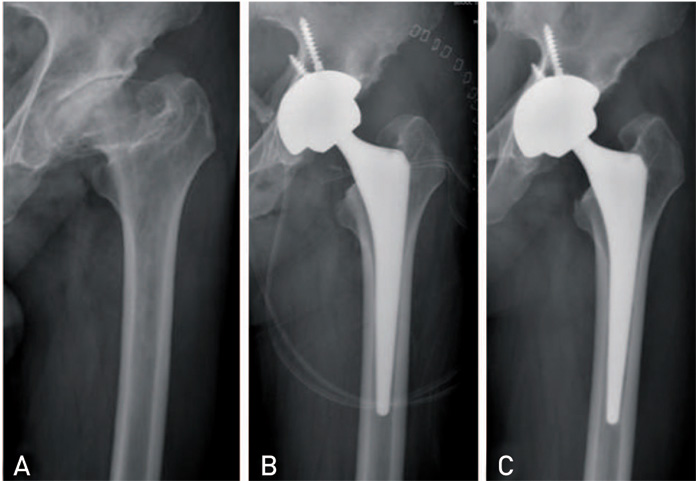
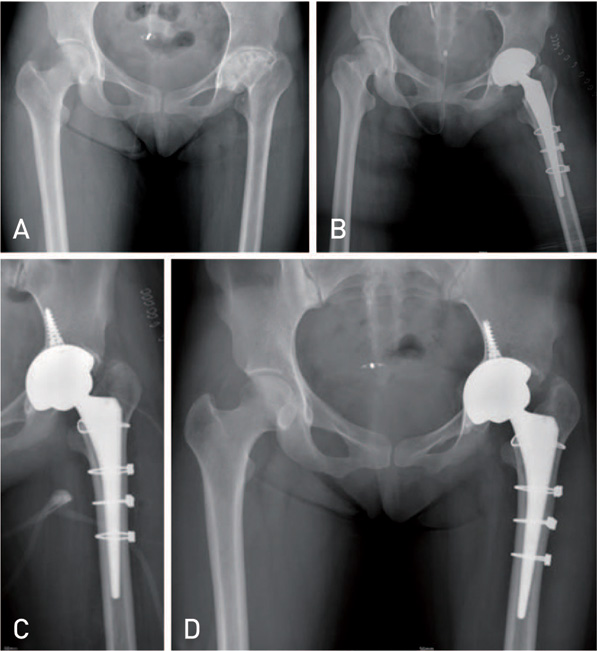
Hip Pelvis.
2014 Dec;26(4):214-219. 10.5371/hp.2014.26.4.214.
Total Hip Arthroplasty in Patient with the Sequelae of Legg-Calve-Perthes Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. yongsik@korea.com
- KMID: 1907696
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5371/hp.2014.26.4.214
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Patients who have secondary hip osteoarthritis as sequelae of Legg-Calve-Perthes disease (LCPD) are severe deformities of femoral head and acetabulum. A few studies have presented that the clinical results and risks associated with total hip arthroplasty (THA) for patients with a history of LCPD were not satisfactory. In this study, we reported the radiographic and clinical outcomes of THA in patients with sequelae of LCPD.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between March 2007 and May 2012, 23 hips (23 patients) underwent cementless THA and were followed up at least 2 years after surgery. There were 11 male patients and 12 female patients with an average age of 49.2 years old (range, 25 to 69 years old), and the average follow up period was 40.8 months (range, 24 to 84 months). The clinical and radiological evaluations were performed.
RESULTS
The Harris hip score improved from 48.3 points preoperatively to 92.4 points at the time of the last follow-up. The shortening of affected limb was improved from -1.6 cm to 0.2 cm. The complications included one case of sciatic nerve palsy that developed after extensive lengthening of lower extremity, three cases of intraoperative femur fractures. There was no component loosening.
CONCLUSION
Fractures and motor nerve palsies may be more frequent in this population. Careful preoperative planning should be performed to overcome the technical pitfalls. If overcoming this early complication, the clinical and radiological evaluations showed excellent outcomes at average 40-month follow-ups.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gower WE, Johnston RC. Legg-Perthes disease. Long-term follow-up of thirty-six patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1971; 5:759–768.2. Kelly FB Jr, Canale ST, Jones RR. Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease. Long-term evaluation of non-containment treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1980; 62:400–407.
Article3. Stulberg SD, Cooperman DR, Wallensten R. The natural history of Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1981; 63:1095–1108.
Article4. Catterall A. The natural history of Perthes' disease. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1971; 53:37–53.
Article5. Larson AN, Sucato DJ, Herring JA, et al. A prospective multicenter study of Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease: functional and radiographic outcomes of nonoperative treatment at a mean follow-up of twenty years. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012; 94:584–592.6. Al-Khateeb H, Kwok IH, Hanna SA, Sewell MD, Hashemi-Nejad A. Custom cementless THA in patients with Legg-Calvé-Perthes Disease. J Arthroplasty. 2014; 29:792–796.7. Baghdadi YM, Larson AN, Stans AA, Mabry TM. Total hip arthroplasty for the sequelae of Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013; 471:2980–2986.
Article8. Radl R, Hungerford M, Materna W, Rehak P, Windhager R. Higher failure rate and stem migration of an uncemented femoral component in patients with femoral head osteonecrosis than in patients with osteoarthrosis. Acta Orthop. 2005; 76:49–55.
Article9. Saito S, Saito M, Nishina T, Ohzono K, Ono K. Long-term results of total hip arthroplasty for osteonecrosis of the femoral head. A comparison with osteoarthritis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989; 244:198–207.10. Gent E, Clarke NM. Joint replacement for sequelae of childhood hip disorders. J Pediatr Orthop. 2004; 24:235–240.
Article11. Sankar WN, Flynn JM. The development of acetabular retroversion in children with Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease. J Pediatr Orthop. 2008; 28:440–443.
Article12. Kawasaki M, Hasegawa Y, Sakano S, Masui T, Ishiguro N. Total hip arthroplasty after failed transtrochanteric rotational osteotomy for avascular necrosis of the femoral head. J Arthroplasty. 2005; 20:574–579.
Article13. Kim YS, Kwon SY, Sun DH, Han SK, Maloney WJ. Modified posterior approach to total hip arthroplasty to enhance joint stability. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008; 46:294–299.
Article14. Harris WH. Preliminary report of results of Harris total hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1973; 95:168–173.
Article15. Gruen TA, McNeice GM, Amstutz HC. "Modes of failure" of cemented stem-type femoral components: a radiographic analysis of loosening. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979; 141:17–27.16. Engh CA, Bobyn JD, Glassman AH. Porous-coated hip replacement. The factors governing bone ingrowth, stress shielding, and clinical results. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1987; 69:45–55.
Article17. Callaghan JJ, Salvati EA, Pellicci PM, Wilson PD Jr, Ranawat CS. Results of revision for mechanical failure after cemented total hip replacement, 1979 to 1982. A two to fiveyear follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1985; 67:1074–1085.
Article18. Dorr LD, Wan Z, Song M, Ranawat A. Bilateral total hip arthroplasty comparing hydroxyapatite coating to porous-coated fixation. J Arthroplasty. 1998; 13:729–736.
Article19. DeLee JG, Charnley J. Radiological demarcation of cemented sockets in total hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976; 121:20–32.
Article20. Ranawat CS, Rao RR, Rodriguez JA, Bhende HS. Correction of limb-length inequality during total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2001; 16:715–720.
Article21. Traina F, De Fine M, Sudanese A, Calderoni PP, Tassinari E, Toni A. Long-term results of total hip replacement in patients with Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011; 93:e25.
Article22. Takenaga RK, Callaghan JJ, Bedard NA, Liu SS, Klaassen AL, Pedersen DR. Cementless total hip arthroplasty in patients fifty years of age or younger: a minimum ten-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012; 94:2153–2159.
Article23. Farrell CM, Springer BD, Haidukewych GJ, Morrey BF. Motor nerve palsy following primary total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87:2619–2625.
Article24. Bargar WL. Shape the implant to the patient. A rationale for the use of custom-fit cementless total hip implants. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989; 249:73–78.25. Upadhyay SS, Burwell RG, Moulton A. Femoral anteversion in Perthes' disease with observations on irritable hips. Application of a new method using ultrasound. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986; 209:70–76.26. Toni A, Traina F, Viceconti M. Computer-assisted tridimensional preoperative planning in hip revision surgery. Chir Organi Mov. 2003; 88:273–280.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Observation of the Legg-Calve-Perthes Disease: Preliminary Report
- Legg - Calve Perthes disease in Monozygotic Male Twins
- Osteochondritis Dissecans of Femoral Head Following Legg-Calve-Perthes Disease
- Innominate Osteotomy in Legg-Calve-Perthes Disease
- A Radiological Observation on the Normal Hip in Legg-Calve-Perthes disease