Korean J Urol.
2010 Aug;51(8):583-585. 10.4111/kju.2010.51.8.583.
Hematuria Secondary to an Internal Iliac Artery Aneurysm
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Hatzikosta General Hospital, Ioannina, Greece. makatsoriaik@yahoo.gr
- KMID: 1997029
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2010.51.8.583
Abstract
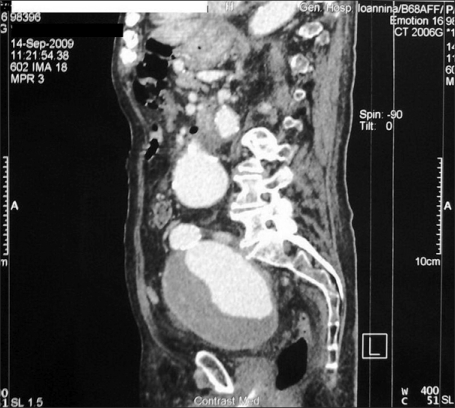
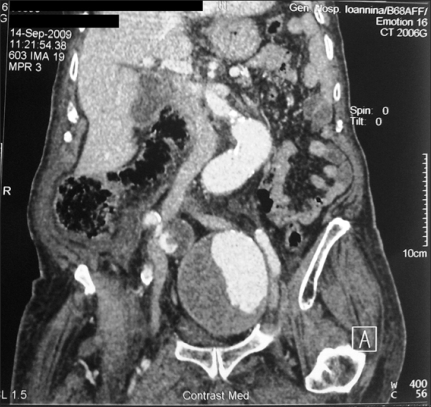
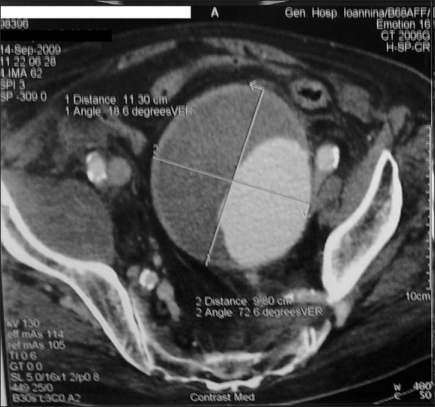
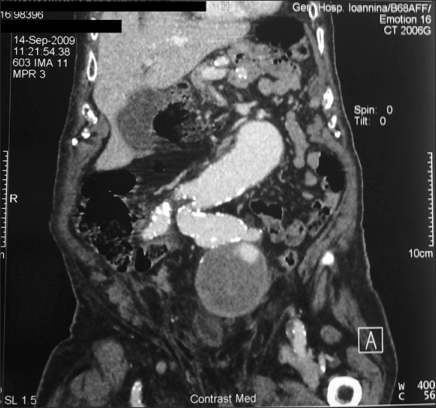
- We report a case of macroscopic hematuria secondary to an aneurysm of the internal iliac artery. An 84-year-old male presented to our department with a 12-hour history of painless gross hematuria. Cystoscopy showed decreased expansion suggesting compression from outside the bladder. At the point of compression, increased vascularization was noted in the bladder mucosa without evidence of active bleeding. No trace of blood was identified coming from the ureteric orifices, the bladder neck, or the prostate. There was no evidence of intra-vesicular masses or other inflammatory changes. The abdominal computed tomography scan revealed left-sided hydronephrosis and an abdominal aortic aneurysm involving the aortic bifurcation and both internal iliac arteries. There was no evidence of rupture. An aneurysm of the internal iliac artery is a rare cause of macroscopic hematuria that can be fatal. Awareness of this as a possible cause of hematuria may assist in immediate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Levi N, Sønksen JR, Iversen P, Helgstrand U. Rupture of an iliac artery pseudo-aneurysm into a ureter. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 1999; 17:264–265. PMID: 10092904.
Article2. Honma I, Takagi Y, Shigyo M, Sunaoshi K, Inaoka M, Miyao N. Massive hematuria after cystoscopy in a patient with an internal iliac artery aneurysm. Int J Urol. 2002; 9:407–409. PMID: 12165025.
Article3. Batter SJ, McGovern FJ, Cambria RP. Ureteroarterial fistula: case report and review of the literature. Urology. 1996; 48:481–489. PMID: 8804509.
Article4. Guru KA, Sarle RC, Reddy D, Peabody JO. Iliac artery aneurysm: a fatal cause of urinary retention. J Endourol. 2003; 17:221–222. PMID: 12816584.
Article5. Hiromatsu S, Hosokawa Y, Egawa N, Yokokura H, Akaiwa K, Aoyagi S. Strategy for isolated iliac artery aneurysms. Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann. 2007; 15:280–284. PMID: 17664198.
Article6. Mulaudzi TV, Robbs JV, Pillay B, Paruk N. Ruptured isolated internal iliac artery aneurysm presenting with haematuria: a case report. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2005; 10:35–37.
Article7. Bhasin N, Jones SM, Patel J, Kessel D, Robertson I, Berridge DC, et al. Internal iliac artery aneurysm--a cause of leg swelling and cellulitis. J R Soc Med. 2004; 97:483–484. PMID: 15459260.
Article8. O'Driscoll D, Fitzgerald E. Isolated iliac artery aneurysms with associated hydronephrosis. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 1999; 44:197–199. PMID: 10372494.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ureteral Stricture from Retroperitoneal Fibrosis Caused by Isolated Common Iliac Artery Aneurysm
- A Case of Iliac Artery Aneurysm Masquerading as Pelvic Sarcoma
- Lower Extremity Weakness and Back Pain from a Ruptured Iliac Artery Aneurysm: A Case Report
- A Case of Internal Iliac Artery Aneurysm as a Fatal Cause Resulting in Acute Urinary Retention
- Endovascular repair of bilateral iliac artery aneurysm with branched iliac stents: case report and review of the current literature