J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg.
2014 Jun;16(2):85-92. 10.7461/jcen.2014.16.2.85.
Diagnostic Value of Thrombus Size on T2*-weighted Gradient Echo Imaging in Acute Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Busan-Ulsan Regional Cardiocerebrovascular Center, Medical Science Research Center, College of Medicine, Dong-A University, Busan, Korea. jthuh@dau.ac.kr
- 2Department of Neurology, Busan-Ulsan Regional Cardiocerebrovascular Center, Medical Science Research Center, College of Medicine, Dong-A University, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 1963175
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2014.16.2.85
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
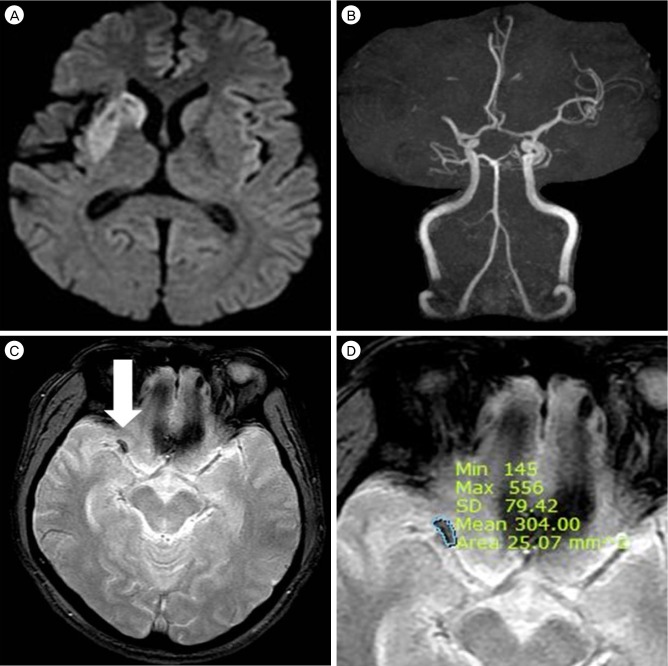
The T2*-weighted gradient echo image susceptibility vessel sign (GRE SVS) is a well-known indicator of intraluminal thrombi in acute cerebral infarction. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the relationships between thrombus size on GRE SVS and recanalization after intravenous administration of tissue plasminogen activator (IV-tPA).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Fifty five patients with GRE SVSs on the M1 were enrolled. Examination of magnetic resonance image (MRI), including diffusion weighted imaging and MR angiography, was performed within 20 minutes of admission. Thrombus size on GRE was calculated using the Picture Archiving and Communication System upon initial MRI. Recanalization was assessed with follow-up MRI or transfemoral cerebral angiography within 24 hours of treatment.
RESULTS
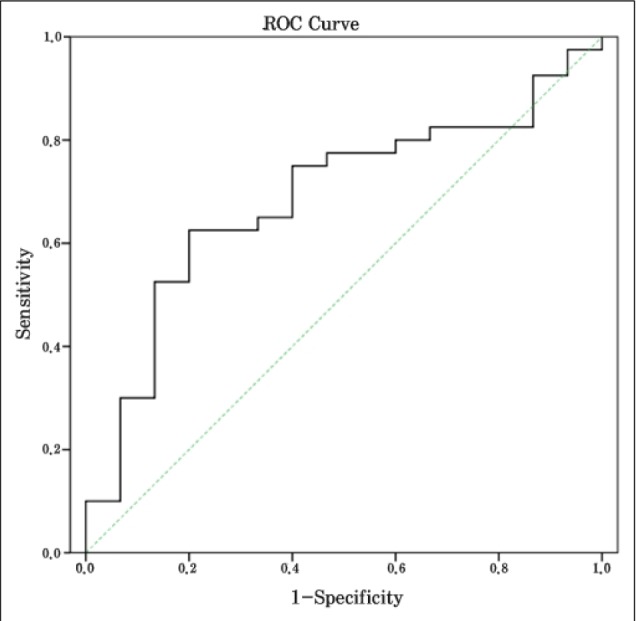
The patient group consisted of 37 males and 18 females with an average age of 63.74 +/- 10.28 years (range: 43 - 77 years). The median NIHSS score was 13. Fifteen of these patients achieved recanalization (27.3%). The average thrombus cross-sectional area in the recanalization group was 38.54 +/- 20.27 mm2, and the corresponding size of the non-recanalization group was 53.38 +/- 24.77 mm2 (p = 0.043). In the receiver operator characteristic curve for thrombus cross-sectional area in relation to recanalization, the cut-off point was 47.28 mm2. The sensitivity at this cut-off point was 73.3%, the specificity was 60%, and the area under the curve was 0.687.
CONCLUSION
Thrombus size on GRE is a simple diagnostic tool that can be easily measured, and thrombus size on GRE SVS was found to be associated with recanalization after IV-tPA.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Aries MJ, Uyttenboogaart M, Koopman K, Rodiger LA, Vroomen PC, De Keyser J, et al. Hyperdense middle cerebral artery sign and outcome after intravenous thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke. J Neurol Sci. 2009; 10. 285(1-2):114–117. PMID: 19576595.
Article2. Arnold M, Schroth G, Nedeltchev K, Loher T, Remonda L, Stepper F, et al. Intra-arterial thrombolysis in 100 patients with acute stroke due to middle cerebral artery occlusion. Stroke. 2002; 7. 33(7):1828–1833. PMID: 12105361.
Article3. Bae YJ, Jung C, Kim JH, Choi BS, Kim E, Han MK, et al. Potential for the use of the Solitaire stent for recanalization of middle cerebral artery occlusion without a susceptibility vessel sign. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2014; 1. 35(1):149–155. PMID: 23744693.
Article4. Cho KH, Kim JS, Kwon SU, Cho AH, Kang DW. Significance of susceptibility vessel sign on T2*-weighted gradient echo imaging for identification of stroke subtypes. Stroke. 2005; 11. 36(11):2379–2383. PMID: 16224077.5. Dávalos A, Pereira VM, Chapot R, Bonafé A, Andersson T, Gralla J, et al. Retrospective multicenter study of Solitaire FR for revascularization in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2012; 10. 43(10):2699–2705. PMID: 22851547.
Article6. Derex L, Nighoghossian N, Hermier M, Adeleine P, Froment JC, Trouillas P. Early detection of cerebral arterial occlusion on magnetic resonance angiography: predictive value of the baseline NIHSS score and impact on neurological outcome. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2002; 13(4):225–229. PMID: 12011545.
Article7. Furlan A, Higashida R, Wechsler L, Gent M, Rowley H, Kase C, et al. Intra-arterial prourokinase for acute ischemic stroke. The PROACT II study: a randomized controlled trial. Prolyse in acute cerebral thromboembolism. JAMA. 1999; 12. 282(21):2003–2011. PMID: 10591382.8. Gralla J, Brekenfeld C, Mordasini P, Schroth G. Mechanical thrombolysis and stenting in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2012; 1. 43(1):280–285. PMID: 22198985.
Article9. Gralla J, Burkhardt M, Schroth G, El-Koussy M, Reinert M, Nedeltchev K, et al. Occlusion length is a crucial determinant of efficiency and complication rate in thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008; 2. 29(2):247–252. PMID: 17974616.
Article10. Higashida RT, Furlan AJ, Roberts H, Tomsick T, Connors B, Barr J, et al. Trial design and reporting standards for intra-arterial cerebral thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2003; 8. 34(8):e109–e137. PMID: 12869717.
Article11. Kharitonova T, Thorén M, Ahmed N, Wardlaw JM, von Kummer R, Thomassen L, et al. Disappearing hyperdense middle cerebral artery sign in ischaemic stroke patients treated with intravenous thrombolysis: clinical course and prognostic significance. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2009; 3. 80(3):273–278. PMID: 18931005.
Article12. Kimura K, Iguchi Y, Shibazaki K, Watanabe M, Iwanaga T, Aoki J. M1 susceptibility vessel sign on T2* as a strong predictor for no early recanalization after IV-t-PA in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2009; 9. 40(9):3130–3132. PMID: 19556532.13. Legrand L, Naggara O, Turc G, Mellerio C, Roca P, Calvet D, et al. Clot burden score on admission T2*-MRI predicts recanalization in acute stroke. Stroke. 2013; 7. 44(7):1878–1884. PMID: 23704103.14. Pai SB, Varma RG, Kulkarni RN. Microsurgical anatomy of the middle cerebral artery. Neurol India. 2005; 6. 53(2):186–190. PMID: 16010057.
Article15. Patel MR, Edelman RR, Warach S. Detection of hyperacute primary intraparenchymal hemorrhage by magnetic resonance imaging. Stroke. 1996; 12. 27(12):2321–2324. PMID: 8969800.
Article16. Penumbra Pivotal Stroke Trial Investigators. The penumbra pivotal stroke trial: safety and effectiveness of a new generation of mechanical devices for clot removal in intracranial large vessel occlusive disease. Stroke. 2009; 8. 40(8):2761–2768. PMID: 19590057.17. Sakamoto Y, Kimura K, Sakai K. M1 susceptibility vessel sign and hyperdense middle cerebral artery sign in hyperacute stroke patients. Eur Neurol. 2012; 68(2):93–97. PMID: 22759539.
Article18. Saqqur M, Uchino K, Demchuk AM, Molina CA, Garami Z, Calleja S, et al. Site of arterial occlusion identified by transcranial Doppler predicts the response to intravenous thrombolysis for stroke. Stroke. 2007; 3. 38(3):948–954. PMID: 17290031.
Article19. Schellinger PD, Chalela JA, Kang DW, Latour LL, Warach S. Diagnostic and prognostic value of early MR Imaging vessel signs in hyperacute stroke patients imaged < 3 hours and treated with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005; 3. 26(3):618–624. PMID: 15764589.20. Smith WS, Tsao JW, Billings ME, Johnston SC, Hemphill JC 3rd, Bonovich DC, et al. Prognostic significance of angiographically confirmed large vessel intracranial occlusion in patients presenting with acute brain ischemia. Neurocrit Care. 2006; 4(1):14–17. PMID: 16498189.
Article21. Tan IY, Demchuk AM, Hopyan J, Zhang L, Gladstone D, Wong K, et al. CT angiography clot burden score and collateral score: correlation with clinical and radiologic outcomes in acute middle cerebral artery infarct. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009; 3. 30(3):525–531. PMID: 19147716.
Article22. The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group. Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 1995; 12. 333(24):1581–1587. PMID: 7477192.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A newly Developed Hyperintensity Within a Posterior Cerebral Artery Susceptibility Vessel Sign in T2*-Weighted Gradient-Echo Imaging: a Case Report and Correlation with Magnetic Resonance Angiography and Black-Blood Imaging
- Gradient-Echo MRI in Defining the Severity of Cerebral Fat Embolism
- An exeprimental study on MRI imaging of jugular venous thrombosis in dogs
- Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced T2*-Weighted Imaging in Acute Cerebral Infarction: Usefulness in Assessment of Cerebral Hemodynamics
- Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in Animal Model with Acute Ischemic Brain Infarction: Evaluation of Reversible Brain Injury