J Korean Soc Surg Hand.
2014 Mar;19(1):29-35. 10.12790/jkssh.2014.19.1.29.
Efficiency of Vein Repair for Distally Based Avulsion Flap Injury of the Hand and Forearm
- Affiliations
-
- 1Cheon & Woo's Institute for Hand and Reconstructive Microsurgery, W Hospital, Daegu, Korea. handwoo@hotmail.com
- KMID: 1896924
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2014.19.1.29
Abstract
- PURPOSE
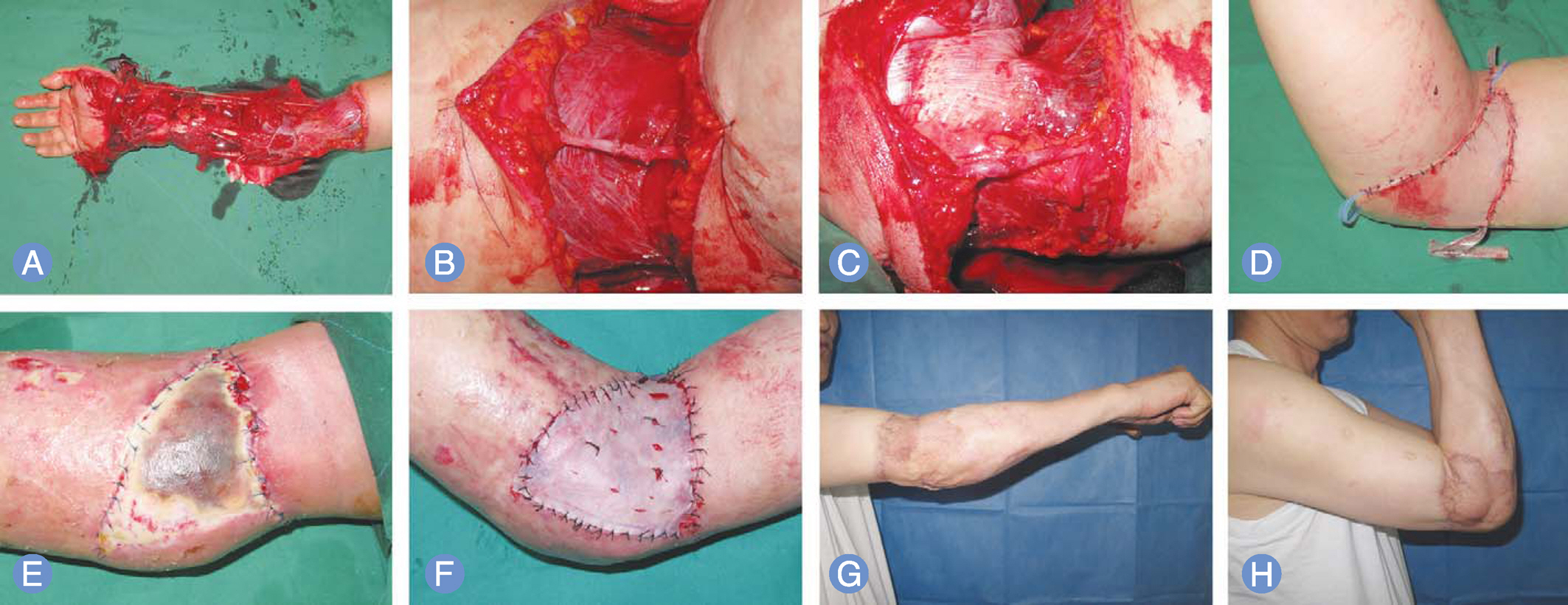
The purpose was to evaluate the efficiency of vein repair on flap survival in distally based avulsion flap injury of the hand and forearm.
METHODS
Sixteen cases of distally based avulsion flap injury larger than 30 cm2 in size of the hand and forearm in which vein repair was done were enrolled. All had a avulsion injury by rolling machine. To survive the flap, extensive debridement was done to reduce the size of distally based flap injury as little as possible. Thereafter, an average of 1.4 vein were repaired. Postoperatively, hyberbaric oxygen therapy was performed for 2 weeks. The flap survival was assessed at three weeks after operation.
RESULTS
When comparing the size of distally based avulsion flap injury and flaps that survived after operation, excellent results were observed in 12 cases, and good results in 4 cases. Additional operation was required including split thickness skin graft in 4 cases. A reverse island fasciocutaneous flap was performed in one case, and elbow joint arthrolysis was performed in another one.
CONCLUSION
Treatment of distally based avulsion flap injury of the hand and forearm using vein repair lead to relatively satisfying results in flap survival by allowing earlier motion of the joint, providing favorable functional results.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Kang JS. Plastic surgery. 3rd ed.Seoul: Koonja;2004. p. 152–3.2. Kim KC, Lee KJ, Kim JS, Woo SH. Revisit of the utilities and indications of reversed radial forearm flap for hand reconstruction. J Korean Soc Surg Hand. 2004; 9:292–8.3. Woo SH, Kim SE, Lee TH, Jeong JH, Seul JH. Effects of blood flow and venous network on the survival of the arterialized venous flap. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1998; 101:1280–9.
Article4. Park WJ, Minn KW, Lee HJ. Clinical study on the effects of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in skin grafts. J Korean Soc Plast Reconstr Surg. 1992; 19:1032–40.5. Gruber RP, Brinkley FB, Amato JJ, Mendelson JA. Hyperbaric oxygen and pedicle flaps, skin grafts, and burns. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1970; 45:24–30.
Article6. Champion WM, McSherry CK, Goulian D Jr. Effect of hyperbaric oxygen on the survival of pedicled skin flaps. J Surg Res. 1967; 7:583–6.
Article7. Jurell G, Kaijser L. The influence of varying pressure and duration of treatment with hyperbaric oxygen on the survival of skin flaps. An experimental study. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg. 1973; 7:25–8.8. McFarlane RM, Wermuth RE. The use of hyperbaric oxygen to prevent necrosis in experimental pedicle flaps and composite skin grafts. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1966; 37:422–30.9. Illingworth CF, Smith G, Lawson DD, et al. Surgical and physiological observations in an experimental pressure chamber. Br J Surg. 1961; 49:222–7.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Reconstruction of Hand and Forearm Injury using Reverse Ulnar Artery Forearm Flap: Six Cases Report
- Cephalic Vein Supercharging to Prevent Venous Congestion for a Reverse Radial Forearm Flap Used in the Reconstruction of Dorsum of Hand: A Case Report
- Venous Island Flap for Reconstruction in the Hand
- Treatment of Soft Tissue Defect on Dorsum of hand by Using the Reverse Radial Forearm Flap: Report of 5 Cases
- Reconstruction of the Soft Tissue Defect of the Lower Leg by Distally Based Superficial Sural Artery Fasciocutaneous Island Flap Using Supercharged Vein