Tuberc Respir Dis.
2008 Apr;64(4):259-265. 10.4046/trd.2008.64.4.259.
The Clinical and Radiology Characteristics of Diabetic or Non-diabetic Tuberculosis Patients: a Retrospective Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Cheongju St. Mary's Hospital, Cheongju, Korea. drahnhy@hanmail.net
- KMID: 1970175
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2008.64.4.259
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: Patients with diabetes mellitus are highly sensitive to infections, including tuberculosis, and the longer the duration of DM, the greater is the prevalance of tuberculosis. We studied the difference of the clinical manifestations, radiologic findings, resistance and others factors of patients with diabetic and non-diabetic pulmonary tuberculosis.
METHODS
The patients we enrolled in this study were newly diagnosed with pulmonary tuberculosis from January 2003 to December 2005.
RESULTS
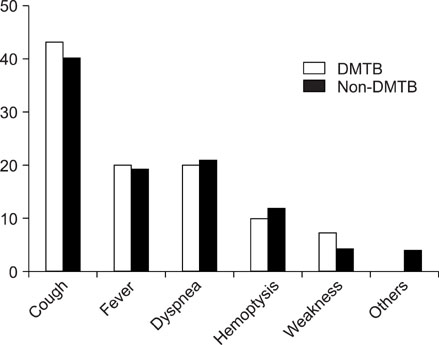
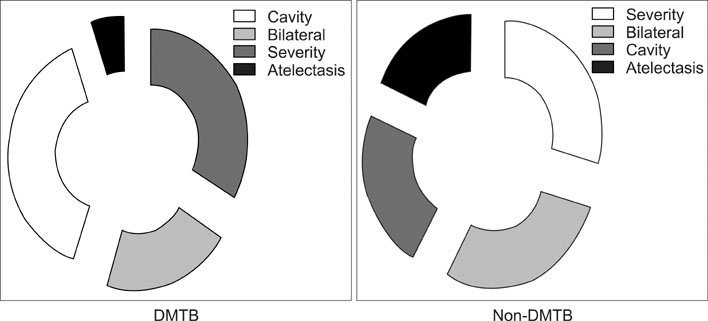
159 patients were enrolled in this study. There were 30 pulmonary tuberculosis patients with diabetic mellitus (DMTB) and 129 pulmonary tuberculosis patients without diabetic mellitus (non-DMTB). There was no difference in the basic characteristics and clinical manifestation between both the groups. For the chest X-ray findings, the moderately advanced tuberculosis patients were the most common (43.3% in the DMTB group and 49.6% in the non-DMTB group). There was no relation between the severity of tuberculosis activity on chest x-ray and the presence of diabetes. The prevalence of cavitory lesions in the DMTB group was significantly higher than that in the non-DMTB group, but the prevalence of atelectasis was higher in the non-DMTB group (p<0.05). There was no difference in the incidence of lower lung involvement, the number of involved lobes, the number of treatment days and the radiological sequelae in both groups.
CONCLUSION
The DMTB patients had a higher incidence of cavitory lesions and a higher incidence of atelectasis than the non-DMTB patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. World Health Organization. Global tuberculosis control: surveillance, planning, financing. 2004. Geneva: World Health Organization.2. Ryu WJ. The actual condition of tuberculosis in Korea. 2004. Seoul: The Korean National Tuberculosis Association.3. Ryu WJ. The present state of tuberculosis in Korea. 2004. Seoul: The Korean National Tuberculosis Association.4. The Ministry of Health and Welfare. Report on 2001 National health and nutrition research. 2002. Gwacheon: The Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea.5. Joshi N, Caputo GM, Weitekamp MR, Karchmer AW. Infections in patients with diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1999. 341:1906–1912.6. Gallacher SJ, Thomson G, Fraser WD, Fisher BM, Gemmell CG, MacCuish AC. Neutrophil bactericidal function in diabetes mellitus: evidence for association with blood glucose control. Diabet Med. 1995. 12:916–920.7. Jabbar A, Hussain SF, Khan AA. Clinical characteristics of pulmonary tuberculosis in adult Pakistani patients with co-existing diabetes mellitus. East Mediterr Health J. 2006. 12:522–527.8. Jeong IK, Yoo JH, Lee SM, Koh KP, Han MS, Kang HM. A clinical study of pulmonary tuberculosis in diabetics. Tuberc Respir Dis. 1998. 45:705–713.9. The Korean Academy of Tuberculosis and Respiratory Disease. Respiratory diseases. 2000. Seoul: KoonJa;856–858.10. American Thoracic Society. Medical Section of the National Tuberculosis Association. 1961. New York: National Tuberculosis Association;Committed on revision of diagnostic standards.11. Lee TH, Ahn MS, Han SO. Clinical analysis of complications in diabetics. Diabetes. 1981. 6:35–40.12. Son SK, Han DH, Heo KB, Lee SY. Statistical studies on diabetes mellitus in Korea. J Korean Diabetes Assoc. 1976. 3:43–50.13. Hong YP, Kim SJ. Tuberculosis. 1993. 4th ed. Seoul: The Korean Academy of Tuberculosis and Respiratory Disease;300–305.14. Nahid P, Pai M, Hopewell PC. Advances in the diagnosis and treatment of tuberculosis. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2006. 3:103–110.15. Choi SI, Lee SC, Kong SJ, Park JH, Son MH. The effect of diabetes mellitus on treatment outcomes in pulmonary tuberculosis. Korean J Med. 2003. 65:558–567.16. Lin S, Shen M, Sun Y. Epidemiological characteristics of tuberculosis patients complicated with diabetes in Shanghai. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 1998. 21:504–506.17. Chung JY, Kim JH. A clinical study of pulmonary tuberculosis associated with diabetes mellitus. Tuberc Respir Dis. 1988. 35:241–245.18. Mason RJ, Broaddus VC, Murray JF, Nadel JA. Murray and Nadel's textbook of respiratory medicine. 2005. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders;986–987.19. Nissapatorn V, Kuppusamy I, Jamaiah I, Fong MY, Rohela M, Anuar AK. Tuberculosis in diabetic patients: a clinical perspective. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2005. 36 Suppl 4:213–220.20. Fauci AS, Kasper DL, Longo DL, Braunwald E, Hauser SL, Jameson JL, et al. Harrison's principles of internal medicine. 2008. 17th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill;2275–2304.21. Kameda K, Kawabata S, Masuda N. Follow-up study of short course chemotherapy of pulmonary tuberculosis complicated with diabetes mellitus. Kekkaku. 1990. 65:791–803.22. Hiro Y. Pulmonary tuberculosis and diabetes mellitus: report of the 29th B series of controlled trials of chemotherapy. Kekkaku. 1989. 64:699–705.23. Altumina MM. Several characteristics of the pulmonary tuberculosis course in patients with different degree of diabetes mellitus compensation. Probl Tuberk. 1995. 6:15–17.24. Bacakoglu F, Basoglu OK, Cok G, Sayiner A, Ates M. Pulmonary tuberculosis in patients with diabetes mellitus. Respiration. 2001. 68:595–600.25. Umut S, Tosun GA, Yildirim N. Radiographic location of pulmonary tuberculosis in diabetic patients. Chest. 1994. 106:326.26. Perez-Guzman C, Torres-Cruz A, Villarreal-Velarde H, Vargas MH. Progressive age-related changes in pulmonary tuberculosis images and the effect of diabetes. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000. 162:1738–1740.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- CT Findings of Tuberculous Pneumonia in Diabetic Patients: Comparison with Tuberculosis in Nondiabetics
- Clinical Results of Phacoemulsification with Scleral Pocket Incision in Diabetic Patients
- Incidence of tuberculosis in Korean diabetics: Comparison with that in non-diabetic hypertensive subjects
- Diabetic Neuropathy: Classification and Pathogenesis
- Health Literacy, Diabetic Knowledge, and Diabetic Self-care among Foreign Diabetic Patients at a Hospital in South Korea