Imaging Sci Dent.
2011 Mar;41(1):29-33. 10.5624/isd.2011.41.1.29.
Unicystic ameloblastoma with diverse mural proliferation - a hybrid lesion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology, Sri Siddhartha Dental College and Hospital, Tumkur, Karnataka, India.
- 2Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Dayananda Sagar College of Dental Sciences, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India.
- 3Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology, Dayananda Sagar College of Dental Sciences, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India. prashantopath@gmail.com
- KMID: 1974397
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2011.41.1.29
Abstract
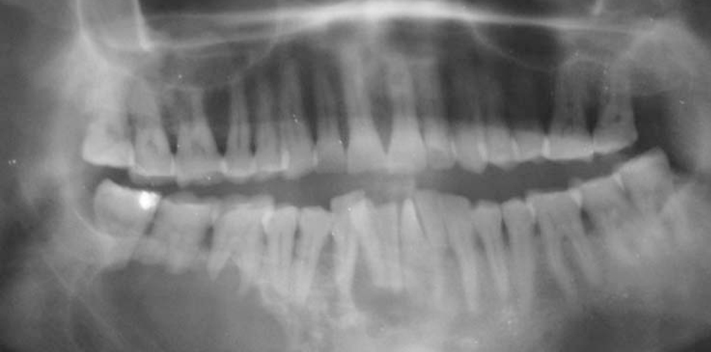
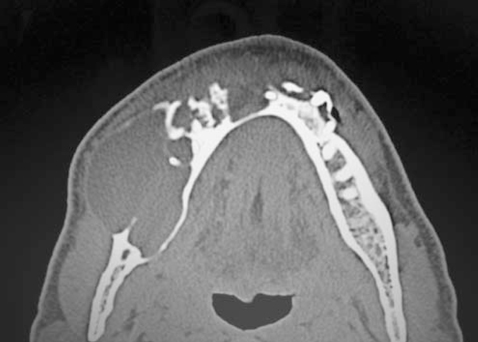
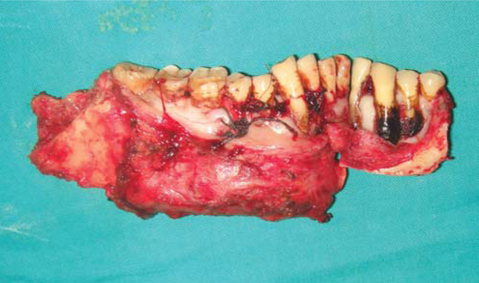
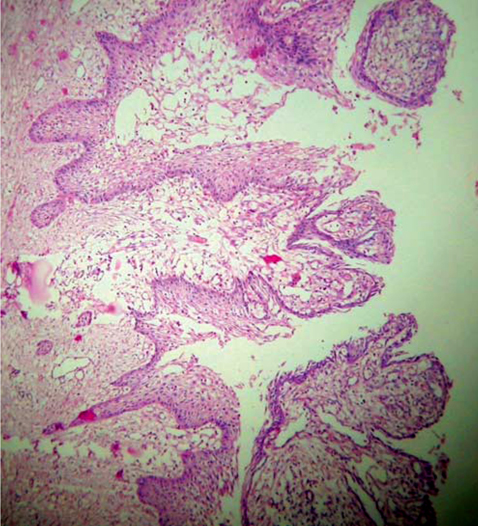
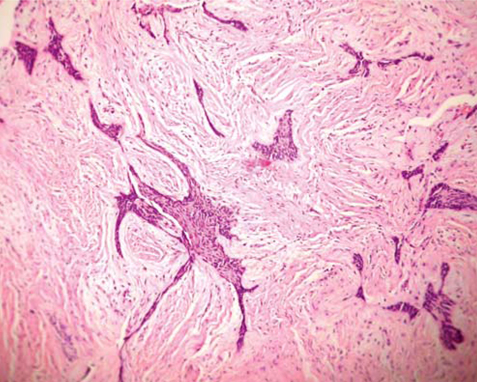
- A 46-year-old man was referred to our hospital for treatment, complaining of swelling on the right mandibular molar region. Radiographic examination revealed a well defined multilocular radiolucent lesion with root resorption of right lower anteriors and molars. Following biopsy, a diagnosis of unicystic ameloblastoma of mural type was made and hemimandibulectomy was performed under general anesthesia. Histopathological examination of the surgical specimen exhibited a unicystic ameloblastoma of luminal, intraluminal, and mural type. Intraluminal proliferation was of plexiform pattern and mural proliferation showed unusual histopathological findings, which revealed follicular, acanthomatous areas coexisted with desmoplastic areas. This mural picture was similar to the so-called 'hybrid lesion of ameloblastoma', whose biological profile is not elicited due to the lack of adequate published reports. Two years follow up till date has not revealed any signs of recurrence.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Neville BW, Damm DD, Allen CM, Bouquot JE. Odontogenic cysts and tumors. Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology. 2002. 2nd ed. St. Louis: WB Saunders Co;610–618.
Article2. Philipsen HP, Reichart PA. Unicystic ameloblastoma. A review of 193 cases from the literature. Oral Oncol. 1998. 34:317–325.
Article3. Robinson L, Martinez MG. Unicystic ameloblastoma: a prognostically distinct entity. Cancer. 1977. 40:2278–2285.4. Ackermann GL, Altini M, Shear M. The unicystic ameloblastoma: a clinicopathological study of 57 cases. J Oral Pathol. 1988. 17:541–546.
Article5. Reichart PA, Philipsen HP. Odontogenic tumors and allied lesions. 2004. Hanover Park: Quintessence Publishing Inc;69–86.6. Gardner DG. Some current concepts on the pathology of ameloblastomas. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1996. 82:660–669.
Article7. Eversole LR, Leider AS, Hansen LS. Ameloblastomas with pronounced desmoplasia. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1984. 42:735–740.
Article8. Waldron CA, el-Mofty SK. A histopathologic study of 116 ameloblastomas with special reference to the desmoplastic variant. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1987. 63:441–451.
Article9. Philipsen HP, Reichart PA, Takata T. Desmoplastic ameloblastoma (including "hybrid" lesion of ameloblastoma). Biological profile based on 100 cases from the literature and own files. Oral Oncol. 2001. 37:455–460.
Article10. Higuchi Y, Nakamura N, Ohishi M, Tashiro H. Unusual ameloblastoma with extensive stromal desmoplasia. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 1991. 19:323–327.
Article11. Philipsen HP, Ormiston IW, Reichart PA. The desmo- and osteoplastic ameloblastoma. Histologic variant or clinicopathologic entity? Case reports. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1992. 21:352–357.12. Takata T, Miyauchi M, Ogawa I, Zhao M, Kudo Y, Sato S, et al. So-called 'hybrid' lesion of desmoplastic and conventional ameloblastoma: report of a case and review of the literature. Pathol Int. 1999. 49:1014–1018.
Article13. Sivapathasundharam B, Einstein A, Syed RI. Desmoplastic ameloblastoma in Indians: report of five cases and review of literature. Indian J Dent Res. 2007. 18:218–221.
Article14. Sun ZJ, Wu YR, Cheng N, Zwahlen RA, Zhao YF. Desmoplastic ameloblastoma - A review. Oral Oncol. 2009. 45:752–759.
Article15. Wakoh M, Harada T, Inoue T. Follicular/desmoplastic hybrid ameloblastoma with radiographic features of concomitant fibro-osseous and solitary cystic lesions. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2002. 94:774–780.
Article16. Gardner DG. Plexiform unicystic ameloblastoma: a diagnostic problem in dentigerous cysts. Cancer. 1981. 47:1358–1363.
Article17. Hirota M, Aoki S, Kawabe R, Fujita K. Desmoplastic ameloblastoma featuring basal cell ameloblastoma: a case report. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2005. 99:160–164.
Article18. Leider AS, Eversole LR, Barkin ME. Cystic ameloblastoma. A clinicopathologic analysis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1985. 60:624–630.19. Ngwenya SP, Raubenheimer EJ, Noffke CE. Internal morphology of ameloblastomas: a study of 24 resected specimens. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2009. 108:754–762.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A radiologic study of ameloblastoma using computed tomography
- Unicystic ameloblastoma arising from dentigerous cyst: case report and literature review
- Literature review & case report : the conservative treatment of unicystic ameloblastoma
- Ameloblastoma originated from a dentigerous cyst: a case report
- Recurrence of maxillary unicystic ameloblastoma: a case report