J Clin Neurol.
2006 Dec;2(4):279-282. 10.3988/jcn.2006.2.4.279.
Ergotism With Ischemia In All Four Extremities: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, South Korea. jeongsk@chonbuk.ac.kr
- 2Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, South Korea.
- KMID: 1980471
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2006.2.4.279
Abstract
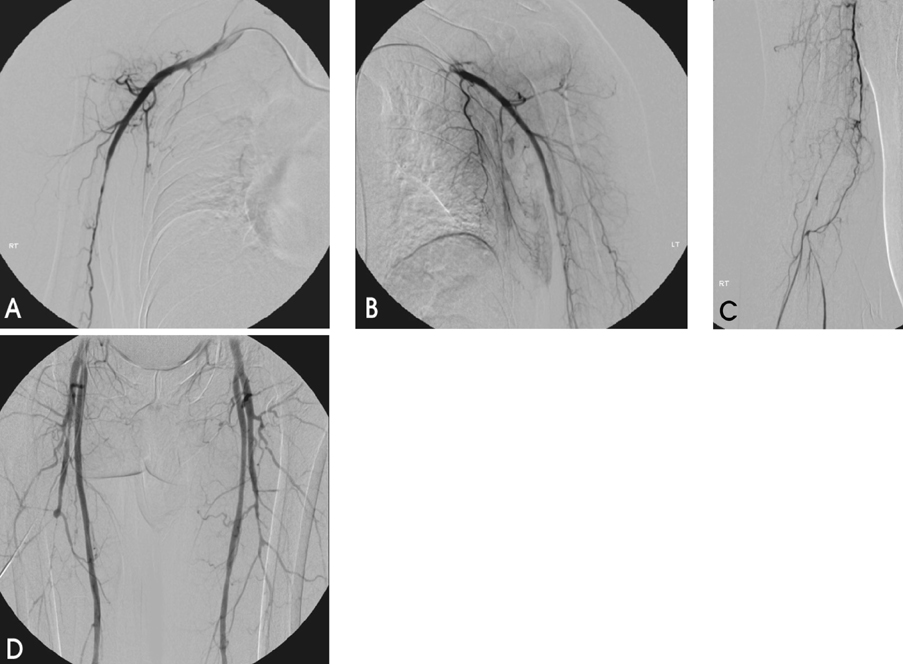
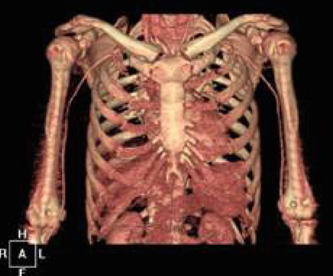
- Here we describe a case of ergotism that presented with ischemia in all four extremities. A 48-year-old man was admitted for pain and weakness in both upper extremities. He had a long history of migraine and had taken 3 mg of ergotamine daily for more than 21 years. Angiography demonstrated vasospasm involving all four extremities, which resolved partially following intra-arterial prostaglandin infusion. Intravenous nitroprusside was administered, and the patient stopped smoking and stopped taking ergotamine in an attempt to counteract the vasospasm. Follow-up computed tomography angiogram revealed that both brachial arteries had normalized. Thus, in this case of ergotism, severe vasospasm in all of the extremities was resolved with appropriate management.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Tfelt-Hansen P, Saxena PR, Dahlof C, Pascual J, Lainez M, Henry P, et al. Ergotamine in the acute treatment of migraine: a review and European consensus. Brain. 2000. 123:9–18.
Article2. Frediani F, Cannata AP, Magnoni A, Peccarisi C, Bussone G. The patient with medication overuse: clinical management problems. Neurol Sci. 2003. 242:S108–S111.
Article3. Wells KE, Steed DL, Zajko AB, Webster MW. Recognition and treatment of arterial insufficiency from cafergot. J Vasc Surg. 1986. 4:8–15.
Article4. Fukui S, Coggia M, Goeau-Brissonniere O. Acute upper extremity ischemia during concomitant use of ergotamine tartrate and ampicillin. Ann Vasc Surg. 1997. 11:420–424.
Article5. Merhoff GC, Porter JM. Ergot intoxication: historical review and description of unusual clinical manifestations. Ann Surg. 1974. 180:773–779.6. McKiernan TL, Bock K, Leya F, Grassman E, Lewis B, Johnson SA, et al. Ergot induced peripheral vascular insufficiency, non-interventional treatment. Cathet Cardiovasc Diagn. 1994. 31:211–214.
Article7. Garcia GD, Goff JM Jr, Hadro NC, O'Donnell SD, Greatorex PS. Chronic ergot toxicity: A rare cause of lower extremity ischemia. J Vasc Surg. 2000. 31:1245–1247.
Article8. Senter HJ, Lieverman AN, Pinto R. Cerebral manifestations of ergotism. Report of a case and review of the literature. Stroke. 1976. 7:88–92.
Article9. Silberstein SD. Chronic daily headache. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2005. 105:23S–29S.10. Evers S, Afra J, Frese A, Goadsby PJ, Linde M, May A, et al. EFNS guideline on the drug treatment of migraine - report of an EFNS task force. Eur J Neurol. 2006. 13:560–572.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Femoral arteriographic finding in acute ergotism
- Spinal Cord Compression Caused by a Metastatic Bone Tumor in Buerger's Disease Patient
- Traumatic False Aneurysm of Posterior Tibial Artery: A case report
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Intracardiac Thrombus Presenting as Acute Limb Ischemia
- Surgical Treatment of Chronic Ischemia of Lower Extremities