J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2010 Mar;17(1):38-48. 10.4184/jkss.2010.17.1.38.
Current Concept on the Classification and Treatment of Spondylolisthesis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. schsbj@hosp.sch.ac.kr
- KMID: 2003098
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2010.17.1.38
Abstract
- STUDY DESIGN: A review of literature including classification and treatment of spondylolisthesis.
OBJECTIVES
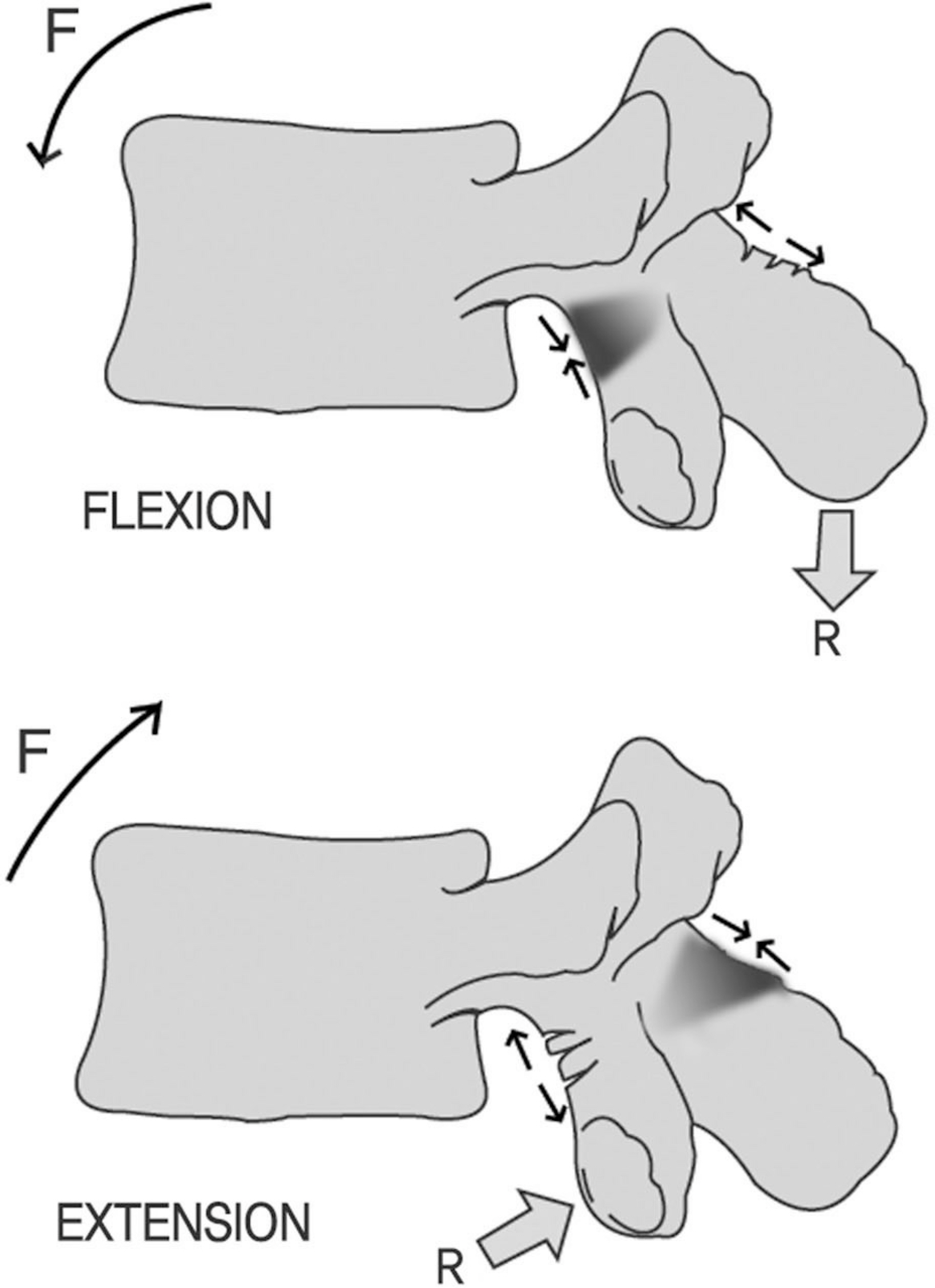
To review and discuss the classification and management of spondylolisthesis. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: Spondylolisthesis is one of the common spinal disorders that can create significant problems for the patients and spine surgeons, but there have been confusion of natural history and treatment strategies. It can be attributed to the absence of etiology-based classification system for individual patient prognosis and treatment decision.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Review of literature.
RESULTS
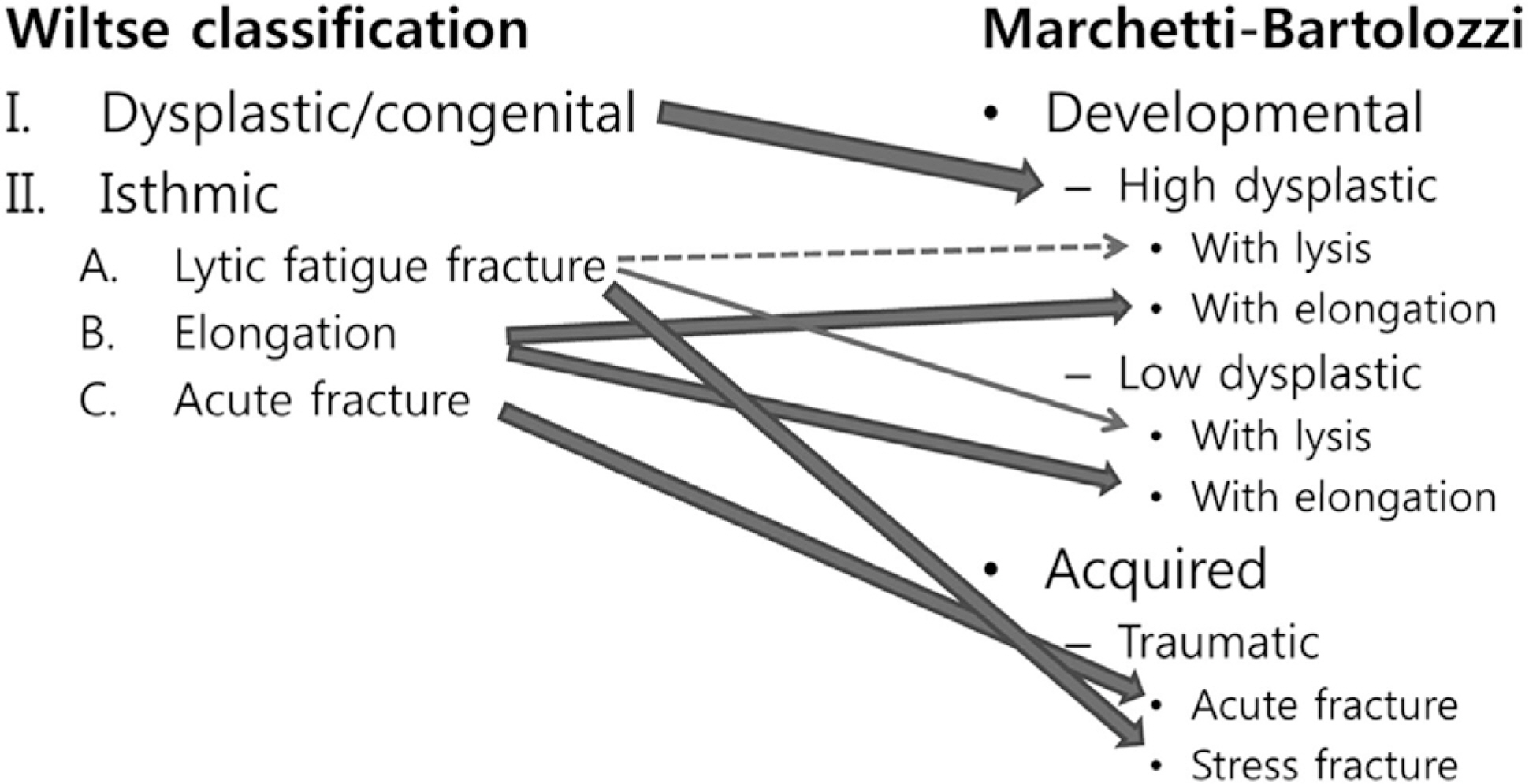
Marchetti and Bartolozzi have developed an etiology-based classification which has two main categories; developmental and acquired. These two types of spondylolisthesis seem to have significantly different natural histories and each of them needs different strategies for treatment.
CONCLUSIONS
Authors recommend using Marchetti and Bartolozzi classification system for spondylolisthesis patients.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1.DeWald R. Spondylolisthesis. Bridwell K, DeWald R, editors. The Textbook of Spinal Surgery. 2nd ed.Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven;1997. p. 1201–10.2.Wiltse LL., Newman PH., Macnab I. Classification of spondylolisis and spondylolisthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976. 23–9.
Article3.Marchetti P., Bartolozzi P. Classification of spondylolisthesis as a guideline for treatment. Bridwell K, DeWald R, editors. The Textbook of Spinal Surgery. 2nd ed.Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven;1997. p. 1211–54.4.Hammerberg KW. New concepts on the pathogenesis and classification of spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005. 30:S4–11.
Article5.Hensinger RN. Spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis in children and adolescents. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1989. 71:1098–107.
Article6.Mardjetko S., Albert T., Andersson G, et al. Spine/SRS spondylolisthesis summary statement. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005. 30:S3.
Article7.Ikata T., Miyake R., Katoh S, et al. Pathogenesis of sports-related spondylolisthesis in adolescents. Radiographic and magnetic resonance imaging study. Am J Sports Med. 1996. 24:94–8.8.Kajiura K., Katoh S., Sairyo K, et al. Slippage mechanism of pediatric spondylolysis: biomechanical study using immature calf spines. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001. 26:2208–12. discussion 12-3.9.Yue WM., Brodner W., Gaines RW. Abnormal spinal anatomy in 27 cases of surgically corrected spondyloptosis: proximal sacral endplate damage as a possible cause of spondyloptosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005. 30:S22–6.10.Lauerman WC., Cain JE. Isthmic Spondylolisthesis in the Adult. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1996. 4:201–8.
Article11.Beutler WJ., Fredrickson BE., Murtland A, et al. The natural history of spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis: 45-year follow-up evaluation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003. 28:1027–35. discussion 35.12.Fredrickson BE., Baker D., McHolick WJ, et al. The natural history of spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984. 66:699–707.
Article13.Saraste H. Long-term clinical and radiological follow-up of spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis. J Pediatr Orthop. 1987. 7:631–8.
Article14.Floman Y. Progression of lumbosacral isthmic spondylo-listhesis in adults. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000. 25:342–7.
Article15.Szypryt EP., Twining P., Mulholland RC, et al. The prevalence of disc degeneration associated with neural arch defects of the lumbar spine assessed by magnetic resonance imaging. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1989. 14:977–81.
Article16.Virta L., Ronnemaa T., Osterman K, et al. Prevalence of isthmic lumbar spondylolisthesis in middle-aged subjects from eastern and western Finland. J Clin Epidemiol. 1992. 45:917–22.
Article17.Seitsalo S., Osterman K., Hyvarinen H, et al. Progression of spondylolisthesis in children and adolescents. A long-term follow-up of 272 patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1991. 16:417–21.18.Friberg O. Instability in spondylolisthesis. Orthopedics. 1991. 14:463–5.
Article19.Davis IS., Bailey RW. Spondylolisthesis: indications for lumbar nerve root decompression and operative technique. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976. 129–34.20.DeWald CJ., Vartabedian JE., Rodts MF, et al. Evaluation and management of high-grade spondylolisthesis in adults. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005. 30:S49–59.
Article21.Frennered AK., Danielson BI., Nachemson AL. Natural history of symptomatic isthmic low-grade spondylolisthesis in children and adolescents: a seven-year follow-up study. J Pediatr Orthop. 1991. 11:209–13.22.Lonstein JE. Spondylolisthesis in children. Cause, natural history, and management. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999. 24:2640–8.23.Anderson K., Sarwark JF., Conway JJ, et al. Quantitative assessment with SPECT imaging of stress injuries of the pars interarticularis and response to bracing. J Pediatr Orthop. 2000. 20:28–33.
Article24.Boxall D., Bradford DS., Winter RB, et al. Management of severe spondylolisthesis in children and adolescents. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979. 61:479–95.
Article25.Antoniades SB., Hammerberg KW., DeWald RL. Sagittal plane configuration of the sacrum in spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000. 25:1085–91.
Article26.Hresko MT., Hirschfeld R., Buerk AA, et al. The effect of reduction and instrumentation of spondylolisthesis on spinopelvic sagittal alignment. J Pediatr Orthop. 2009. 29:157–62.
Article27.Labelle HMD., Roussouly PMD., Berthonnaud EP, et al. The importance of spinopelvic balance in L5-s1 developmental spondylolisthesis: a review of pertinent radiologic measurements. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005. 30:S27–34.28.Lindholm TS., Ragni P., Ylikoski M, et al. Lumbar isthmic spondylolisthesis in children and adolescents. Radiologic evaluation and results of operative treatment. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1990. 15:1350–5.29.Wiltse LL., Jackson DW. Treatment of spondylolisthesis and spondylolysis in children. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976. 92–100.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Clinical Analysis of Spondylolisthesis
- Radiological Characteristics of Low-Grade Lytic Spondylolisthesis: Similarity to Dysplastic Spondylolisthesis
- Surgical Treatment of Degenerative and Isthmic Spondylolisthesis
- Clinical study on treatment of spondylolisthesis
- Surgical Treatment of Spondylolisthesis