Korean J Orthod.
2010 Feb;40(1):40-49. 10.4041/kjod.2010.40.1.40.
Comparison of transition temperature range and phase transformation behavior of nickel-titanium wires
- Affiliations
-
- 1Private Practice.
- 2Department of Dental Biomaterials Science, Dental Research Institute, School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Korea.
- 3Department of Orthodontics, School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Korea. drwhite@unitel.co.kr
- KMID: 1975624
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4041/kjod.2010.40.1.40
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The aim of this research was to evaluate the mechanical properties (MP) and degree of the phase transformation (PT) of martensitic (M-NiTi), austenitic (A-NiTi) and thermodynamic nickel-titanium wire (T-NiTi).
METHODS
The samples consisted of 0.016 x 0.022 inch M-NiTi (Nitinol Classic, NC), A-NiTi (Optimalloy, OPTI) and T-NiTi (Neo-Sentalloy, NEO). Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), three-point bending test, X-ray diffraction (XRD), and microstructure examination were used. Statistical evaluation was undertaken using ANOVA test.
RESULTS
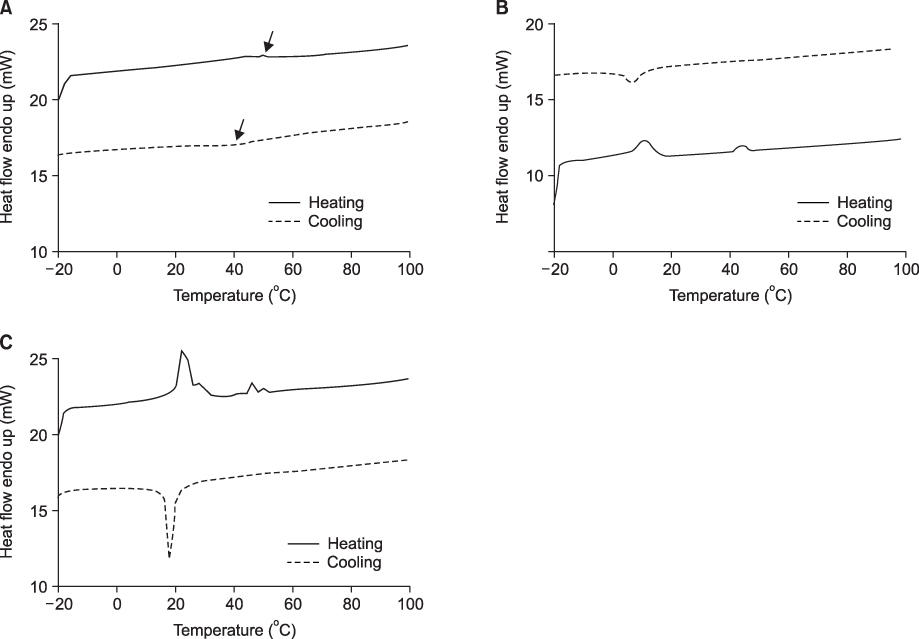
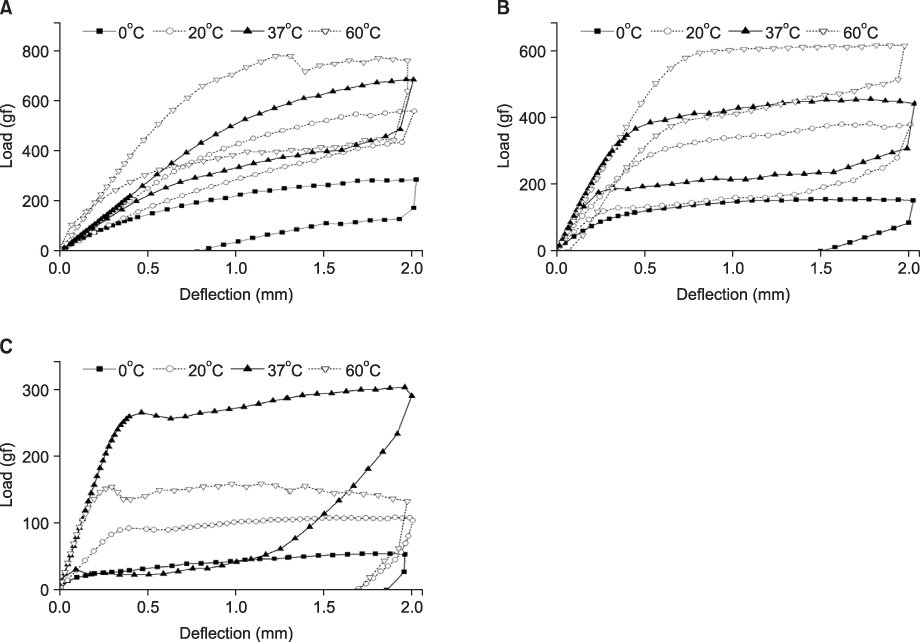
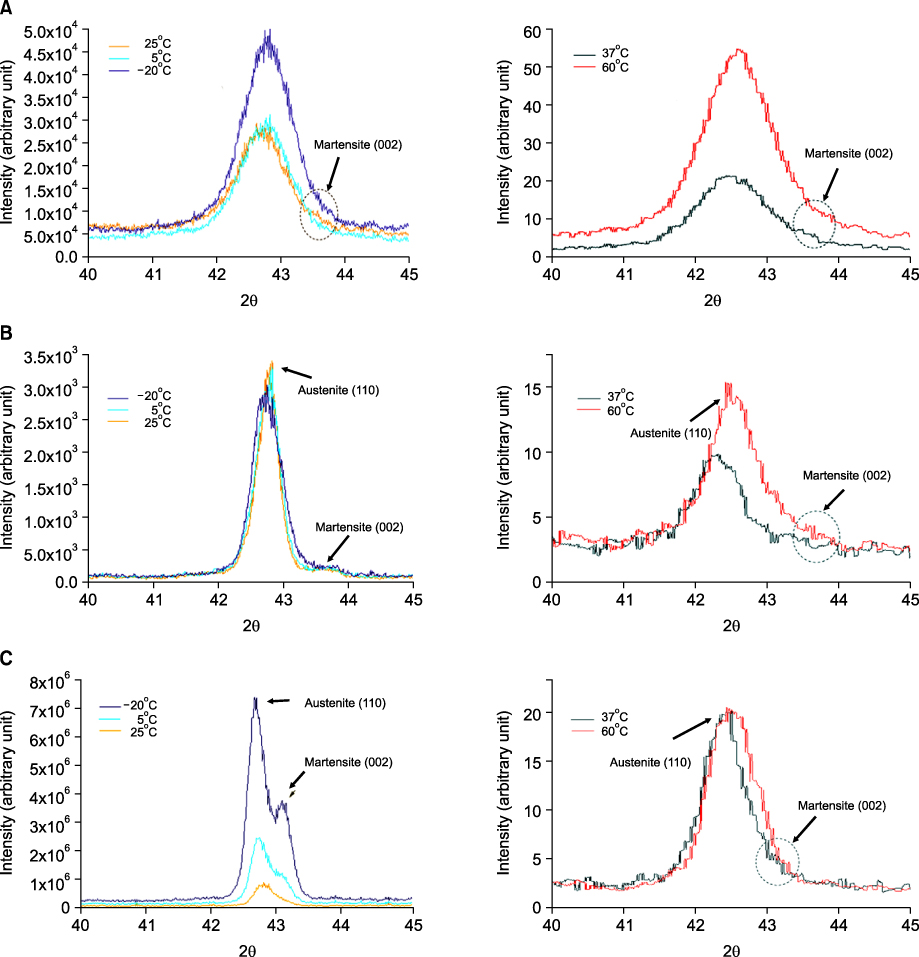
In DSC analysis, OPTI and NEO showed two peaks in the heating curves and one peak in the cooling curves. However, NC revealed one single broad and weak peak in the heating and cooling curves. Austenite finishing (Af) temperatures were 19.7degrees C for OPTI, 24.6degrees C for NEO and 52.4degrees C for NC. In the three-point bending test, residual deflection was observed for NC, OPTI and NEO. The load ranges of NC and OPTI were broader and higher than NEO. XRD and microstructure analyses showed that OPTI and NEO had a mixture of martensite and austenite at temperatures below Martensite finishing (Mf). NEO and OPTI showed improved MP and PT behavior than NC.
CONCLUSIONS
The mechanical and thermal behaviors of NiTi wire cannot be completely explained by the expected degree of PT because of complicated martensite variants and independent PT induced by heat and stress.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sakima MT, Dalstra M, Melsen B. How does temperature influence the properties of rectangular nickel-titanium wires? Eur J Orthod. 2006. 28:282–291.
Article2. Gil FJ, Planell JA. Shape memory alloys for medical applications. Proc Inst Mech Eng [H]. 1998. 212:473–488.
Article3. Khier SE, Brantley WA, Fournelle RA. Bending properties of superelastic and nonsuperelastic nickel-titanium orthodontic wires. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1991. 99:310–318.
Article4. Ren CC, Bai YX, Wang HM, Zheng YF, Li S. Phase transformation analysis of varied nickel-titanium orthodontic wires. Chin Med J (Engl). 2008. 121:2060–2064.
Article5. Meling TR, Ødegaard J. The effect of temperature on the elastic responses to longitudinal torsion of rectangular nickel titanium archwires. Angle Orthod. 1998. 68:357–368.6. Meling TR, Ødegaard J. The effect of short-term temperature changes on the mechanical properties of rectangular nickel titanium archwires tested in torsion. Angle Orthod. 1998. 68:369–376.7. Kusy RP, Wilson TW. Dynamic mechanical properties of straight titanium alloy arch wires. Dent Mater. 1990. 6:228–236.
Article8. Santoro M, Beshers DN. Nickel-titanium alloys: stress-related temperature transitional range. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2000. 118:685–692.
Article9. Brantley WA, Iijima M, Grentzer TH. Temperature-modulated DSC provides new insight about nickel-titanium wire transformations. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2003. 124:387–394.
Article10. Iijima M, Ohno H, Kawashima I, Endo K, Mizoguchi I. Mechanical behavior at different temperatures and stresses for superelastic nickel-titanium orthodontic wires having different transformation temperatures. Dent Mater. 2002. 18:88–93.
Article11. Bradley TG, Brantley WA, Culbertson BM. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) analyses of superelastic and nonsuperelastic nickel-titanium orthodontic wires. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1996. 109:589–597.
Article12. Burstone CJ, Qin B, Morton JY. Chinese NiTi wire - a new orthodontic alloy. Am J Orthod. 1985. 87:445–452.13. Miura F, Mogi M, Ohura Y, Hamanaka H. The super-elastic property of the Japanese NiTi alloy wire for use in orthodontics. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1986. 90:1–10.
Article14. Brantley WA, Guo W, Clark WA, Iijima M. Microstructural-studies of 35 degrees C copper Ni-Ti orthodontic wire and TEM confirmation of low-temperature martensite transformation. Dent Mater. 2008. 24:204–210.
Article15. Iijima M, Ohno H, Kawashima I, Endo K, Brantley WA, Mizoguchi I. Micro X-ray diffraction study of superelastic nickel-titanium orthodontic wires at different temperatures and stresses. Biomaterials. 2002. 23:1769–1774.
Article16. Thayer TA, Bagby MD, Moore RN, DeAngelis RJ. X-ray diffraction of nitinol orthodontic arch wires. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1995. 107:604–612.
Article17. Brantley WA, Iijima M, Grentzer TH. Temperature-modulated DSC provides new insight about nickel-titanium wires transformations. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2003. 124:387–394.
Article18. Barwart O, Rollinger JM, Burger A. An evaluation of the transition temperature range of superelastic orthodontic NiTi springs using differential scanning calorimetry. Eur J Orthod. 1999. 21:497–502.
Article19. Rondelli G, Vicentini B. Evaluation by electrochemical tests of the passive film stability of equiatomic Ni-Ti alloy also in presence of stress-induced martensite. J Biomed Mater Res. 2000. 51:47–54.
Article20. Airoldi G, Riva G. Innovative materials: the NiTi alloys in orthodontics. Biomed Mater Eng. 1996. 6:299–305.
Article21. Airoldi G, Riva G, Vanelli M, Filippi V, Garattini G. Oral environment temperature changes induced by cold/hot liquid intake. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1997. 112:58–63.
Article22. Volchansky A, Cleaton-Jones P. Variations in oral temperature. J Oral Rehabil. 1994. 21:605–611.
Article23. Moore RJ, Watts JT, Hood JA, Burritt DJ. Intra-oral temperature variation over 24 hours. Eur J Orthod. 1999. 21:249–261.
Article24. Dalstra M, Melsen B. Does the transition temperature of Cu-NiTi archwires affect the amount of tooth movement during alignment? Orthod Craniofac Res. 2004. 7:21–25.
Article25. Yoneyama T, Doi H, Hamanaka H, Yamamoto M, Kuroda T. Bending properties and transformation temperatures of heat-treated Ni-Ti alloy wire for orthodontic appliances. J Biomed Mater Res. 1993. 27:399–402.
Article26. Tonner RI, Waters NE. The characteristics of super-elastic Ni-Ti wires in three-point bending. Part I: the effect of temperature. Eur J Orthod. 1994. 16:409–419.
Article27. Bishara SE, Winterbottom JM, Sulieman AA, Rim K, Jakobsen JR. Comparisons of the thermodynamic properties of three nickel-titanium orthodontic archwires. Angle Orthod. 1995. 65:117–122.28. Filleul MP, Jordan L. Torsional properties of Ni-Ti and copper Ni-Ti wires: the effect of temperature on physical properties. Eur J Orthod. 1997. 19:637–646.
Article29. Oltjen JM, Duncanson MG Jr, Ghosh J, Nanda RS, Currier GF. Stiffness-deflection behavior of selected orthodontic wires. Angle Orthod. 1997. 67:209–218.30. Nakano H, Satoh K, Norris R, Jin T, Kamegai T, Ishikawa F, et al. Mechanical properties of several nickel-titanium alloy wires in three-point bending tests. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1999. 115:390–395.
Article31. Gurgel JA, Kerr S, Powers JM, LeCrone V. Force-deflection properties of superelastic nickel-titanium archwires. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2001. 120:378–382.
Article32. Wilkinson PD, Dysart PS, Hood JA, Herbison GP. Load-deflection characteristics of superelastic nickel-titanium orthodontic wires. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2002. 121:483–495.
Article33. Fischer-Brandies H, Es-Souni M, Kock N, Raetzke K, Bock O. Transformation behavior, chemical composition, surface topography and bending properties of five selected 0.016" × 0.022" NiTi archwires. J Orofac Orthop. 2003. 64:88–99.
Article34. Parvizi F, Rock WP. The load/deflection characteristics of thermally activated orthodontic archwires. Eur J Orthod. 2003. 25:417–421.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of heat treatment on the load-deflection properties of nickel-titanium wire
- Mechanical properties of nickel titanium and steel alloys under stress- strain test
- The effect of heat sterilization on the surface topography and the tensile properties in various nickel titanium wires including a Korean product
- The effect of temperature changes on force level of superelastic nickel-titanium archwires
- Effects of recycling on the mechanical properties and the surface topography of Nickel-Titanium alloy wires