Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2009 Oct;13(5):357-360. 10.4196/kjpp.2009.13.5.357.
Social Isolation Selectively Increases Anxiety in Mice without Affecting Depression-like Behavior
- Affiliations
-
- 1National Creative Research Initiative Center for Memory, Department of Biological Sciences, College of Natural Sciences, Seoul National University, Seoul 151-747, Korea. kaang@snu.ac.kr
- 2Brain and Cognitive Sciences, College of Natural Sciences, Seoul National University, Seoul 151-747, Korea.
- KMID: 1982568
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2009.13.5.357
Abstract
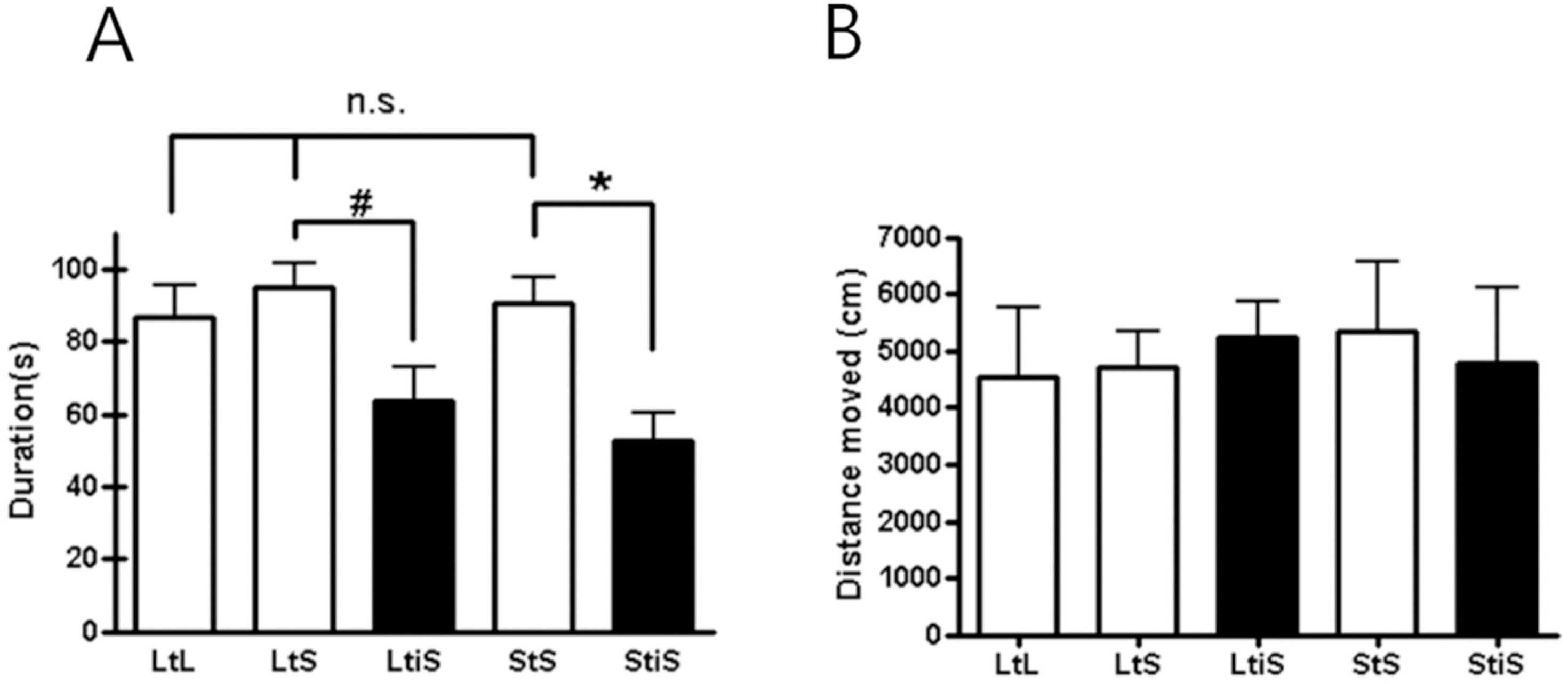
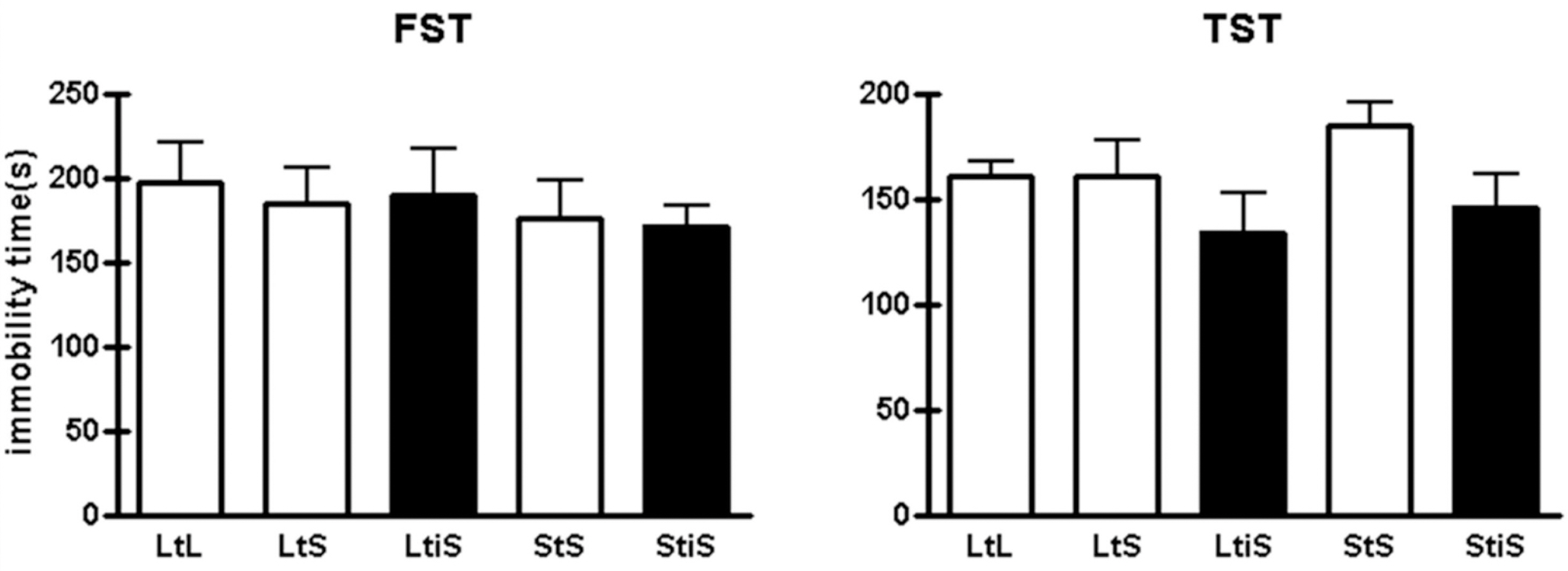
- It is hypothesized that a number of environmental factors affect animals' behavior. Without controlling these variables, it is very hard for researchers to get not only reliable, but replicable data from various behavioral experiments testing animals' cognitive as well as emotional functions. For example, laboratory mice which had restricted environment showed different synaptic potentiation properties with wild mice (Zhao MG et al., 2009). While performing behavioral experiments, however, it is sometimes inevitable that the researcher changes the animals' environments, as by switching the cages in which experimental animals are housed and separating animals raised together into small experimental groups. In this study, we investigated the effect of environmental changes on mice's emotional behaviors by socially isolating them or reducing the size of their cage. We found that social isolation selectively increases the animals' levels of anxiety, while leaving depression-like behaviors unchanged. On the other hand, alteration of the housing dimensions affected neither their anxiety levels nor their depression-like behaviors. These results suggest that environmental variables may have a prominent impact on experimental animals' emotional behaviors and possibly their psychological states, leading to bias in the behavioral data produced from experiments.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Chronic Non-Social Stress Affects Depressive Behaviors But Not Anxiety in Mice
Sang Ho Yoon, Byung-Hak Kim, Sang-Kyu Ye, Myoung-Hwan Kim
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2014;18(3):263-268. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2014.18.3.263.
Reference
-
References
Chourbaji S., Zacher C., Sanchis-Segura C., Spanagel R., Gass P. Social and structural housing conditions influence the development of a depressive-like phenotype in the learned helplessness paradigm in male mice. Behav Brain Res. 164:100–106. 2005.
ArticleDeacon RM. Housing, husbandry and handling of rodents for behavioral experiments. Nat Protoc. 1:936–946. 2006.
ArticleHattori S., Hashimoto R., Miyakawa T., Yamanaka H., Maeno H., Wada K., Kunugi H. Enriched environments influence depression-related behavior in adult mice and the survival of newborn cells in their hippocampi. Behav Brain Res. 180:69–76. 2007.
ArticleKarolewicz B., Paul IA. Group housing of mice increases immobility and antidepressant sensitivity in the forced swim and tail suspension tests. Eur J Pharmacol. 415:197–201. 2001.
ArticleKirbya LG., Panb YZ., Freeman-Danielsa E., Rania S., Nunana JD., Akanwab A., Beckb SG. Cellular effects of swim stress in the dorsal raphe nucleus. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 32:712–723. 2007.
ArticleMalberg JE., Duman RS. Cell proliferation in adult hippocampus is decreased by inescapable stress: reversal by fluoxetine treatment. Neuropsychopharmacology. 28:1562–1571. 2003.
ArticleMillstein RA., Holmes A. Effects of repeated maternal separation on anxiety- and depression-related phenotypes in different mouse strains. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 31:3–17. 2007.
ArticlePorsolt RD., Anton G., Blavet N., Jalfre M. Behavioural despair in rats: a new model sensitive to antidepressant treatments. Eur J Pharmacol. 4:379–391. 1978.
ArticlePrut L., Belzung C. The open field as a paradigm to measure the effects of drugs on anxiety-like behaviors: a review. Eur J Pharmacol. 463:3–33. 2003.
ArticleSteru L., Chermat R., Thierry B., Simon P. The tail suspension test: a new method for screening antidepressants in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 85:367–370. 1985.
ArticleZhao MG., Toyoda H., Wang YK., Zhuo M. Enhanced synaptic long-term potentiation in the anterior cingulate cortex of adult wild mice as compared with that in laboratory mice. Mol Brain. 2:11. 2009.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Chronic Non-Social Stress Affects Depressive Behaviors But Not Anxiety in Mice
- Effects of single housing on behavior, corticosterone level and body weight in male and female mice
- Normal Anxiety, Fear and Depression-related Behaviors in Mice Lacking alpha-Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide
- Associations among Uncertainty, Depression, and Anxiety in Isolated Inpatients
- Effects of Envy on Depression: The Mediating Roles of Psychological Resilience and Social Support