Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2011 May;15(2):83-89. 10.14701/kjhbps.2011.15.2.83.
Risk Factors for Intrahepatic Recurrence
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Gospel Hospital, College of Medicine, Kosin University, Korea. ymh479@kosinmed.or.kr
- KMID: 1980946
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/kjhbps.2011.15.2.83
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Although surgical resection offers patients with HCC the chance of a cure, the post-resection tumor recurrence rate is high, with reported cumulative 5-year tumor recurrence rates ranging from 40 to 70%. The objective of this study was to investigate risk factors for intrahepatic recurrence after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma, especially in patients with hepatitis B virus infection.
METHODS
Between January 1999 and December 2003, 59 patients in our Hospital with hepatitis B virus infection underwent liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clinical, biological, and histopathological characteristics of these patients were collected and tested for their prognostic significance using a Chi-square test and a Student's t-test. Time to recurrence and survival rate were analyzed by the Kaplan-Meier method.
RESULTS
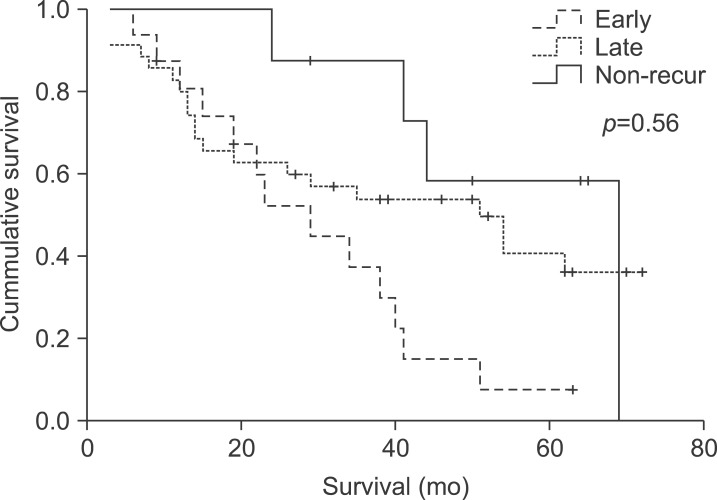
Of the 59 patients who underwent liver resection, 24 (41%) experienced intrahepatic recurrence. The 1-, 3-, and 5-year overall survival rates of total enrolled patients were 83%, 63%, and 42%, respectively. The 1-, 3-, and 5-year overall survival rates after recurrence were 87%, 52%, and 20%, respectively. The risk factors for early recurrence were elevated serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST) level (p=0.044) and larger tumor size (p=0.049). For late recurrence, greater tumor size (p=0.039) was the only risk factor.
CONCLUSION
Tumor size and serum aspartate aminotransferase are risk factors of intrahepatic recurrence after resection of HCC in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. This finding indicates that patients who have these risk factors should be under more careful supervision and have more aggressive follow-up.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Tan A, Yeh SH, Liu CJ, Cheung C, Chen PJ. Viral hepatocarcinogenesis: from infection to cancer. Liver Int. 2008; 28:175–188. PMID: 18251977.
Article2. Ministry of Health and Welfare. 2002 Annual Report of the Korea Central Cancer Registry. 2003. Gyeonggi-do: Ministry of Health and Welfare.3. Shah SA, Greig PD, Gallinger S, et al. Factors associated with early recurrence after resection for hepatocellular carcinoma and outcomes. J Am Coll Surg. 2006; 202:275–283. PMID: 16427553.
Article4. Chen WT, Chau GY, Lui WY, et al. Recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatic resection: prognostic factors and long-term outcome. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2004; 30:414–420. PMID: 15063895.
Article5. Park KW, Park JW, Choi JI, et al. Survival analysis of 904 patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in a hepatitis B virus-endemic area. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008; 23:467–473. PMID: 17764529.
Article6. Poon RT, Fan ST, Lo CM, Liu CL, Wong J. Intrahepatic recurrence after curative resection of hepatocellular carcinoma: long-term results of treatment and prognostic factors. Ann Surg. 1999; 229:216–222. PMID: 10024103.7. Poon RT, Fan ST, Ng IO, Lo CM, Liu CL, Wong J. Different risk factors and prognosis for early and late intrahepatic recurrence after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 2000; 89:500–507. PMID: 10931448.
Article8. Poon RT, Fan ST, Lo CM, et al. Improving perioperative outcome expands the role of hepatectomy in management of benign and malignant hepatobiliary diseases: analysis of 1222 consecutive patients from a prospective database. Ann Surg. 2004; 240:698–708. PMID: 15383797.9. Chen WT, Chau GY, Lui WY, et al. Recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatic resection: prognostic factors and long-term outcome. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2004; 30:414–420. PMID: 15063895.
Article10. Choi GH, Kim DH, Kang CM, et al. Prognostic factors and optimal treatment strategy for intrahepatic nodular recurrence after curative resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2008; 15:618–629. PMID: 18004628.
Article11. Cha C, Fong Y, Jarnagin WR, Blumgart LH, DeMatteo RP. Predictors and patterns of recurrence after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Am Coll Surg. 2003; 197:753–758. PMID: 14585409.
Article12. Nagasue N, Uchida M, Makino Y, et al. Incidence and factors associated with intrahepatic recurrence following resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 1993; 105:488–494. PMID: 8392955.
Article13. Kumada T, Nakano S, Takeda I, et al. Patterns of recurrence after initial treatment in patients with small hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 1997; 25:87–92. PMID: 8985270.
Article14. Lupberger J, Hildt E. Hepatitis B virus-induced oncogenesis. World J Gastroenterol. 2007; 13:74–81. PMID: 17206756.
Article15. Ibrahim S, Roychowdhury A, Hean TK. Risk factors for intrahepatic recurrence after hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Surg. 2007; 194:17–22. PMID: 17560903.
Article16. Ou DP, Yang LY, Huang GW, Tao YM, Ding X, Chang ZG. Clinical analysis of the risk factors for recurrence of HCC and its relationship with HBV. World J Gastroenterol. 2005; 11:2061–2066. PMID: 15810069.
Article17. Adachi E, Maeda T, Matsumata T, et al. Risk factors for intrahepatic recurrence in human small hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 1995; 108:768–775. PMID: 7875479.
Article18. van Zonneveld M, Honkoop P, Hansen BE, et al. Long-term follow-up of alpha-interferon treatment of patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2004; 39:804–810. PMID: 14999700.
Article19. Choi DR, Jang MK, Moon HK, et al. Long-term follow-up of alpha-interferon treatment in patients with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. Korean J Med. 2005; 69:150–156.20. Lang H, Sotiropoulos GC, Brokalaki EI, et al. Survival and recurrence rates after resection for hepatocellular carcinoma in noncirrhotic livers. J Am Coll Surg. 2007; 205:27–36. PMID: 17617329.
Article21. Park UJ, Kim YH, Kang KJ, Lim TJ. Risk factors for early recurrence after surgical resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Korean J Hepatol. 2008; 14:371–380. PMID: 18815460.
Article22. Shah SA, Wei AC, Cleary SP, et al. Prognosis and results after resection of very large (> or =10 cm) hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastrointest Surg. 2007; 11:589–595. PMID: 17393258.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Risk Factors for the Intrahepatic Recurrence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Curative Resection
- Prognosis after intrahepatic recurrence in the patients who underwent curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma
- The Risk Factors for Intrahepatic Early Recurrence after Resection for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- A Case of Fetal Cholelithiasis Related to Maternal Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy
- A comparison of the risk factors of intrahepatic recurrence, early recurrencen, and multiple recurrences after resection for single nodular hepatocellular carcinoma