliminary results: Spine,. 18:983. 1991.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Local Bone versus Autogenous Iliac Bone Graft for Posterolateral Lumbar Fusion in the Same Patient
- Relationship between Union of Grafted Autologous Bone and Clinical Results of Operative Treatment of Degenerative Spondylolisthesis by Posterolateral Fusion
- Comparison Between Allograft Mixed with Local Bone and Autograft in Posterolateral Lumbar Fusion
- Lumbar Posterolateral Fusion Using Demineralized Bone Matrix
- Usefulness of Posterolateral Fusion of Lumbar Spine with Allogeneic Bone (Tutoplast)