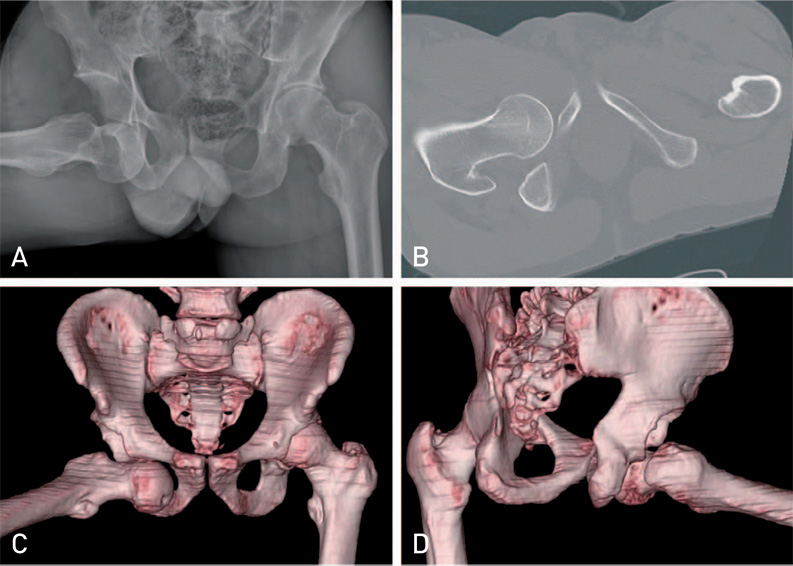
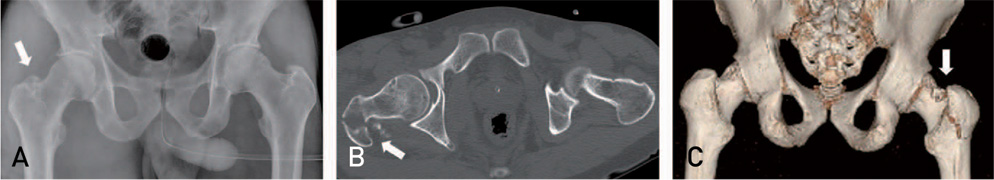
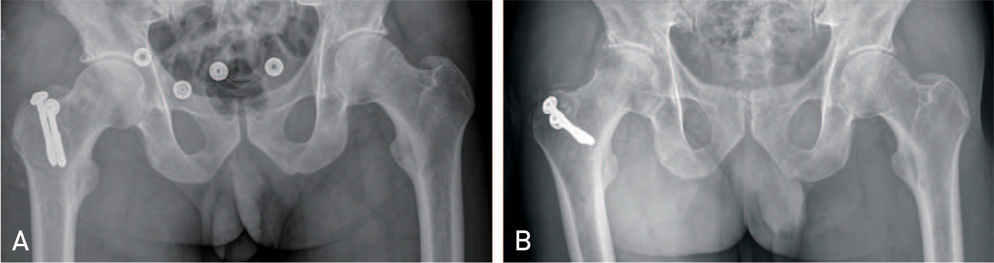
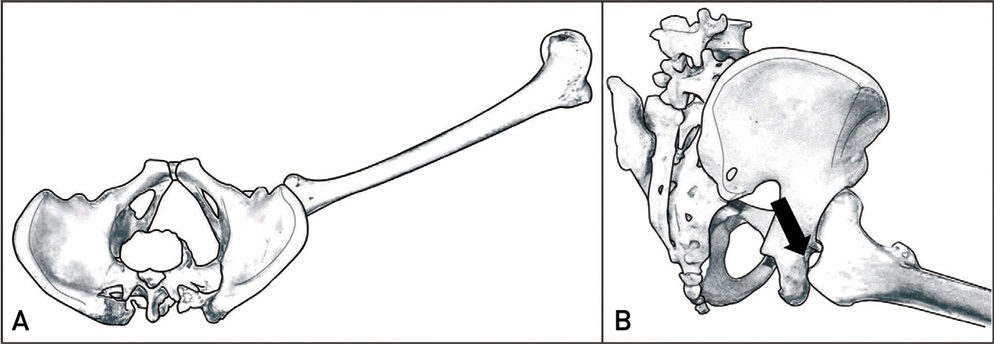
Hip Pelvis.
2014 Dec;26(4):275-278. 10.5371/hp.2014.26.4.275.
Fracture of the Greater Trochanter during Closed Reduction of Obturator Type Hip Dislocation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Veterans Health Service Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Oxford Super-specialty and Trauma Hospital, Jalandhar, SGL Charitable Hospital, Subhanpur, Kapurthala, India.
- 3Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Konkuk University Medical Center, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. damioh@gmail.com
- KMID: 1907705
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5371/hp.2014.26.4.275
Abstract
- Obturator (Inferior) type dislocation of the hip joint is a rare and the fracture of greater trochanter during closed reduction for it has never been reported in literature. In this report, we present a case of a fracture of greater trochanter during difficult closed reduction which required operative fixation. Surgeons need to be aware of this complication and excessive force for reduction should be avoided when treating of this type dislocation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Korovessis P, Droutsas P, Spastris P, Christodoulou G. Anterior dislocation of the hip associated with fracture of the ipsilateral greater trochanter. A case report. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990; 253:164–167.2. Maruoka A, Naka N, Saito M, Toma Y. Pubic-type dislocation of the hip combined with fracture of the ipsilateral greater trochanter. A case report. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1993; 112:299–301.
Article3. Scham SM, Fry LR. Traumatic anterior dislocation of the hip with fracture of the femoral head. A case report. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1969; 62:133–135.4. Singh R, Sharma SC, Goel T. Traumatic inferior hip dislocation in an adult with ipsilateral trochanteric fracture. J Orthop Trauma. 2006; 20:220–222.
Article5. Tornetta P 3rd. Hip dislocations and fractures of the femoral head. In : Rockwood CA, Green DP, Bucholz RW, editors. Rockwood and Green's fractures in adults. 6th ed. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott Company;2006. p. 1715–1752.6. Lamberti PM, Rabin SI. Open anterior-inferior hip dislocation. J Orthop Trauma. 2003; 17:65–66.
Article7. Tawari AA, Bahuva VD, Goregaonkar AB, Subaraman R. A rare case of open anterior hip dislocation. J Surg Case Rep. 2013; doi:10.1093/jscr/rjs035.
Article8. Sankarankutty M. Traumatic inferior dislocation of the hip (luxatio erecta) in a child. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1967; 49:145.
Article9. Toms AD, Williams S, White SH. Obturator dislocation of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001; 83:113–115.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Obturator Neuropathy after Traumatic Posterior Hip Dislocation: A case report
- The Cause of Primary Reduction Failure in Hip Dislocation with or without Hip Fracture
- Traumatic Bilateral Anterior Hip Dislocation: A Case Report
- An Irreducible Hip Dislocation with Femoral Head Fracture
- The Treatment of Traumntic Posterior Fracture-Dislocation of the Hip