Tuberc Respir Dis.
2007 Aug;63(2):194-199. 10.4046/trd.2007.63.2.194.
A Case of Low-grade B-cell Lymphoma of Bronchial Associated Lymphoid Tissue Mimicking Lipoid Pneumonia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Departments of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Ajou University School of Medine, Suwon, Korea. sssheen@ajou.ac.kr
- 2Departments of Hemato-oncology, Ajou University School of Medine, Suwon, Korea.
- KMID: 1910100
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2007.63.2.194
Abstract
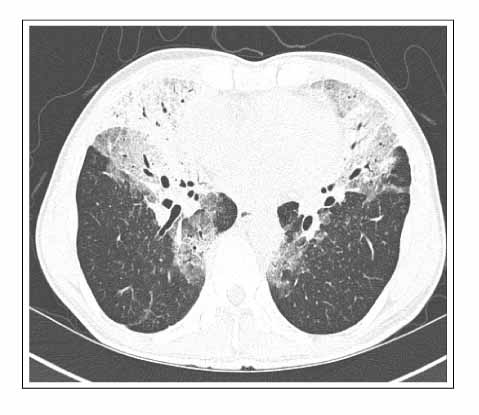
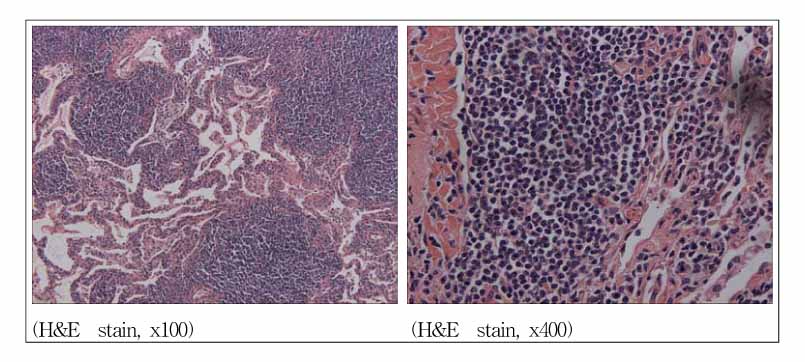
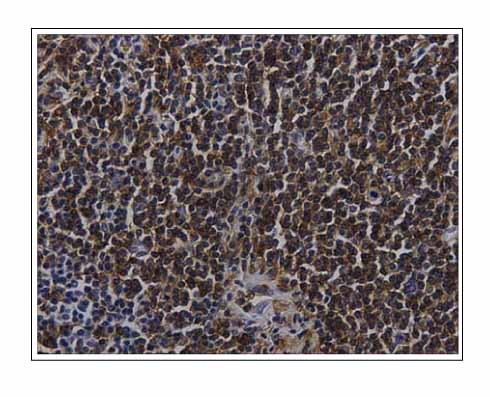
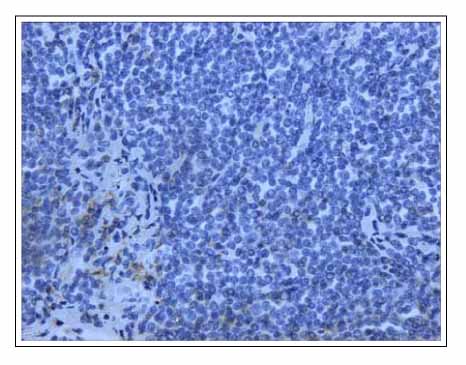
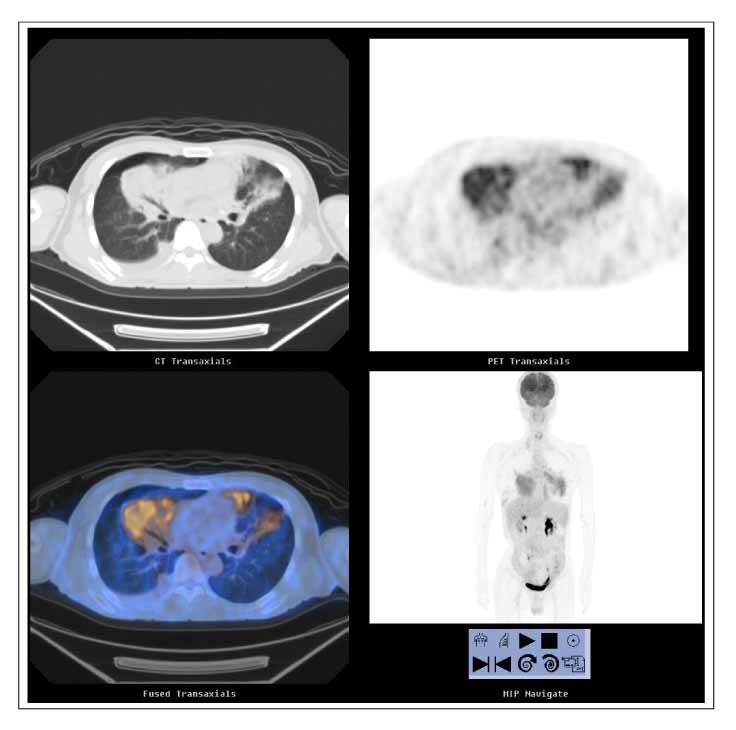
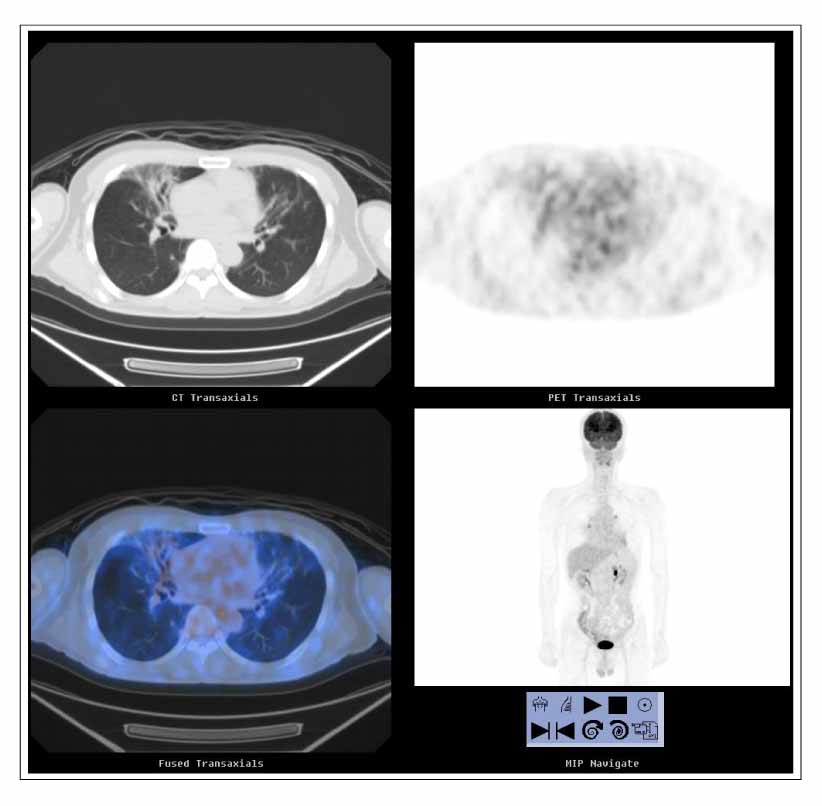
- BALT(bronchial associated lymphoid tissue) lymphomas are a distinct subgroup of low-grade B-cell extranodal non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, which are classified as a marginal-zone lymphomas. The majority of the patients are asymptomatic or their pulmonary lesions is often discovered incidentally on a routine chest radiograph. A 50-year-old man was admitted for an the evaluation of cough, dyspnea and fever. His chest CT showed ground glass appearance with interlobular septal thickening in both lower lobes, right middle lobe and left lingular division. He had been initially diagnosed with lipoid pneumonia and was kept under observation. However, his chest lesion showed continuous progression and a video-associated thoracoscopy was performed His pulmonary lesion was confirmed histologically to be a BALT(bronchial associated lymphoid tissue) lymphoma. We report a case of a BALT lymphoma, which was initially misdiagnosed as lipoid pneumonia.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Zinzani PL, Magagnoli M, Galieni P, Martelli M, Poletti V, Zaja F, et al. Nongastrointestinal low-grade mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma: analysis of 75 patients. J Clin Oncol. 1999. 17:1254.2. Ahmed S, Kussick SJ, Siddiqui AK, Bhuiya TA, Khan A, Sarewitz S, et al. Bronchial-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma: a clinical study of rare disease. Eur J Cancer. 2004. 40:1320–1326.3. Hara S, Yokote T, Oka S, Akioka T, Kobayashi K, Tsuji M, et al. Bronchial infiltration with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leuk Res. 2006. 30:1319–1322.4. Varoczy L, Gergely L, Illes A. Diagnostics and treatment of pulmonary BALT lymphoma: a repert on four cases. Ann Hematol. 2003. 82:363–366.5. Kang MJ, Lee JM, Lee SJ, Son JW, Kim DG, Lee MG, et al. A case of Broncus-Associated Lymphoid Tissue lymphoma in the lung of the patient with primary Sjogren's Syndrome. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2002. 52:179–185.6. Kurtin PJ, Myers JL, Adlakha H, Strickler JG, Lohse C, Pankratz VS, et al. Pathologic and clinical features of primary pulmonary extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of MALT type. Am J Surg Pathol. 2001. 25:997–1008.7. Isaacson P, Wright DH. Malignant lymphoma of mucosa associated lymphoid tissue. A distinctive type of B-cell lymphoma. Cancer. 1983. 52:1410–1416.8. Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Diebold J, Flandrin G, Muller-Hermelink HK, Vardiman J, et al. The WHO classification of neoplastic disease of hematopoietic and lymphoid tissue: report of the Clinical Advisory Committee meeting-Airlie House, Virginia, November 1997. Histopathology. 2000. 36:69–86.9. Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Stein H, Banks PM, Chan JK, Cleary ML, et al. A revised European-American Classification of lymphoid neoplasms: a proposal from the International Lymphoma Study Group. Blood. 1994. 84:1361–1392.10. Matsushima AY, Hamele-bena D, Osborne BM. Fine-needle aspiration biopsy findings in marginal zone B cell lymphoma. Diagn Cytopathol. 1999. 20:190–198.11. Ferraro P, Trastek VF, Adlakha H, Deschamps C, Allen MS, Pairolero PC. Primary non-Hodgkin's lymphoma of lung. Ann Thorac Surg. 2000. 69:993–997.12. Takamori M, Noma S, Kobashi Y, Inoue T, Gohma I, Mino M, et al. CT findings of BALTOMA. Radiat Med. 1999. 17:349–354.13. Ahmed S, Siddiqui AK, Rai KR. Low-grade B-cell bronchial associated lymphoid tissue(BALT) lymphoma. Cancer Invest. 2002. 20:1059–1068.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case report of the Pulmonary Malignant Lymphomaof the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue(MALT)
- Ileal Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (MALT) Lymphoma with a Large-Cell Component That Regressed Spontaneously
- Expression Pattern of p27 Protein in Primary Gastric Lymphomas
- A Case of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma Transformed from a Duodenal Low Grade MALT Lymphoma
- Cases of the Pulmonary Malignant Lymphoma of the Bronchus-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (BALT)