J Korean Foot Ankle Soc.
2014 Mar;18(1):24-28. 10.14193/jkfas.2014.18.1.24.
Surgical Treatment of the Fifth Metatarsal Base Fracture Using Multiple Kirschner Wires
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. kjh12344@hanmail.net
- KMID: 1958735
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14193/jkfas.2014.18.1.24
Abstract
- PURPOSE
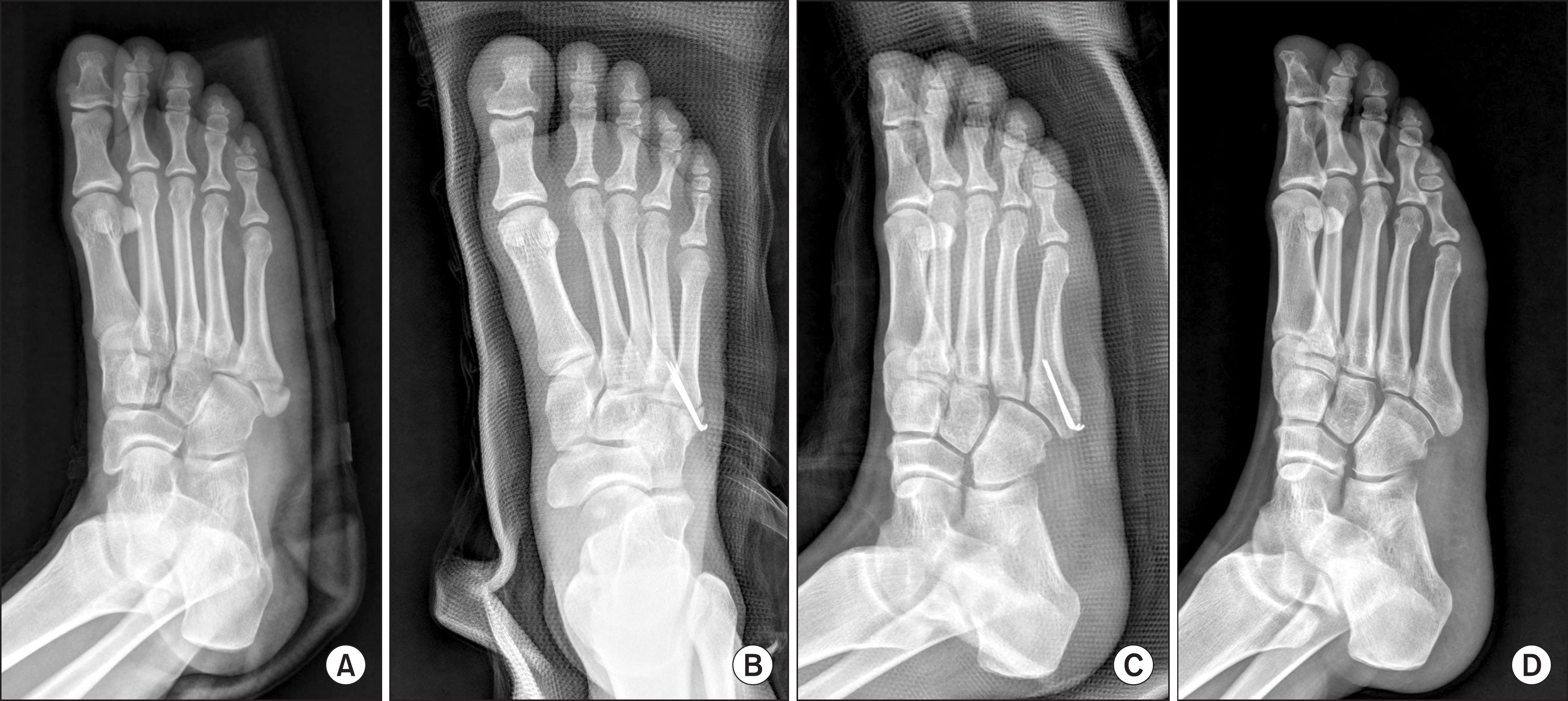
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the clinical and radiographic results of internal fixation using multiple Kirschner wires (K-wires) for the fifth metatarsal base fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
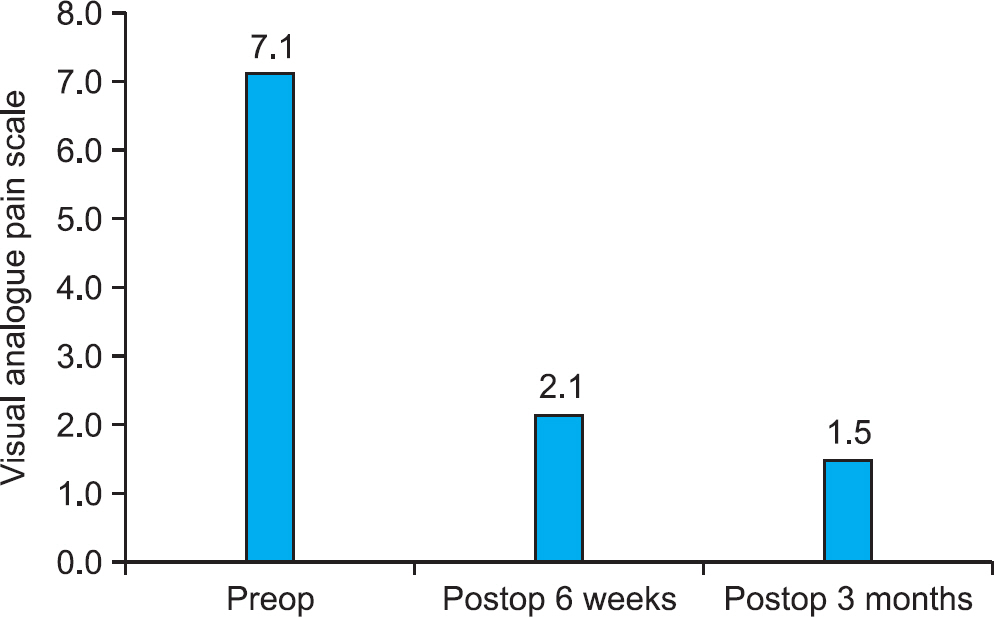
We retrospectively reviewed 14 patients with a displaced fifth metatarsal base fracture. We measured the distance of fracture displacement on the foot oblique radiograph pre- and post-operatively. We evaluated the clinical results using the visual analog pain scale at six weeks and three months postoperatively and the American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society (AOFAS) midfoot score at six months postoperatively.
RESULTS
In our series, 10 cases were zone I fracture and four cases were zone II fracture. We achieved anatomical reduction and bony union in all of our cases. The average time to bone union was 43 days. The degree of pain around the fifth metatarsal base was significantly decreased after surgery. The average AOFAS score was 95 at six months postoperatively.
CONCLUSION
Multiple K-wire fixation is a relatively simple fixation method for displaced fifth metatarsal base fractures. If we place a K-wire into the medial cortex of the fifth metatarsal, we could prevent proximal migration of the K-wire.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The Short Term Outcome of Surgical Treatment for the Fifth Metatarsal Base Fracture Using a Headless Cannulated Compression Screw
Je-Gyun Chon, Hyun Choi, Jun-Beom Kim, Doo-Hun Sun, Sang-Yeop Shin
J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2016;20(3):131-134. doi: 10.14193/jkfas.2016.20.3.131.
Reference
-
References
1. Hasselman CT, Vogt MT, Stone KL, Cauley JA, Conti SF. Foot and ankle fractures in elderly white women. Incidence and risk factors. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003; 85:820–4.2. Petrisor BA, Ekrol I, Court-Brown C. The epidemiology of metatarsal fractures. Foot Ankle Int. 2006; 27:172–4.
Article3. Lawrence SJ, Botte MJ. Jones' fractures and related fractures of the proximal fifth metatarsal. Foot Ankle. 1993; 14:358–65.
Article4. Sung KS, Koh KH, Koo KH, Park JC. Conservative treatment of nondisplaced fifth metatarsal base zone I and II fractures. J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2008; 12:185–8.5. Thomas JL, Davis BC. Three-wire fixation technique for displaced fifth metatarsal base fractures. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2011; 50:776–9.
Article6. Dameron TB Jr. Fractures and anatomical variations of the proximal portion of the fifth metatarsal. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1975; 57:788–92.
Article7. Wiener BD, Linder JF, Giattini JF. Treatment of fractures of the fifth metatarsal: a prospective study. Foot Ankle Int. 1997; 18:267–9.
Article8. Quill GE Jr. Fractures of the proximal fifth metatarsal. Orthop Clin North Am. 1995; 26:353–61.
Article9. Jones R. I. Fracture of the base of the fifth metatarsal bone by indirect violence. Ann Surg. 1902; 35:697–700. .2.10. Rammelt S, Heineck J, Zwipp H. Metatarsal fractures. Injury. 2004; 35(Suppl 2):SB77–86.
Article11. Hatch RL, Alsobrook JA, Clugston JR. Diagnosis and management of metatarsal fractures. Am Fam Physician. 2007; 76:817–26.12. Ahn JK, Chung HJ, Bae SY, Park JY. Treatment of fifth metatarsal base fracture using tension band wiring. J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2011; 15:18–21.13. Suh JS, Kim JH, Choi JY. Operative treatment of fractures of the fifth metatarsal base. J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2008; 12:189–96.14. Husain ZS, DeFronzo DJ. Relative stability of tension band versus two-cortex screw fixation for treating fifth metatarsal base avulsion fractures. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2000; 39:89–95.
Article15. Meena S, Nag HL, Kumar S, Barwar N, Mittal S, Singla A. Delayed migration of K-wire into popliteal fossa used for tension band wiring of patellar fracture. Chin J Traumatol. 2013; 16:186–8.16. Konda SR, Dayan A, Egol KA. Progressive migration of broken Kirschner wire into the proximal tibia following tension-band wiring technique of a patellar fracture–case report. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2012; 70:279–82.17. Park SY, Kang JW, Yang DH, Lim TH. Intracardiac migration of a Kirschner wire: case report and literature review. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2011; 27(Suppl 1):85–8.
Article18. Kędra M, Rybojad P, Jendrej J, Sawicki M. Intraspinal K-wire migration after humeral fracture fixation. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2011; 39:1079.
Article19. Huang TW, Wu CC, Fan KF, Tseng IC, Lee PC, Chou YC. Tension band wiring for olecranon fractures: relative stability of Kirschner wires in various configurations. J Trauma. 2010; 68:173–6.
Article20. Karlsson MK, Hasserius R, Karlsson C, Besjakov J, Josefsson PO. Fractures of the olecranon: a 15- to 25-year followup of 73 patients. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002; 403:205–12.21. Mullett JH, Shannon F, Noel J, Lawlor G, Lee TC, O'Rourke SK. K-wire position in tension band wiring of the olecranon – a comparison of two techniques. Injury. 2000; 31:427–31.
Article22. Prayson MJ, Williams JL, Marshall MP, Scilaris TA, Lingenfelter EJ. Biomechanical comparison of fixation methods in transverse olecranon fractures: a cadaveric study. J Orthop Trauma. 1997; 11:565–72.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment of Fracture - Dislocation of Tarsometatarsal Joint
- Reduction of comminuted fractures of the anterior wall of the frontal sinus using threaded Kirschner wires and a small eyebrow incision
- Stress Fracture on the 4th Metatarsal Bone after Treatment of Stress Fracture on the 5th Metatarsal Bone: A Case Report
- Operative Treatment of Fractures of the Fifth Metatarsal Base
- Multiple Pinning in Treatment of the Proximal End of Femur Fracture