Imaging Sci Dent.
2013 Jun;43(2):129-134. 10.5624/isd.2013.43.2.129.
A unique case of Turner syndrome accompanying prolactinoma and unexpected elongated styloid process: Clinical and cone-beam computed tomographic features
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry, Cukurova University, Adana, Turkey. burcukeles@yahoo.com
- 2Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Faculty of Dentistry, Cukurova University, Adana, Turkey.
- 3Department of Pediatric Dentistry, Faculty of Dentistry, Cukurova University, Adana, Turkey.
- 4Department of Neurology, Faculty of Medicine, Cukurova University, Adana, Turkey.
- KMID: 1974441
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2013.43.2.129
Abstract
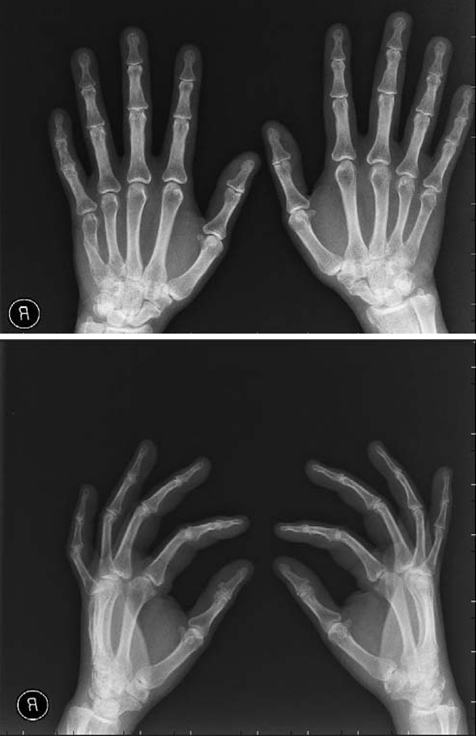
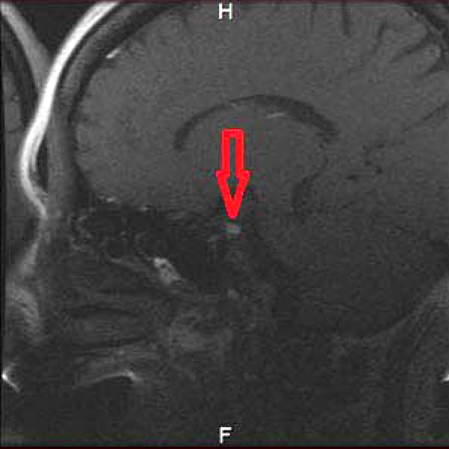
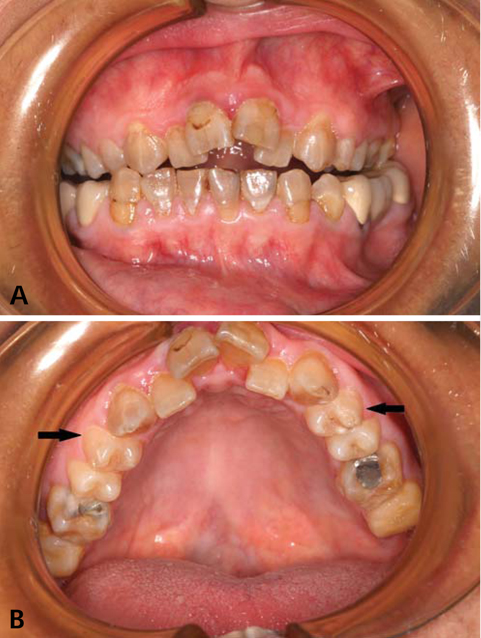
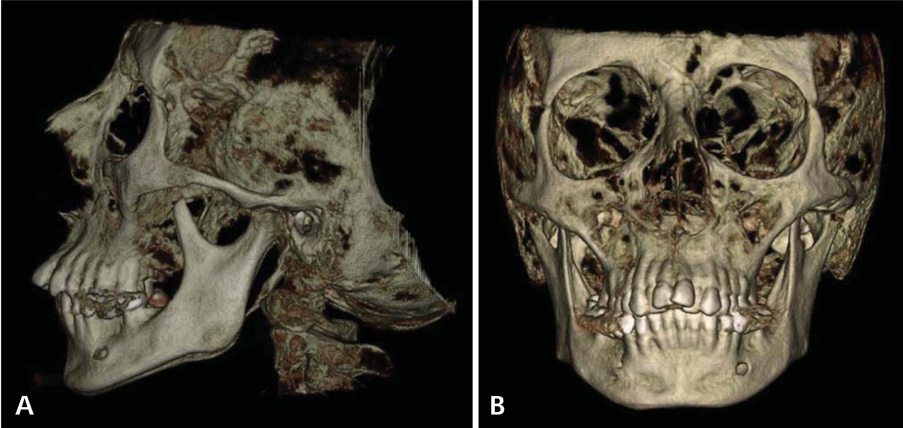
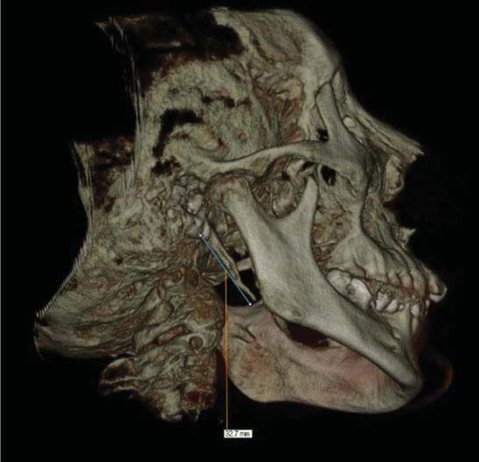
- Turner syndrome (TS) is one of the most common chromosomal abnormalities, with an estimated frequency among female live births of 1/2,000-3,000. The syndrome is characterized by the partial or complete absence of one X chromosome (45,X karyotype). We reported a unique case of a 40-year-old woman with TS accompanying unexpected elongated styloid process specific to Eagle syndrome (ES) and followed up-prolactinoma. The present article is the first report to define the cone-beam computed tomographic (CBCT) features of TS accompanying ES. Patients with TS carry various risks that make treatment more complicated; thus advanced imaging techniques for proper treatment and follow-up are extremely important. In the light of CBCT examination, craniofacial abnormalities specific to TS and accompanying syndromes such as the crowding of teeth especially in the maxillary anterior region caused by maxillary narrowness, micrognatic maxilla and mandible, relative mandibular retrusion, malocclusion, open-bite, and an elongated styloid process (length of 32.7 mm) on the right side were illustrated in detail.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Turner HH. A syndrome of infantilism, congenital webbed neck, cubitus valgus. Endocrinology. 1938. 23:566–574.2. Cassidy SB, Allanson JE. Management of genetic syndromes. 2005. 2nd ed. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons.3. Trolle C, Mortensen KH, Hjerrild BE, Cleemann L, Gravholt CH. Clinical care of adult Turner syndrome - new aspects. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2012. 9:Suppl 2. 739–749.4. Morgan T. Turner syndrome: diagnosis and management. Am Fam Physician. 2007. 76:405–410.5. Sutton EJ, McInerney-Leo A, Bondy CA, Gollust SE, King D, Biesecker B. Turner syndrome: four challenges across the lifespan. Am J Med Genet A. 2005. 139A:57–66.
Article6. Lopez ME, Bazan C, Lorca IA, Chervonagura A. Oral and clinical characteristics of a group of patients with Turner syndrome. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2002. 94:196–204.7. Saenger P, Wikland KA, Conway GS, Davenport M, Gravholt CH, Hintz R, et al. Recommendations for the diagnosis and management of Turner syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001. 86:3061–3069.
Article8. Szilagyi A, Keszthelyi G, Nagy G, Madlena M. Oral manifestations of patients with Turner syndrome. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2000. 89:577–584.9. Rizell S, Barrenäs ML, Andlin-Sobocki A, Stecksén-Blicks C, Kjellberg H. Turner syndrome isochromosome karyotype correlates with decreased dental crown width. Eur J Orthod. 2012. 34:213–218.
Article10. Nomikos P, Buchfelder M, Fahlbusch R. Current management of prolactinomas. J Neurooncol. 2001. 54:139–150.11. Casanueva FF, Molitch ME, Schlechte JA, Abs R, Bonert V, Bronstein MD, et al. Guidelines of the Pituitary Society for the diagnosis and management of prolactinomas. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2006. 65:265–273.
Article12. Zinnuroglu M, Ural A, Günendi Z, Meray J, Köybaşoğlu A. Is there a relationship between Eagle syndrome and cervicofacial painful soft tissue rheumatisms? Laryngoscope. 2008. 118:1569–1573.
Article13. Murtagh RD, Caracciolo JT, Fernandez G. CT findings associated with Eagle syndrome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001. 22:1401–1402.14. Eagle WW. Elongated styloid processes: report of two cases. Arch Otolaryngol. 1937. 25:584–587.
Article15. Dunn-Ryznyk LR, Kelly CW. Eagle syndrome: a rare cause of dysphagia and head and neck pain. JAAPA. 2010. 23:2831–32. 4816. Corvo G, Tartaro GP, Stoppoloni F, Balzano G. Cephalometric evaluation of patients with Turner syndrome. Authors' experience. Minerva Stomatol. 1998. 47:127–133.17. Madlena M, Szilagyi Z, Keszthelyi G. Turner's syndrome: review of the literature and report of a case. ASDC J Dent Child. 1994. 4:394–396.18. Midtbø M, Halse A. Rooth length, crown height, and root morphology in Turner syndrome. Acta Odontol Scand. 1994. 52:303–314.19. Harju M, Laine T, Alvesalo L. Occlusal anomalies in 45,X/46,XX- and 46,Xi (Xq)-women (Turner-syndrome). Scand J Dent Res. 1989. 97:387–391.20. Laine T, Alvesalo L. Size of the alveolar arch of the mandible in relation to that of the maxilla in 45,X females. J Dent Res. 1986. 65:1432–1434.
Article21. Gorlin RJ, Redman RS, Shapiro BL. Effect of X-chromosome aneuploidy on jaw growth. J Dent Res. 1965. 44:269–282.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case Report of the Eagle's Syndrome Treated by Surgical Shortening of the Elongated Styloid Process
- Morphological study of styloid process of the temporal bone and its clinical implications
- Fractured styloid process masquerading as neck pain: Cone-beam computed tomography investigation and review of the literature
- A Case of Eagle’s Syndrome Treated with Carbon Dioxide Laser
- Carotid Artery Dissection Caused by an Elongated Styloid Process: A Case Report