Imaging Sci Dent.
2014 Sep;44(3):193-198. 10.5624/isd.2014.44.3.193.
Correlation of morphological variants of the soft palate and Need's ratio in normal individuals: A digital cephalometric study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology, Surendera Dental College and Research Institute, Sriganganagar, India.
- 2Department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry, Surendera Dental College and Research Institute, Sriganganagar, India. praddy_verma@yahoo.co.in
- 3Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, Farooqia Dental College, Mysore, India.
- 4Department of Periodontics, J.S.S Dental College, Mysore, India.
- KMID: 1974482
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2014.44.3.193
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The present study was aimed to investigate the variation of soft palate morphology in different age and gender groups. The correlations of radiographic velar length (VL), velar width (VW), pharyngeal depth (PD), and Need's ratio with soft palate variants were also studied in the North Indian subpopulation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
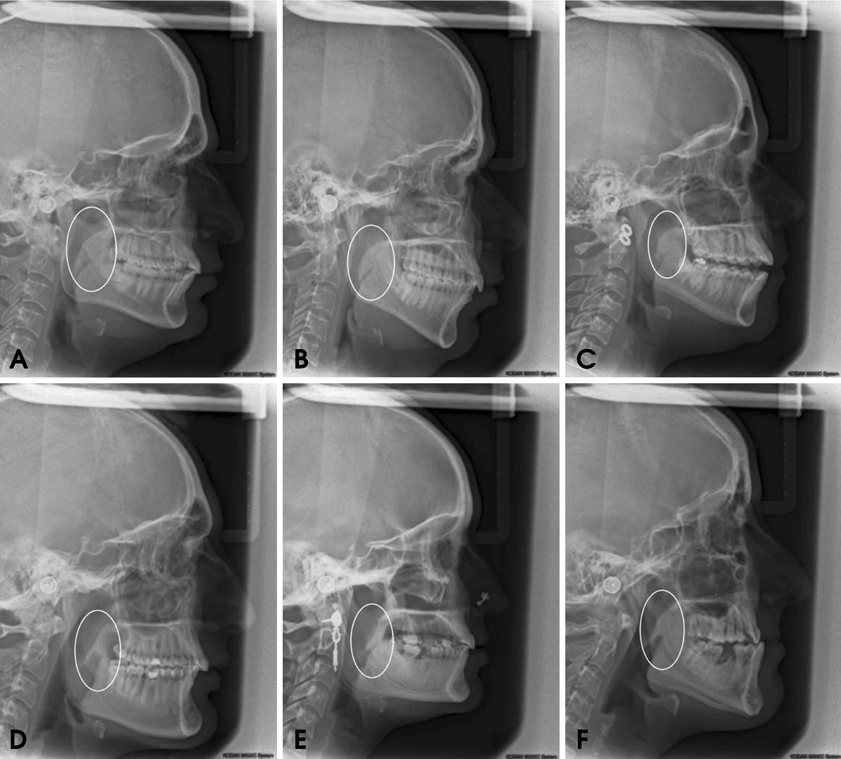
The study sample consisted of 300 subjects aged between 15 and 45 (mean: 31.32) years. The velar morphology on lateral cephalograms was examined and grouped into six types. The results obtained were subjected to a statistical analysis to find the correlation between variants of the soft palate with gender and different age groups.
RESULTS
The most frequent type of soft palate was leaf shaped (48.7%), and the least common was crook shaped (3.0%) among both the genders and various age groups, showing a significant correlation. The mean VL, VW, and PD values were significantly higher in males and significantly correlated with the types of soft palate. A significant correlation was observed between the mean VL, VW, PD, and Need's ratio with various age groups, showing an inconsistent pattern with an increase in age. The types of soft palate, gender, and Need's ratio were also significantly correlated, with an overall higher mean value of the Need's ratio among female subjects and the S-shaped soft palate.
CONCLUSION
The knowledge of a varied spectrum of velar morphology and the variants of the soft palate help in a better understanding of the velopharyngeal closure and craniofacial anomalies.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Morphological variation of the velum in children and adults using magnetic resonance imaging
Katelyn J. Kotlarek, Abigail E. Haenssler, Kori E. Hildebrand, Jamie L. Perry
Imaging Sci Dent. 2019;49(2):153-158. doi: 10.5624/isd.2019.49.2.153.
Reference
-
1. You M, Li X, Wang H, Zhang J, Wu H, Liu Y, et al. Morphological variety of the soft palate in normal individuals: a digital cephalometric study. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2008; 37:344–349.
Article2. Moore KL, Agur AM. Essential clinical anatomy. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2002.3. Kumar DK, Gopal KS. Morphological variants of soft palate in normal individuals: a digital cephalometric study. J Clin Diagn Res. 2011; 5:1310–1313.4. Pepin JL, Veale D, Ferretti GR, Mayer P, Levy PA. Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: hooked appearance of the soft palate in awake patients - cephalometric and CT findings. Radiology. 1999; 210:163–170.5. Subtelny JD. A Cephalometric study of the growth of the soft palate. Plast Reconstr Surg (1946). 1957; 19:49–62.
Article6. Stellzig-Eisenhauer A. The influence of cephalometeric parameters on resonance of speech in cleft lip and palate patients. An interdisciplinary study. J Orofac Orthop. 2001; 62:202–223.7. Akcam MO, Toygar TU, Wada T. Longitudinal investigation of soft palate and nasopharyngeal airway relations in different rotation types. Angle Orthod. 2002; 72:521–526.8. Mazaheri M, Krogman WM, Harding RL, Millard RT, Mehta S. Longitudinal analysis of growth of the soft palate and nasopharynx from six months to six years. Cleft Palate J. 1977; 14:52–62.9. Haapanen ML, Kalland M, Heliovaara A, Hukki J, Ranta R. Velopharyngeal function in cleft patients undergoing maxillary advancement. Folia Phoniatr Logop. 1997; 49:42–47.
Article10. Simpson RK, Colton J. A cephalometric study of velar stretch in adolescent subjects. Cleft Palate J. 1980; 17:40–47.11. Taylor M, Hans MG, Strohl KP, Nelson S, Broadbent BH. Soft tissue growth of the oropharynx. Angle Orthod. 1996; 66:393–400.12. Niu YM, Wang H, Zheng Q, He X, Zhang J, Li XM, et al. Morphology of the soft palate in normal humans with digital cephalometry. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2006; 24:321–327.13. Guttal KS, Breh R, Bhat R, Burde KN, Naikmasur VG. Diverse morphologies of soft palate in normal individuals: a cephalometric perspective. J Indian Acad Oral Med Radiol. 2012; 24:15–19.14. Cohen SR, Chen L, Trotman CA, Burdi AR. Soft-palate myogenesis: a developmental field paradigm. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 1993; 30:441–446.
Article15. Maltais F, Carrier G, Cormier Y, Series F. Cephalometric measurements in snorers, non-snorers, and patients with sleep apnoea. Thorax. 1991; 46:419–423.
Article16. Praveen BN, Amrutesh S, Pal S, Shubhasini AR, Vaseemuddin S. Various shapes of soft palate: a lateral cephalometric study. World J Dent. 2011; 2:207–210.
Article17. Johnston CD, Richardson A. Cephalometric changes in adult pharyngeal morphology. Eur J Orthod. 1999; 21:357–362.
Article18. Kollias I, Krogstad O. Adult craniocervical and pharyngeal changes - a longitudinal cephalometric study between 22 and 42 years of age Part II Morphology of uvulo-glossopharyngeal changes. Eur J Orthod. 1999; 21:345–355.19. Johns DF, Rohrich RJ, Awada M. Velopharyngeal incompetence: a guide for clinical evaluation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003; 112:1890–1898.20. Nakamura N, Ogata Y, Kunimitsu K, Suzuki A, Sasaguri M, Ohishi M. Velopharyngeal morphology of patients with persistent velopharyngeal incompetence following repushback surgery for cleft palate. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2003; 40:612–617.
Article21. Hoopes JE, Dellon AL, Fabrikant JI, Edgerton MT Jr, Soliman AH. Cineradiographic definition of the functional anatomy and apathophysiology of the velopharynx. Cleft Palate J. 1970; 7:443–454.22. Wada T, Satoh K, Tachimura T, Tatsuta U. Comparison of nasopharyngeal growth between patients with clefts and noncleft controls. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 1997; 34:405–409.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A cephalometric study on the position of the hyoid bone in cleft lip and palate individuals
- A study on the craniofacial growth of cleft lip and palate individuals by means of cephalometric roentgenogram
- A cephalometric study on the airway size according to the types of the malocclusion
- Comparison of palatal bone thickness between 3D model and lateral cephalometric radiograph
- The comparison of landmark identification errors and reproducibility between conventional lateral cephalometric radiography and digital lateral cephalometric radiography