J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2007 Jun;14(2):105-109. 10.4184/jkss.2007.14.2.105.
Cervical and Thoracolumbar Epidural Abscess: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Korea. hyparkys@hanyang.ac.kr
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Korea.
- 3Devision of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Korea.
- KMID: 1941663
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2007.14.2.105
Abstract
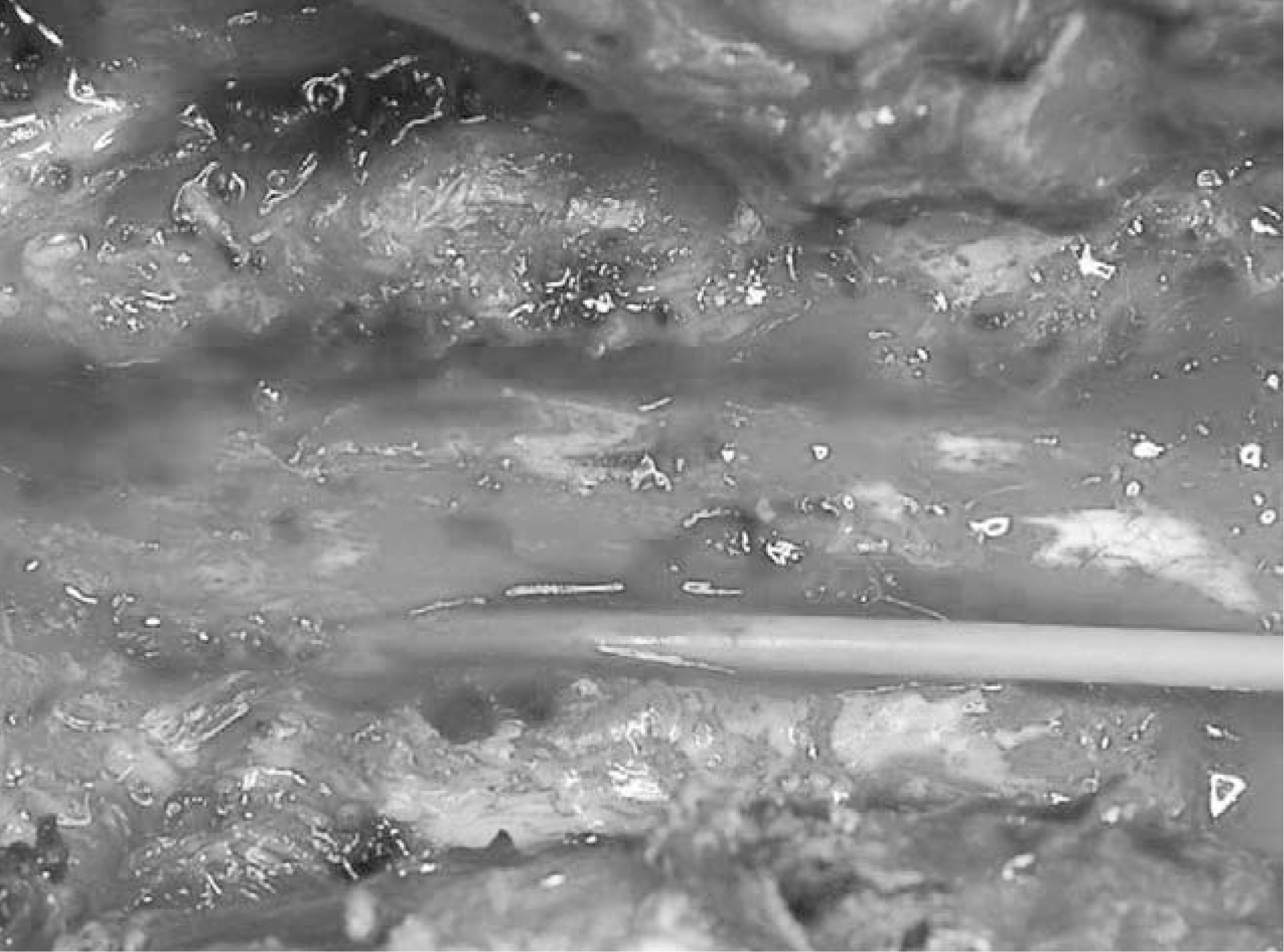
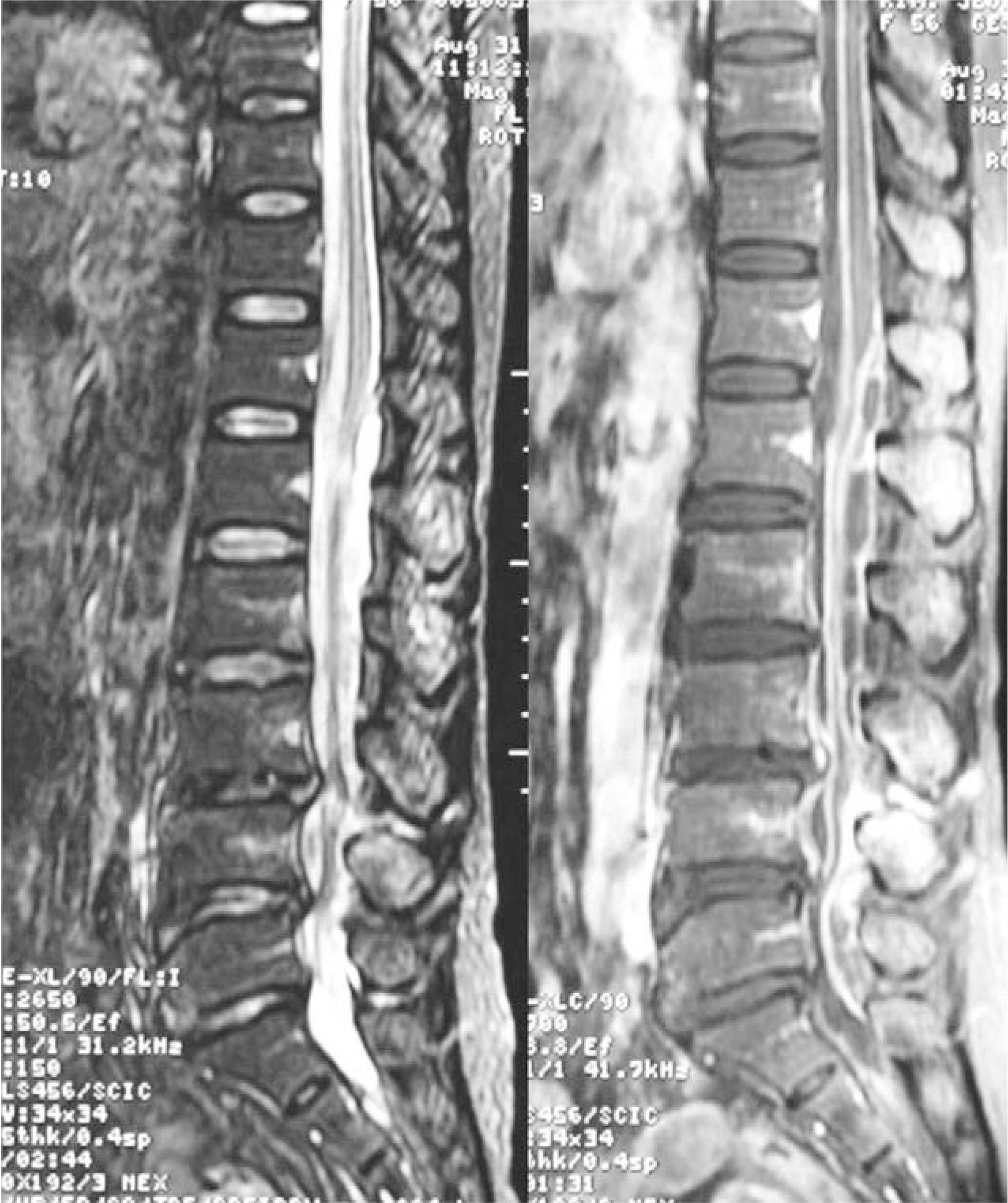
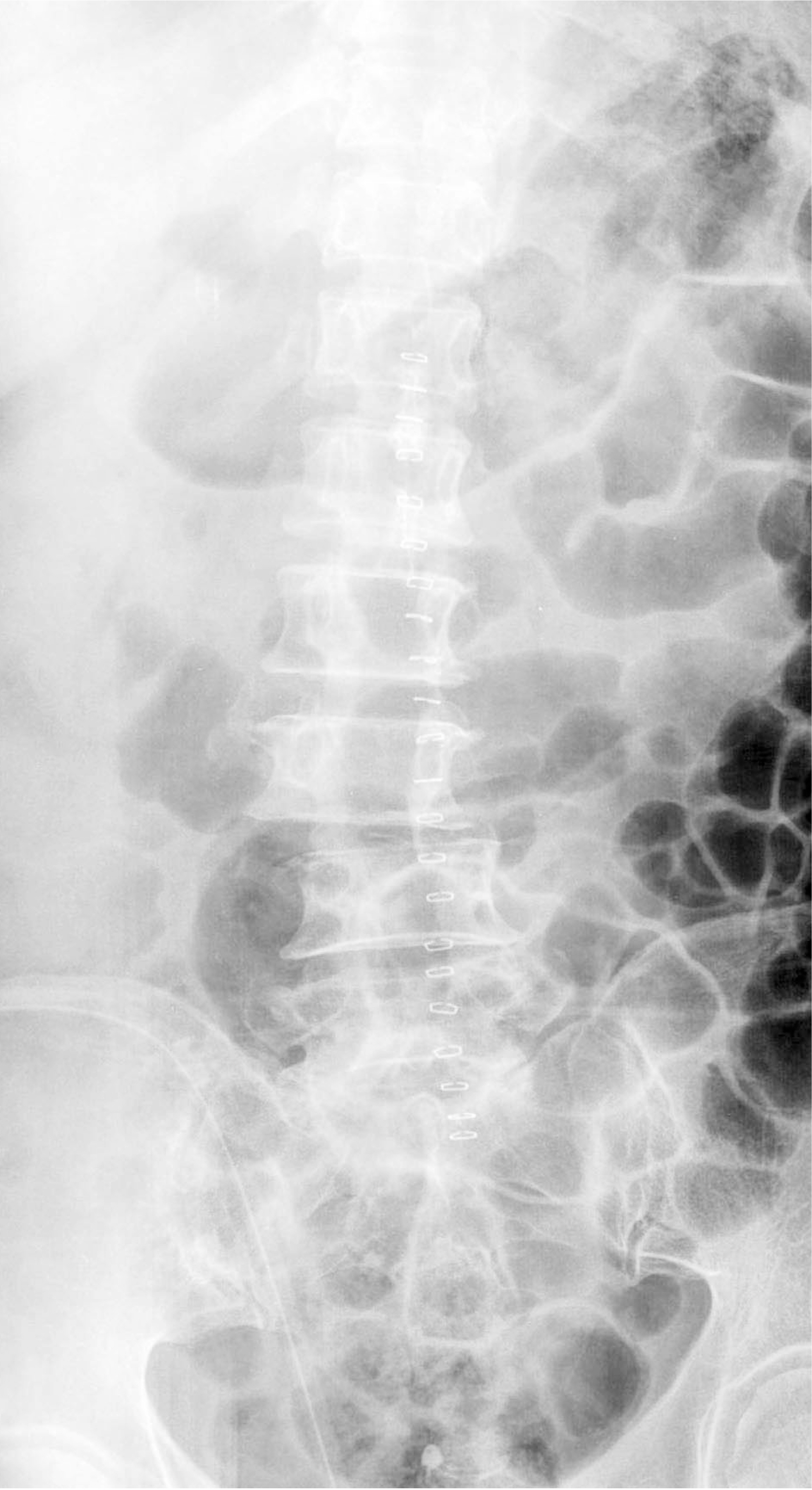
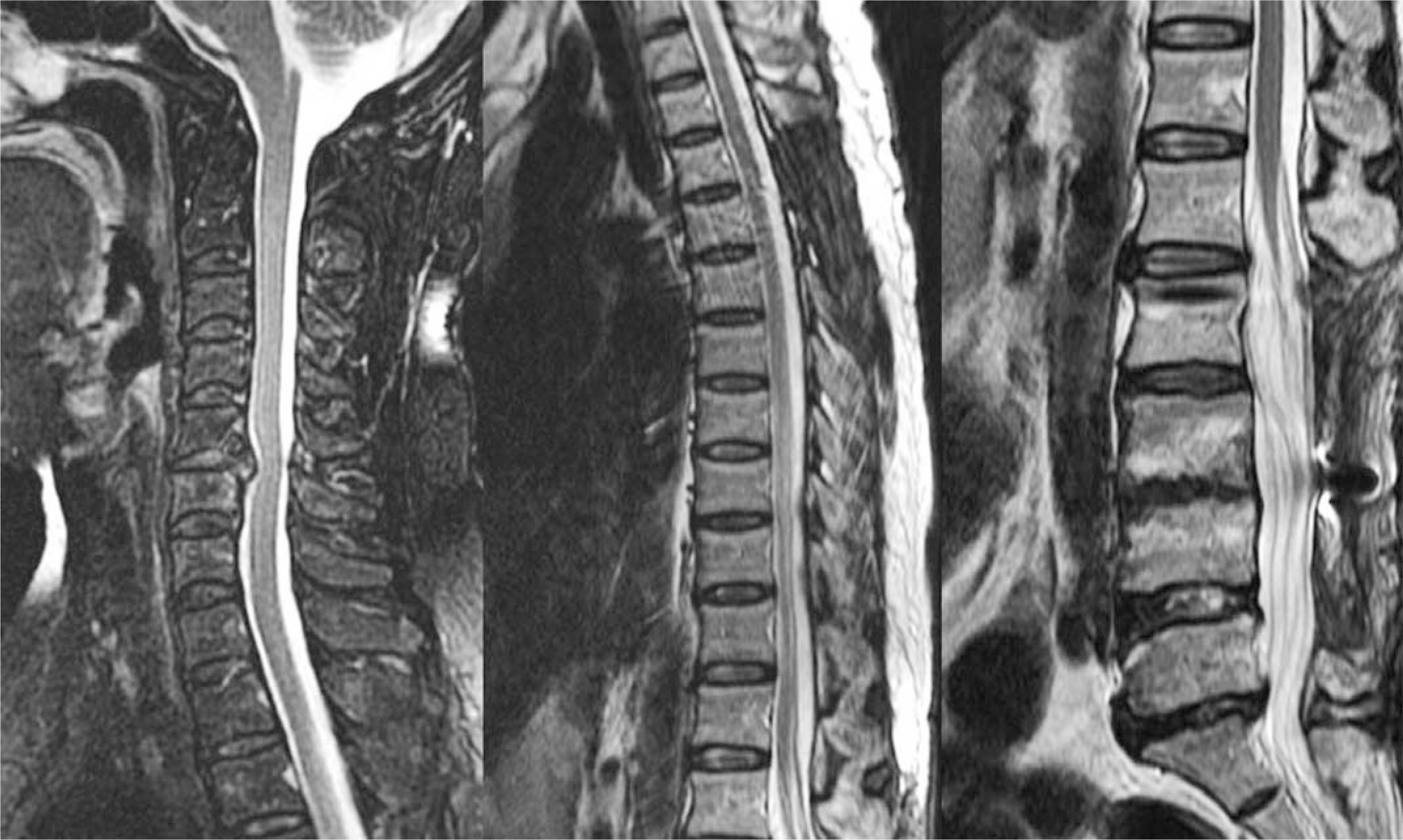
- Epidural abscess is a rare disease that can cause severe neurological complications or death if it is not recognized and treated early. Authors report a case of panspinal epidural abscess, which is diagnosed by MRI and treated with surgical drainage and antibiotics.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Bluman EM, Palumbo MA, Lucas PR. Spinal epidural abscess in adults. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2004; 12:155–163.
Article2). Baker AS, Ojeman RG, Swarz MN, Richardson EP Jr. Spinal epidural abscess. N Engl J Med. 1975; 293:463–468.
Article3). Kim H, Oh SH, Choi IS, et al. .:. Acute panspinal epidural abscess. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 1999; 28:392–397.4). Rigamonti D, Leim L, Sampath P, et al. .:. Spinal epidural abscess: Contemporary trends in etiology, evaluation and management. Surg Neurol. 1988; 52:189–197.
Article5). Simpson RK Jr, Azordegan PA, Sirbasku DM, Weath-ers SW, Lidsky MD, Baskin DS. Rapid onset of quadri-plegia from a panspinal epidural abscess. Spine. 1991; 16:1002–1005.
Article6). Reihsaus F, Waldbaur H, Seeling W. Spinal epidural abscess: A meta-analysis of 915 patients. Neurosurg Rev. 2000; 23:175–205.
Article7). Danner RL, Hartmann BJ. Update of spinal epidural abscess: 35 cases and review of the literature. Rev Infect Dis. 1987; 9:265–274.
Article8). Lang IM, Hughes JPR, St Clair Forbes W, MaKenna F. MR imaging appearances of cervical epidural abscess. Clinical Radiology. 1995; 50:446–471.
Article9). Choi WT, Choi BY, Lee JW, Moon MS. Pyogenic spinal epidural abscess - A case report -. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2002; 37:319–323.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Infectious Spondylodiscitis Accompanied by Widespread Thoracolumbar Subdural Abscess
- Full Endoscopic Removal of Cervical Spinal Epidural Abscess: Case Report and Technical Note
- Chronic Spinal Epidural Abscess after Epidural Analgesia: Case Report
- Epidural Abscess Secondary to Acute Osteomyelitis of the Cervical Spine Caused by E. coli(A Case Report)
- Epidural Abscess following Longterm Epidural Catheterization