J Korean Acad Prosthodont.
2014 Apr;52(2):82-89. 10.4047/jkap.2014.52.2.82.
Rheological properties of dental resin cements during polymerization
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics and Dental Research Institute, School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Seoul, Republic of Korea. swallow@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Dentistry, Ajou University, School of Medicine, Suwon, Republic of Korea.
- 3Department of Prosthodontics, Veterans Health Service Medical Center Seoul, Republic of Korea.
- KMID: 2000133
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jkap.2014.52.2.82
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to observe the change of viscoelastic properties of dental resin cements during polymerization.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Six commercially available resin cement materials (Clearfil SA luting, Panavia F 2.0, Zirconite, Variolink N, RelyX Unicem clicker, RelyX U200) were investigated in this study. A dynamic oscillation-time sweep test was performed with AR1500 stress controlled rheometer at 32degrees C. The changes in shear storage modulus (G'), shear loss modulus (G"), loss tangent (tan delta) and displacement were measured for twenty minutes and repeated three times for each material. The data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA and Tukey's post hoc test (alpha=0.05).
RESULTS
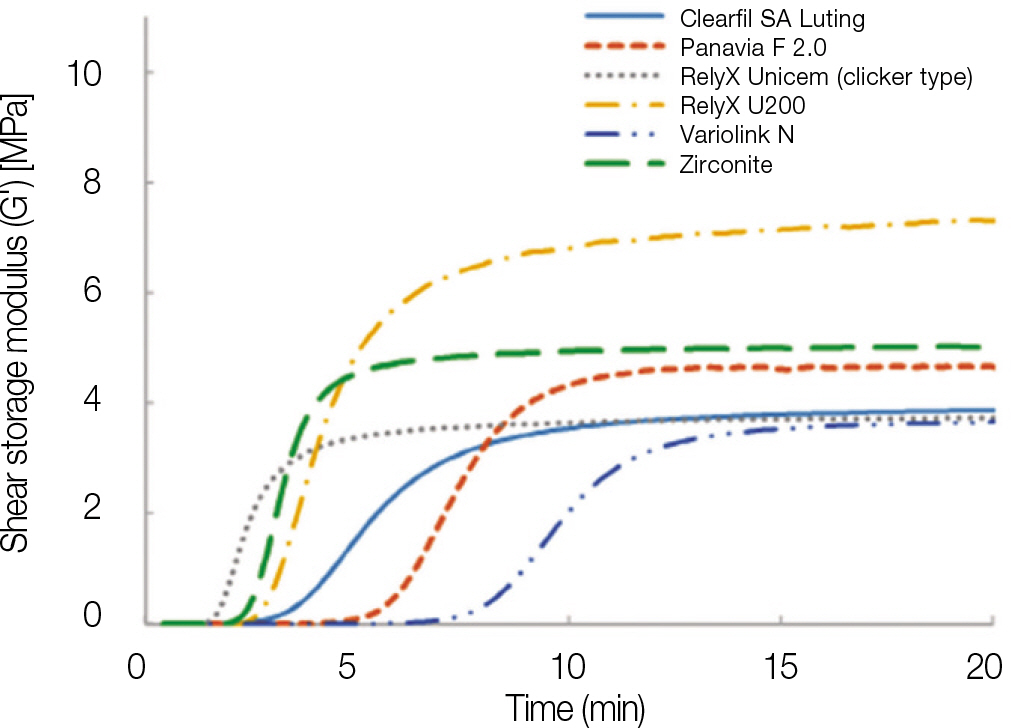
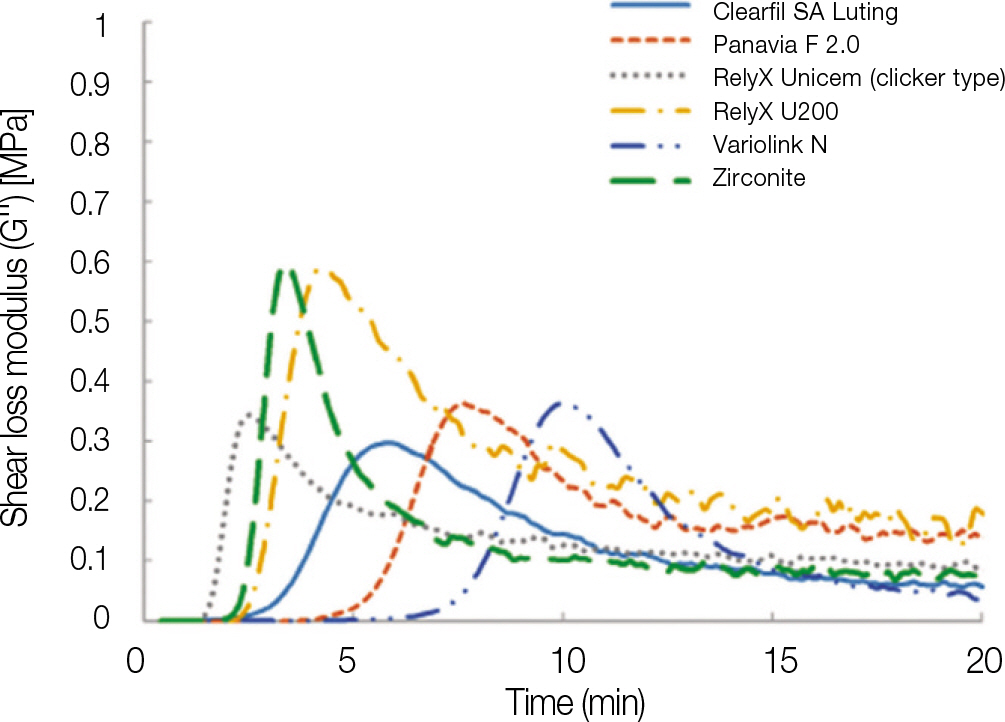
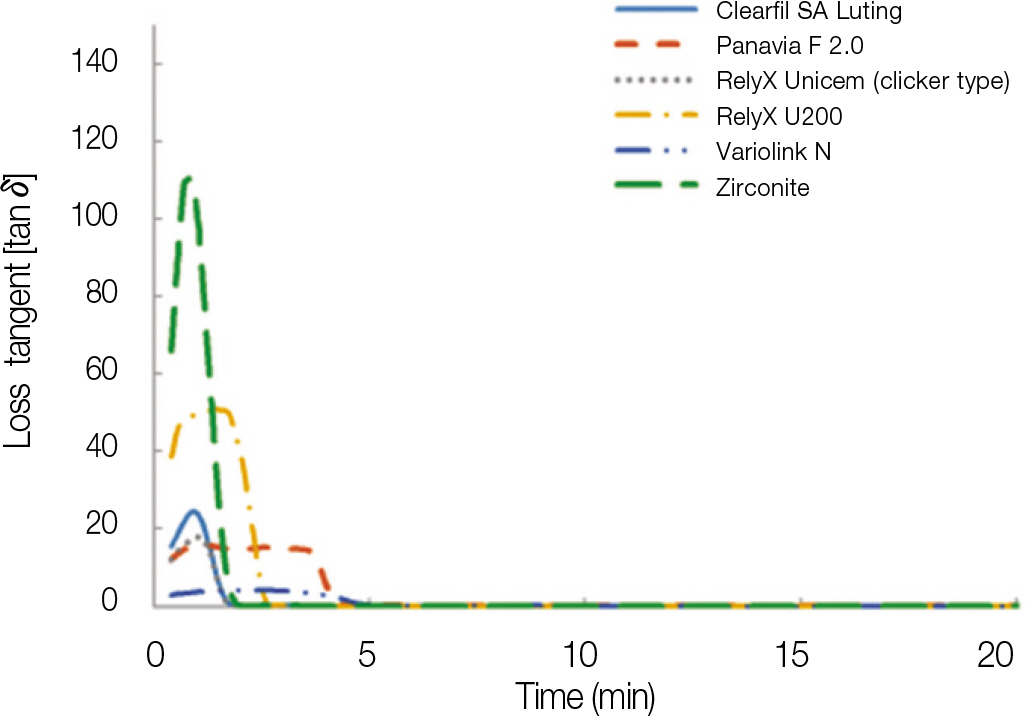
After mixing, all materials demonstrated an increase in G' with time, reaching the plateau in the end. RelyX U200 demonstrated the highest G' value, while RelyX Unicem (clicker type) and Variolink N demonstrated the lowest G' value at the end of experimental time. Tan delta was maintained at some level and reached the zero at the starting point where G' began to increase. The tan delta and displacement of the tested materials showed similar pattern in the graph within change of time. The displacement of all 6 materials approached to zero within 6 minutes.
CONCLUSION
Compared to other resin cements used in this study, RelyX U200 maintained plastic property for a longer period of time. When it completed the curing process, RelyX U200 had the highest stiffness. It is convenient for clinicians to cement multiple units of dental prostheses simultaneously.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Jorgensen KD., Esbensen AL. The relationship between the film thickness of zinc phosphate cement and the retention of veneer crowns. Acta Odontol Scand. 1968. 26:169–75.2.Wilson PR. The effect of die spacing on crown deformation and seating time. Int J Prosthodont. 1993. 6:397–401.3.Van Nortwick WT., Gettleman L. Effect of internal relief, vibration, and venting on the vertical seating of cemented crowns. J Prosthet Dent. 1981. 45:395–9.
Article4.Judge RB., Wilson PR. The effects of oscillating forces upon the flow of dental cements. J Oral Rehabil. 1999. 26:892–9.
Article5.Piemjai M. Effect of seating force, margin design, and cement on marginal seal and retention of complete metal crowns. Int J Prosthodont. 2001. 14:412–6.6.J�rgensen KD. Factors affecting the film thickness of zinc phosphate cements. Acta Odonto Scand. 2009. 18:479–90.7.de Freitas Oliveira J., Ishikiriama A., Vieira DF., Mondelli J. Influence of pressure and vibration during cementation. J Prosthet Dent. 1979. 41:173–7.
Article8.Park EK., Song KW. Rheological evaluation of petroleum jelly as a base material in ointment and cream formulations with respect to rubbing onto the human body. Korea-Aust Rheol J. 2010. 22:279–89.9.Rosenstiel SF., Land MF., Crispin BJ. Dental luting agents: A review of the current literature. J Prosthet Dent. 1998. 80:280–301.
Article10.Diaz-Arnold AM., Vargas MA., Haselton DR. Current status of luting agents for fixed prosthodontics. J Prosthet Dent. 1999. 81:135–41.
Article11.White SN., Yu Z. Physical properties of fixed prosthodontic, resin composite luting agents. Int J Prosthodont. 1993. 6:384–9.12.Wilson AD., Lewis BG. The flow properties of dental cements. J Biomed Mater Res. 1980. 14:383–91.
Article13.Vlachodimitropoulos H., Wilson PR. Characterization of the development of elasticity in dental luting cements. J Dent. 1998. 26:173–6.
Article14.Osman SA., McCabe JF., Walls AW. Film thickness and rheological properties of luting agents for crown cementation. Eur J Prosthodont Restor Dent. 2006. 14:23–7.15.Lorton L., Moore BK., Swartz ML., Phillips RW. Rheology of luting cements. J Dent Res. 1980. 59:1486–92.
Article16.Kious AR., Roberts HW., Brackett WW. Film thicknesses of recently introduced luting cements. J Prosthet Dent. 2009. 101:189–92.
Article17.Cook WD., Brockhurst P. The oscillating rheometer-what does it measure? J Dent Res. 1980. 59:795–9.18.Batchelor RF., Wilson AD. Zinc oxide-eugenol cements. I. The effect of atmospheric conditions on rheological properties. J Dent Res. 1969. 48:883–7.
Article19.Plant CG., Jones IH., Wilson HJ. Setting characteristics of lining and cementing materials. Br Dent J. 1972. 133:21–4.
Article20.Vermilyea S., Powers JM., Craig RG. Rotational viscometry of a zinc phosphate and a zinc polyacrylate cement. J Dent Res. 1977. 56:762–7.
Article21.Pae AR., Lee HR., Kim HS. Effect of temperature on the rheological properties of dental interocclusal recording materials. Korea-Aust Rheol J. 2008. 20:221–6.22.Lee HO., Lee IB. Rheological properties of polyvinylsiloxane impression materials before mixing and during setting related to handling characteristics. Korea-Aust Rheol J. 2012. 24:211–9.
Article23.Cook WD., Standish PM. Polymerization kinetics of resin-based restorative materials. J Biomed Mater Res. 1983. 17:275–82.
Article24.Barnes HA., Hutton JF., Walters K. An introduction to rheology,. Amsterdam: Elsevier;1989.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- In vitro study of Polymerization shrinkage-strain kinetics of dental resin cements
- Comparison of polymerization shrinkage of dual-cure core build-up resin according to shade and curing mode
- Effects of immediate and delayed light activation on the polymerization shrinkage-strain of dual-cure resin cements
- A study on the bond strength of porcelain laminate and composite resin cements
- Effect of film thickness of resin cement on bonding efficiency in indirect composite restoration