J Breast Cancer.
2013 Dec;16(4):438-441. 10.4048/jbc.2013.16.4.438.
Expander/Implant Breast Reconstruction after Reconstruction Using an Extended Cutaneous Thoracoabdominal Flap: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery, Campus Bio-Medico University of Rome, Rome, Italy. b.cagli@unicampus.it
- KMID: 1976383
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2013.16.4.438
Abstract
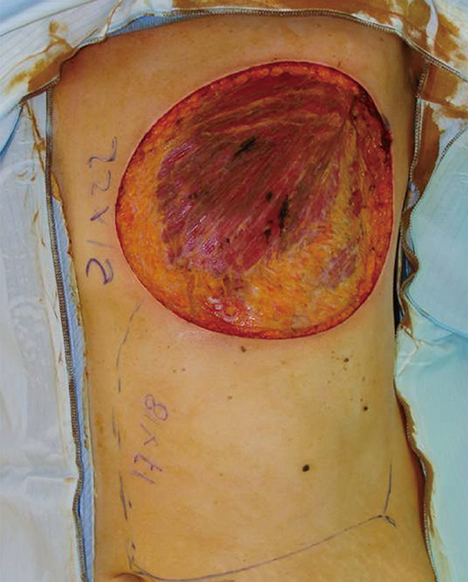
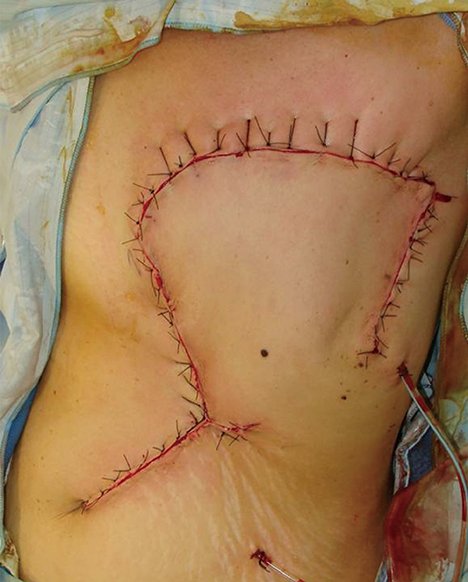
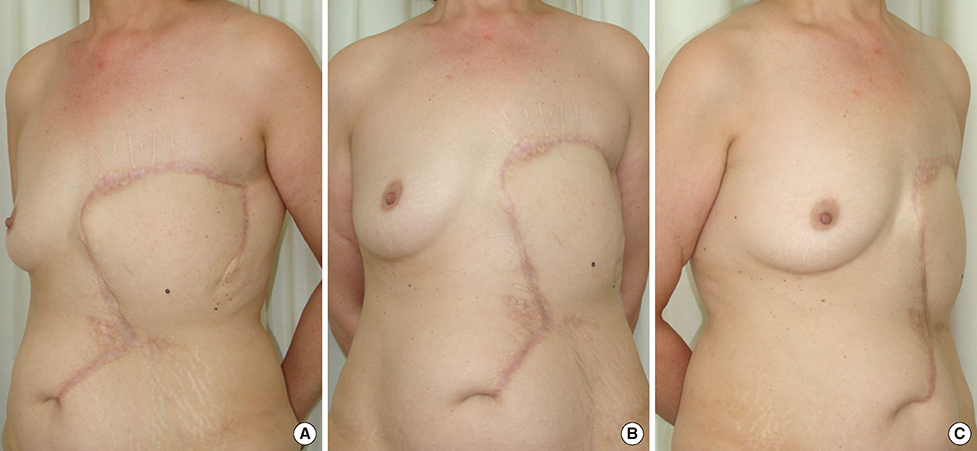
- Many flaps have been described and are being used in the reconstruction of extensive tissue defects in the thoracic wall. The extended cutaneous thoracoabdominal flap, described in 2006, is an excellent option for chest wall reconstruction in patients with advanced breast cancer, being associated with a low morbidity rate and good functional results. The main disadvantage of this technique is the poor cosmetic outcome and the complete absence of a breast crease. We present the first case of a two-stage heterologous breast reconstruction after reconstruction using an extended cutaneous thoracoabdominal flap.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Single vertical incision thoracoabdominal flap for chest wall reconstruction following mastectomy of locally advanced breast cancer
Kyunghyun Min, Eun Jeong Choi, Yeon Hoon Lee, Jin Sup Eom, Byung Ho Son, Sei Hyun Ahn, Eun Key Kim
Ann Surg Treat Res. 2019;97(4):168-175. doi: 10.4174/astr.2019.97.4.168.
Reference
-
1. Mansour KA, Thourani VH, Losken A, Reeves JG, Miller JI Jr, Carlson GW, et al. Chest wall resections and reconstruction: a 25-year experience. Ann Thorac Surg. 2002; 73:1720–1725.
Article2. Chagpar A, Langstein HN, Kronowitz SJ, Singletary SE, Ross MI, Buchholz TA, et al. Treatment and outcome of patients with chest wall recurrence after mastectomy and breast reconstruction. Am J Surg. 2004; 187:164–169.
Article3. Papadopoulos O, Georgiou P, Christopoulos A, Tsakoniatis N. Chest wall reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg. 2002; 48:105–107.
Article4. Chang RR, Mehrara BJ, Hu QY, Disa JJ, Cordeiro PG. Reconstruction of complex oncologic chest wall defects: a 10-year experience. Ann Plast Surg. 2004; 52:471–479.5. Losken A, Thourani VH, Carlson GW, Jones GE, Culbertson JH, Miller JI, et al. A reconstructive algorithm for plastic surgery following extensive chest wall resection. Br J Plast Surg. 2004; 57:295–302.
Article6. Persichetti P, Tenna S, Cagli B, Scuderi N. Extended cutaneous 'thoracoabdominal' flap for large chest wall reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg. 2006; 57:177–183.
Article7. Mayo JL, Dupin C, St Hilaire H. Outcomes in autologous breast reconstruction. J Am Coll Surg. 2013; 217:172–174.
Article8. Fischer JP, Nelson JA, Cleveland E, Sieber B, Rohrbach JI, Serletti JM, et al. Breast reconstruction modality outcome study: a comparison of expander/implants and free flaps in select patients. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013; 131:928–934.9. Cordeiro PG. Breast reconstruction after surgery for breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2008; 359:1590–1601.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Nipple Reconstruction using the C-V Flap Technique after Breast Reconstruction with the Only Breast Expander
- A Comparison of Permanent Expander-Implant in Immediate and Delayed Breast Reconstruction after Modified Radical Mastectomy
- Breast Reconstruction with the Extended Latissimus Dorsi Musculocutancous Flap
- A Clinical Study of Subcutaneous Mastectomy with Immediate Reconstruction as Treatment for Early Breast Carcinoma
- Breast Reconstruction with an Anatomical Expander and Implant: our clinical experience