J Korean Acad Prosthodont.
2013 Oct;51(4):292-299. 10.4047/jkap.2013.51.4.292.
Dental implant cost estimation using the Activity-Based Costing approach
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Humanities and Social Dentistry, Dental College, Wonkwang University, Iksan, Korea. shinhosung@gmail.com
- KMID: 2000153
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jkap.2013.51.4.292
Abstract
- PURPOSE
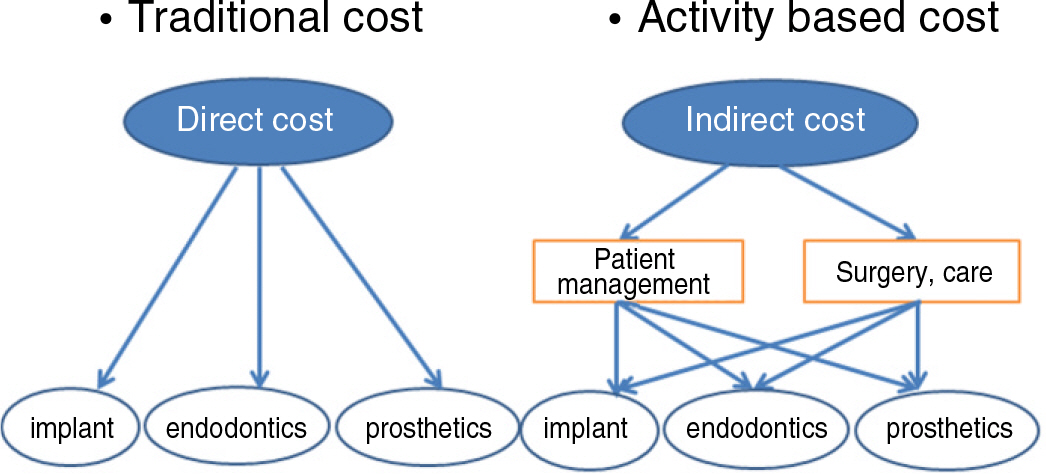
There is a growing concern for the cost management of medical institutions. The purpose of this study was to estimate Activity-Based Costing (ABC) for dental implant cost. ABC refers to allocating resources or cost based on the activities of services.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A dental institution located in the metropolitan area was selected in this study. The tax accounting data of the institution were utilized to confirm total cost, and the institution was asked to make out clinical activities to figure out what activities were carried out. The direct cost and indirect cost for dental implant were separately estimated, and cost driver was analyzed to estimate the indirect cost accurately.
RESULTS
The rates of the direct and indirect cost respectively stood at 35.8 and 49.5 percent. The cost for a dental implant was found to be approximately 1,579 won, and the cost of prosthetic surgery and treatment that included implant surgery accounted for the largest portion of the cost, which was 470 thousand won (30%). And the weight of training and education on dentistry was relatively higher than that of the other kinds of treatment.
CONCLUSION
In order to ensure accurate and scientific costing for dental implant, not only direct medical procedure but every pre- and post-procedure activity should fully be taken into account. Pre-activities, post-activities, education and training are included in the indirect cost, but all these activities are mandatory and associated with the quality of treatment and the satisfaction level of patients.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Dental implant bottom-up cost analysis
Min-Young Kim, Ha-Na Choi, Ho-Sung Shin
J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2014;52(1):18-26. doi: 10.4047/jkap.2014.52.1.18.
Reference
-
1.Korean Dental Association for the internal data. Hyundai Marine & Fire Insurance data.2.Kim KK. Using activity-based costing study on the rationalization of the management of service companies-focusing on hospital management. J Korean Assoc Tax Account. 2002. 12:123–39.3.Jung JK. Case study on assessment of hospital management-focusing on problems and improvement. J Korean Hosp Assoc. 1995. 24:22–38.4.Shin HS., Oh YH., Choi HN. Dental implant cost analysis. Korean Inst Health Soc Aff;2008. p. 19–22.5.Udpa S. Activity-based costing for hospitals. Health Care Manag Rev. 1996. 21:83–96.
Article6.Ahn TS., O DI., Jung HR. Prescription costs and conversion factor estimation using the activity-based costing approach. J Account Econ. 2007. 8:33–52.7.Chun KH., Ahn TS., Cho WH., Kim BK. The study on the cost analysis based on ABC system in clinical laboratory. Korean J Health Policy Adm. 1998. 8:88–109.8.Jung YM., Yang DH., Lee YC., Leem BH. A case study on activity-based costing for a hospital. J Korean Hosp Assoc. 2005. 10:25–47.9.Ahn TS., O DI., Jung HR. A study on the cost separation and conversion factor of the physician office based on activity based costing model. J Manag Account Assoc Korea. 2005. 5:57–85.10.Kuchta D., Zabek S. Activity-based costing for health care institutions. 8th international conference on enterprise systems. 2011.11.Suomeksi T. Rationale for adopting activity based costing in hospitals. Janne Jarvinen;2005. p. 45–50.12.Lee JY., Song HS. A study on the activity - Based costing system for general hospital. J Korean Ind Econ. 2001. 14:245–59.13.Ahn TS., Chun KH., Kim BK. Costing of hospital laboratory tests using ABC. Korean Account Rev. 1999. 24:117–40.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Dental implant bottom-up cost analysis
- Analysis of Cost and Efficiency of a Medical Nursing Unit Using Time-Driven Activity-Based Costing
- Model Development of Hospital Process Reengineering by Activity-Based Costing
- Development and Application of Cost Management Program for Visiting Nursing Centers Using Time-Driven Activity-Based Costing
- Cost Analysis of Home Care with Activity-Based Costing(ABC)