Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2014 Sep;7(3):226-228. 10.3342/ceo.2014.7.3.226.
Maxillary Sinus Retention Cysts Protruding Into the Inferior Meatus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea. st-dragonhong@hanmail.net
- 2Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea.
- KMID: 1973475
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2014.7.3.226
Abstract
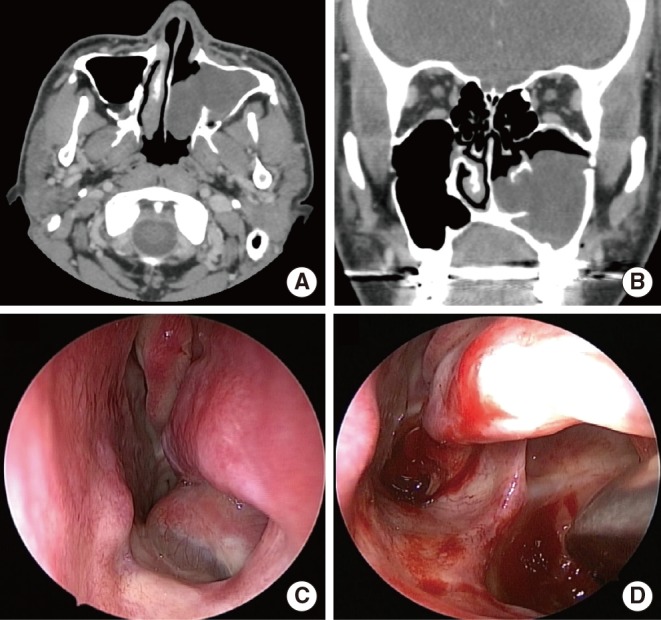
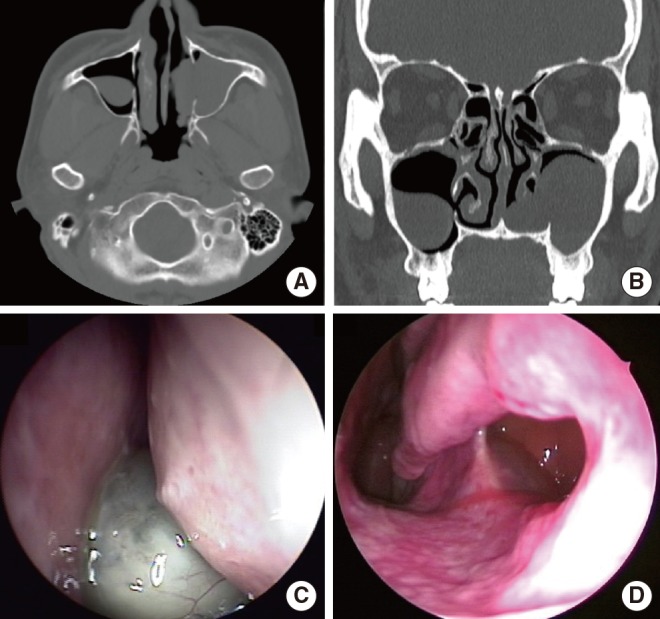
- Although most of the maxillary sinus retention cysts are asymptomatic, a few of them increase in size and cause symptoms. However, they rarely erode bony walls nor protrude into the inferior meatus. I present 2 cases with maxillary sinus retention cysts protruding into the inferior meatus by making a large defect on the medial wall of the maxillary sinus.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
A Case of Symptomatic Maxillary Retention Cyst
Hankyeol Kim, Eun Kyu Lee, Hyo Yeol Kim, Sang-Duck Hong, Hun-Jong Dhong, Seung-Kyu Chung
J Rhinol. 2018;25(1):59-62. doi: 10.18787/jr.2018.25.1.59.A Giant Maxillary Mucocele Presenting Left Cheek Swelling
Moon Seung Baeg, Hyeok Ro Kwon, Jin Soon Chang
J Rhinol. 2022;29(3):172-175. doi: 10.18787/jr.2022.00413.
Reference
-
1. Moon IJ, Kim SW, Han DH, Shin JM, Rhee CS, Lee CH, et al. Mucosal cysts in the paranasal sinuses: long-term follow-up and clinical implications. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2011; Mar-Apr. 25(2):98–102. PMID: 21679512.
Article2. Składzien J, Litwin JA, Nowogrodzka-Zagorska M, Wierzchowski W. Morphological and clinical characteristics of antrochoanal polyps: comparison with chronic inflammation-associated polyps of the maxillary sinus. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2001; 4. 28(2):137–141. PMID: 11240321.
Article3. Moon IJ, Lee JE, Kim ST, Han DH, Rhee CS, Lee CH, et al. Characteristics and risk factors of mucosal cysts in the paranasal sinuses. Rhinology. 2011; 8. 49(3):309–314. PMID: 21858261.
Article4. Bósio JA, Tanaka O, Rovigatti E, de Gruner SK. The incidence of maxillary sinus retention cysts in orthodontic patients. World J Orthod. 2009; Summer. 10(2):e7–e8. PMID: 19582248.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Characteristics According to the Radiological Classifications of Maxillary Sinus Fungus Ball
- Treatment Strategy for the Retention Cyst of the Maxillary Sinus
- Sinus lifts in the presence of pseudoantral and mucous retention cysts
- Inferior Meatal Fenestration Operation of the Postoperative Maxillary Cysts
- Correlation of Middle Meatus, Ethmoid Sinus and Maxillary Sinus Microbiology in Patients with Chronic Sinusitis