Prog Med Phys.
2015 Jun;26(2):99-105. 10.14316/pmp.2015.26.2.99.
Development of Monitor Chamber Prototype and Basic Performance Testing
- Affiliations
-
- 1Research Center, Dongnam Inst. of Radiological & Medical Sciences, Busan, Korea. physics7@empas.com
- KMID: 1889942
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2015.26.2.99
Abstract
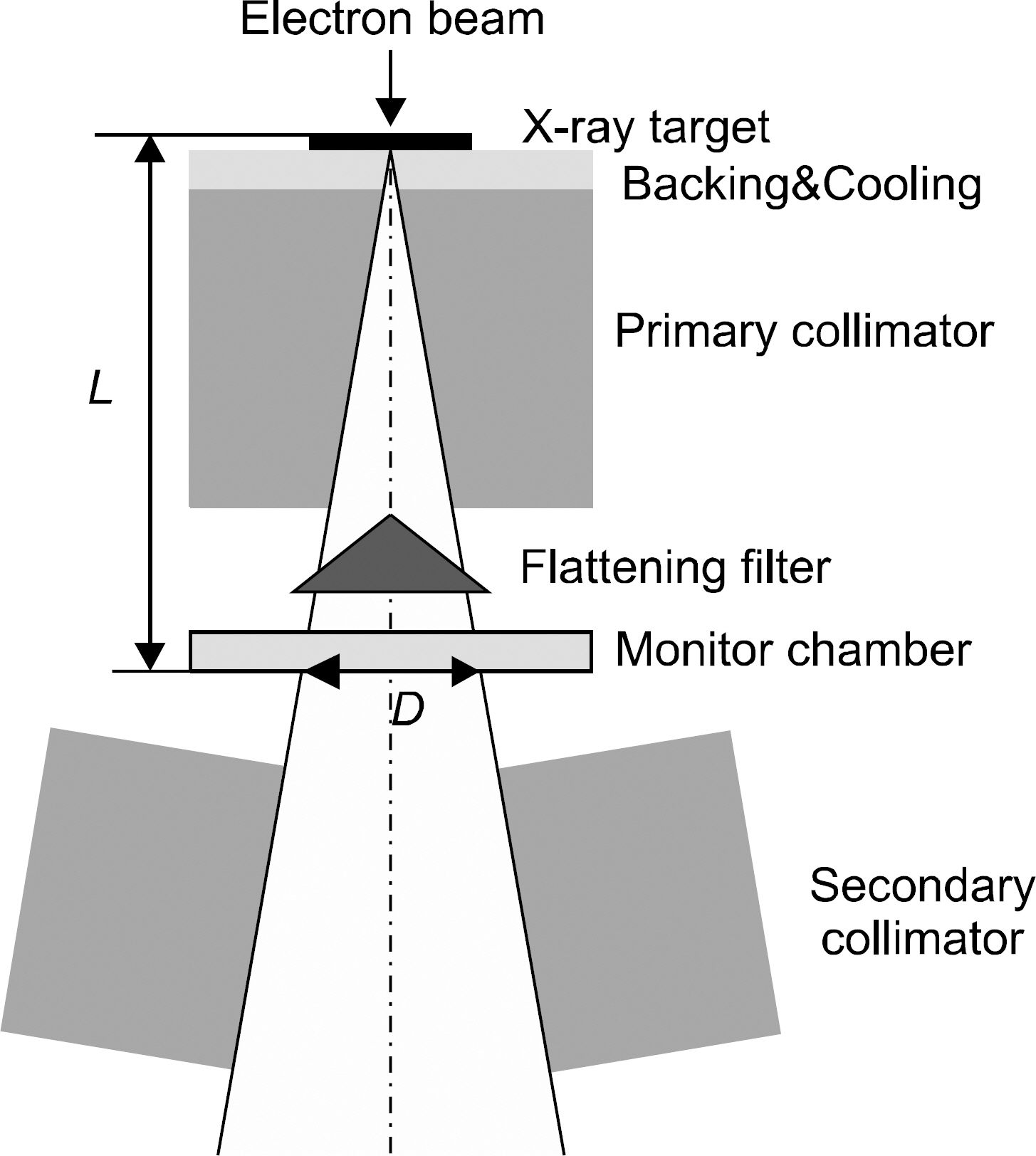
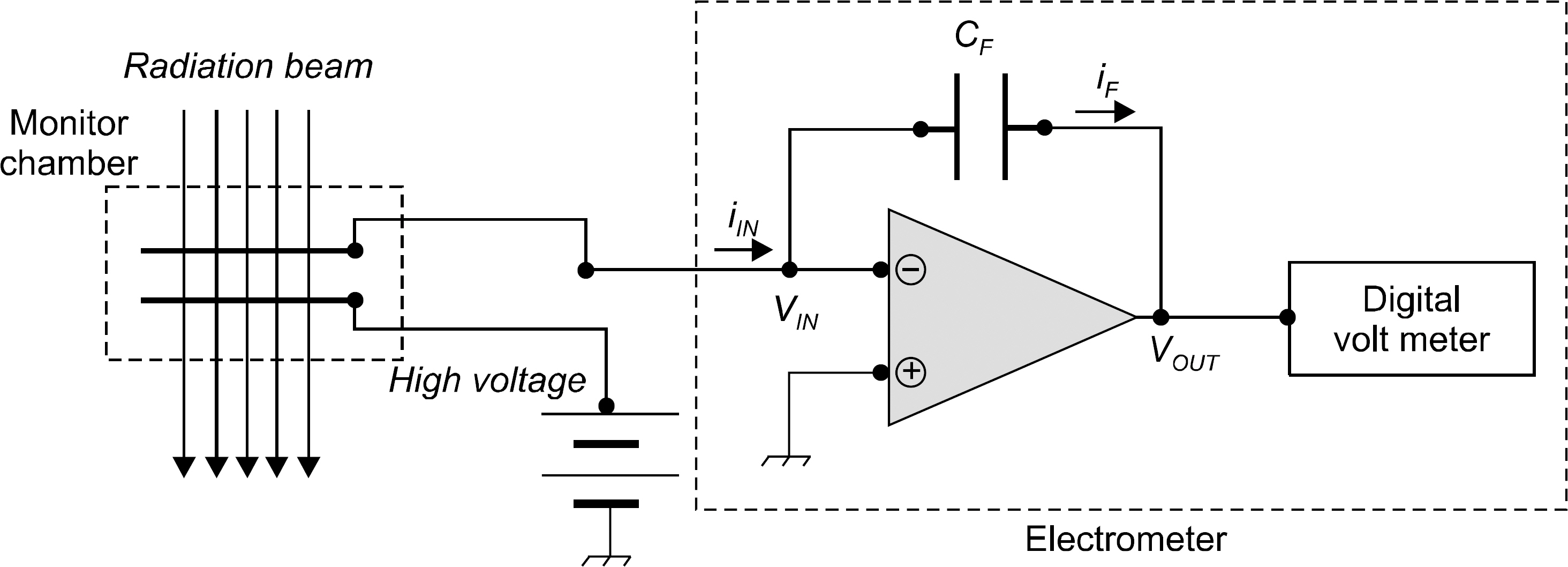
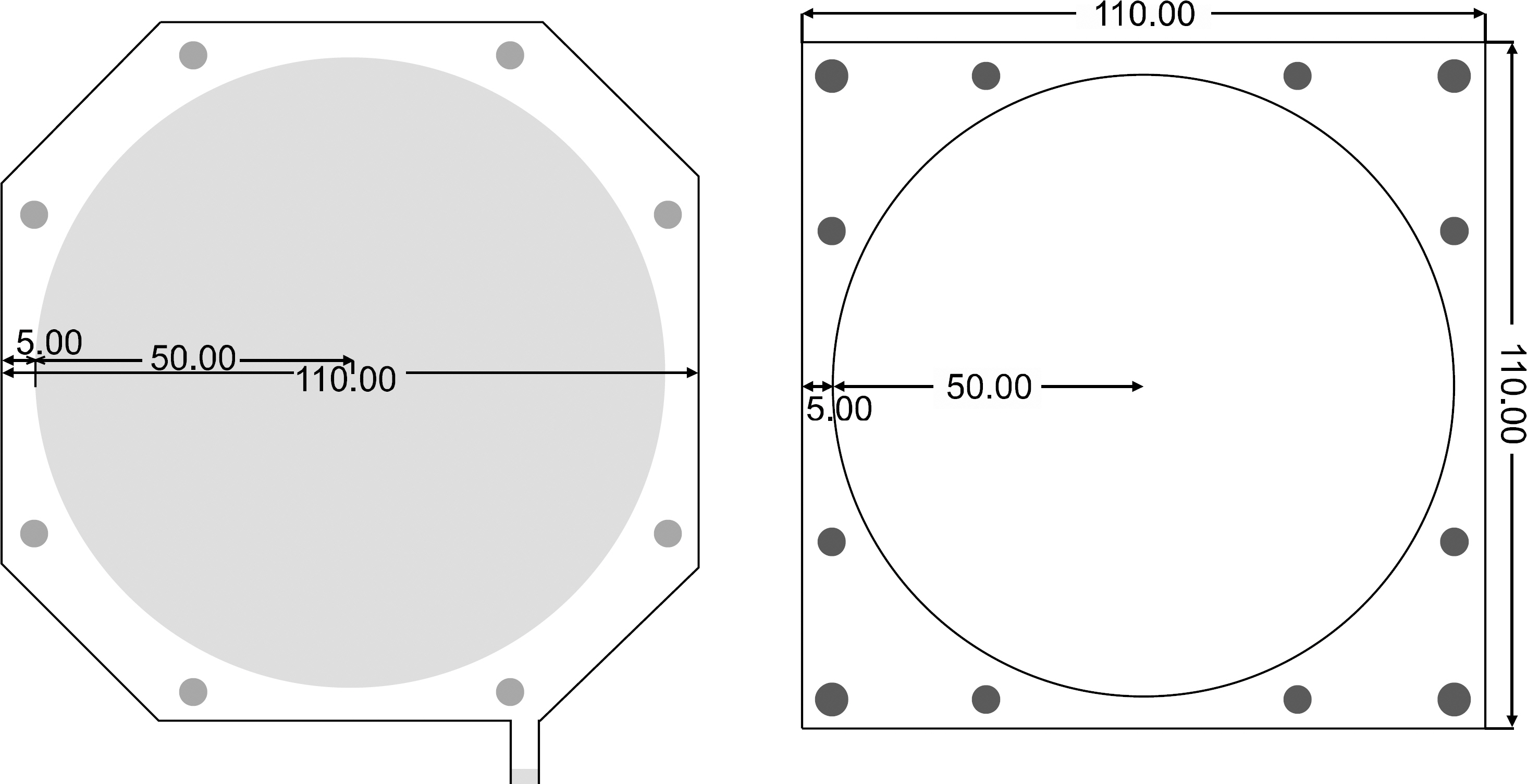
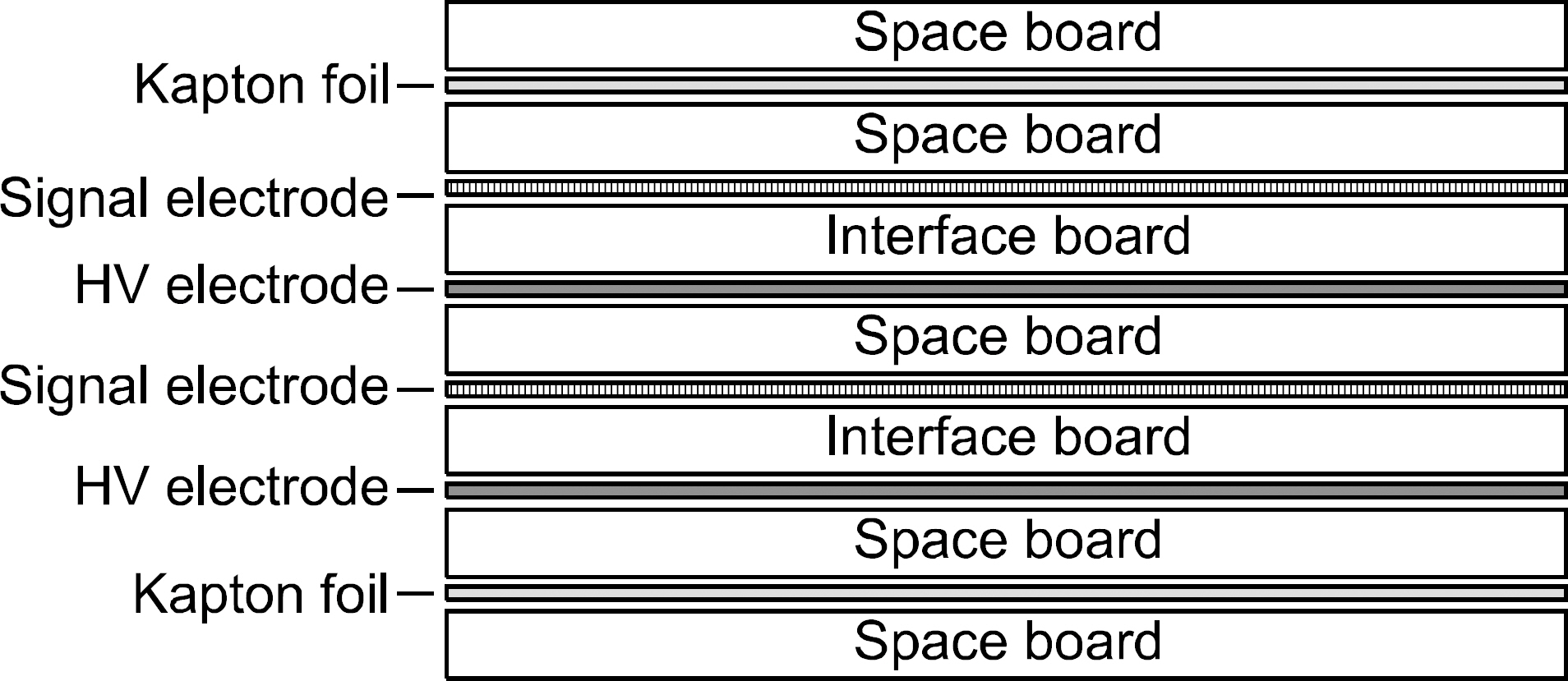
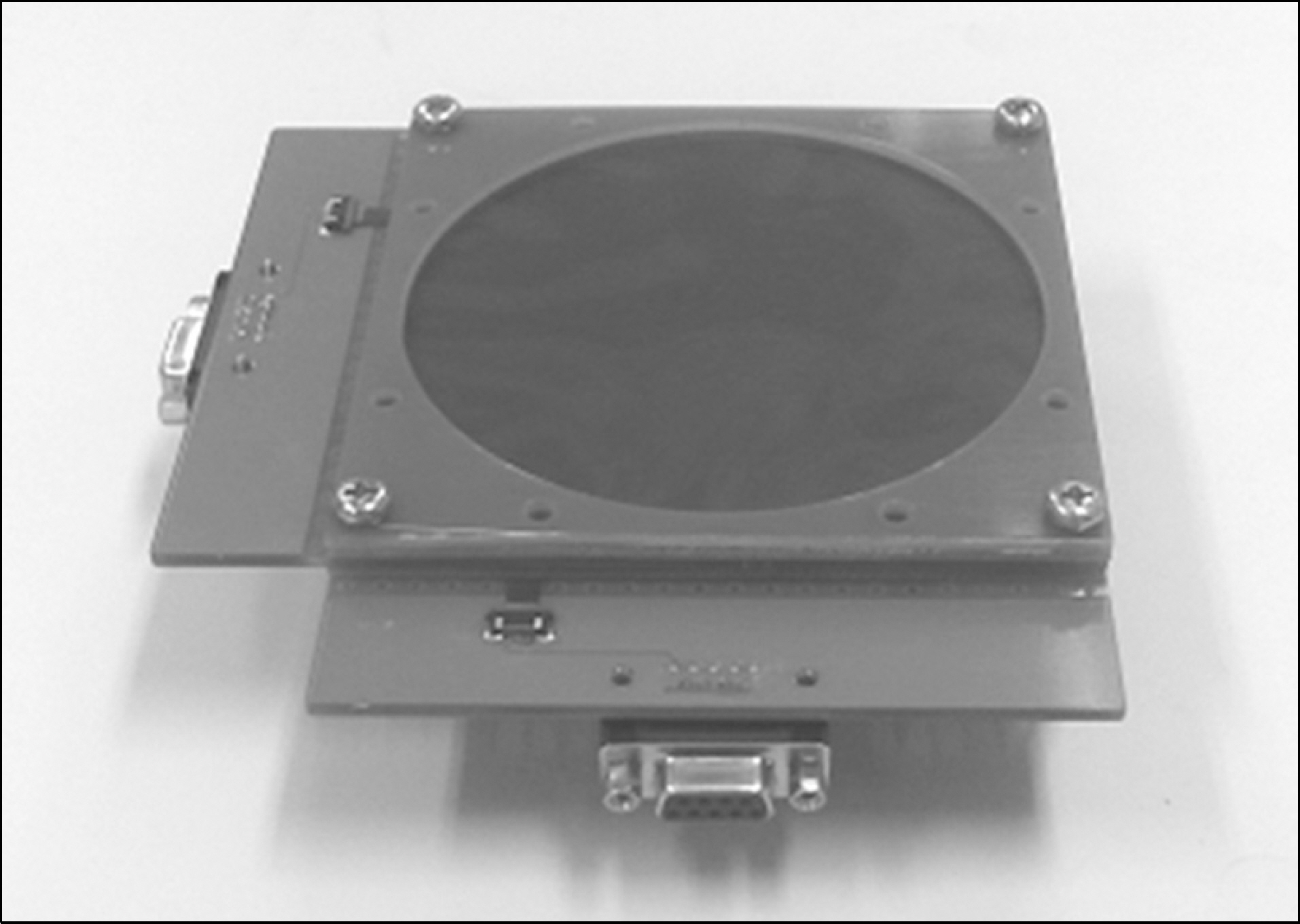
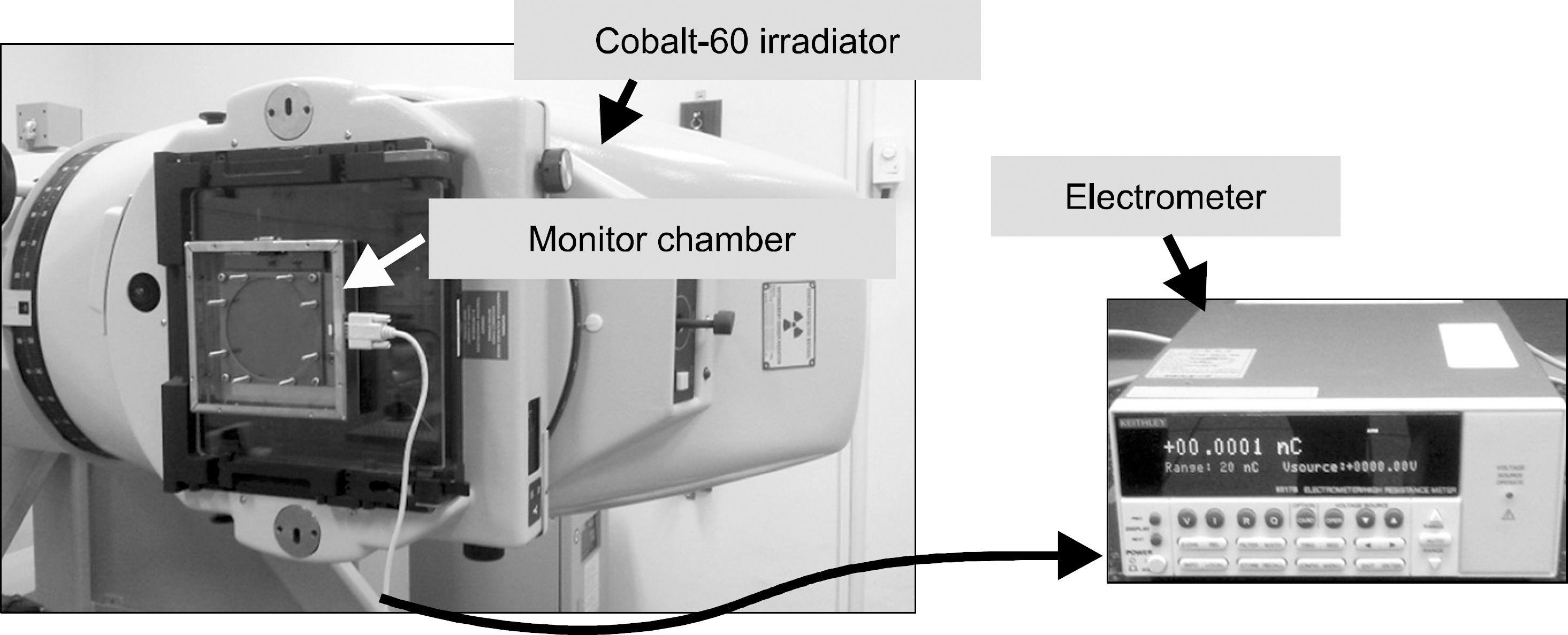
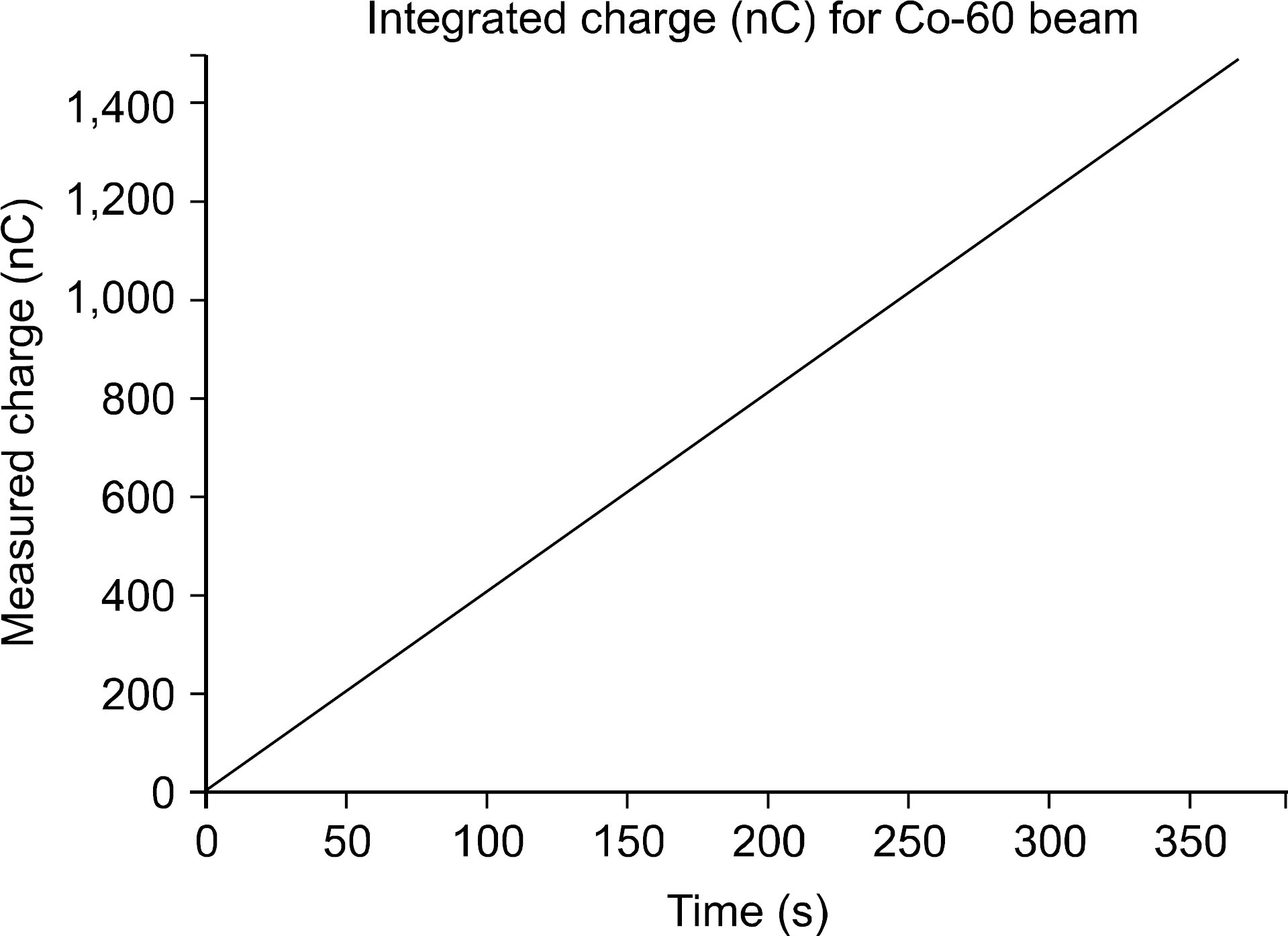
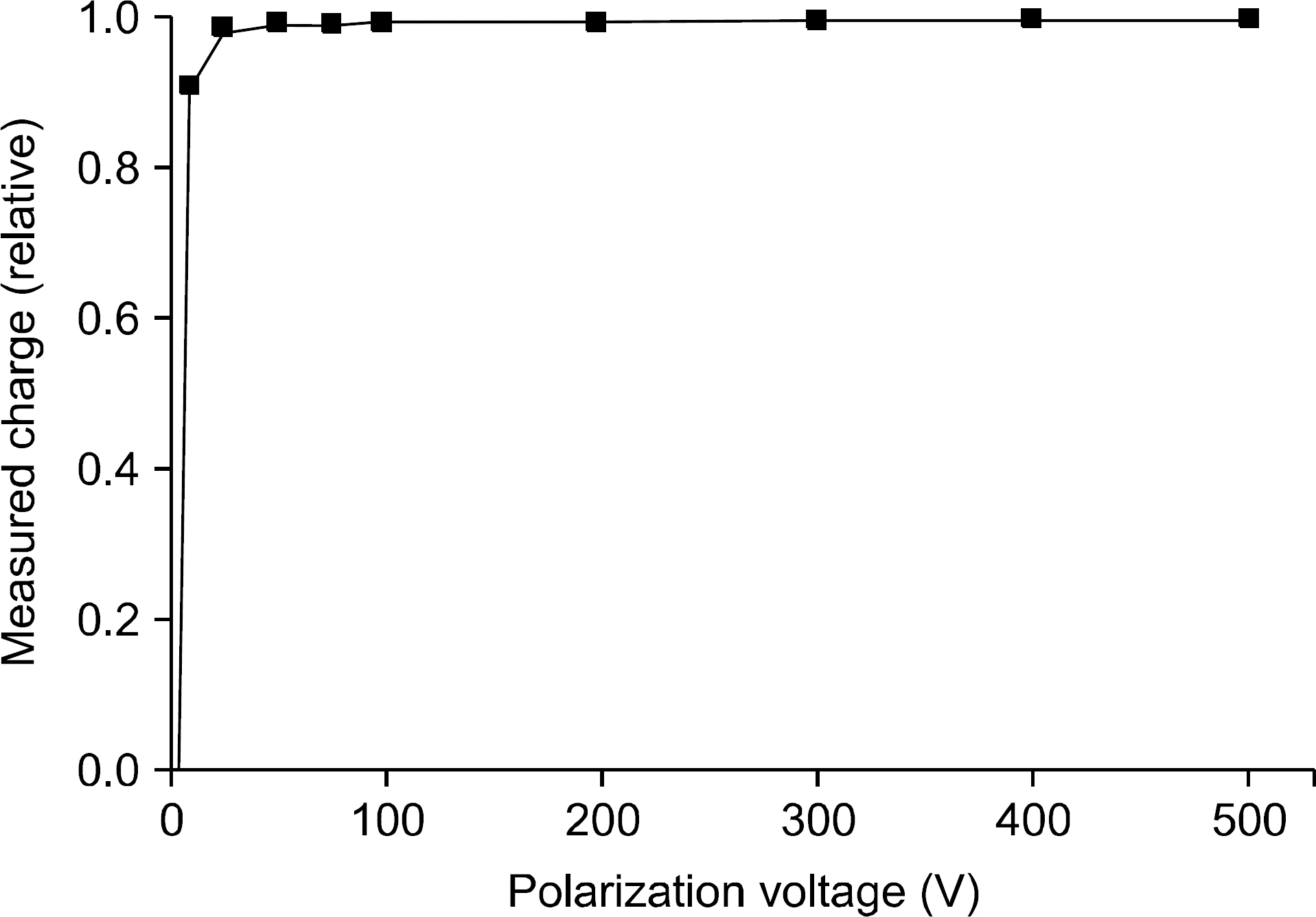
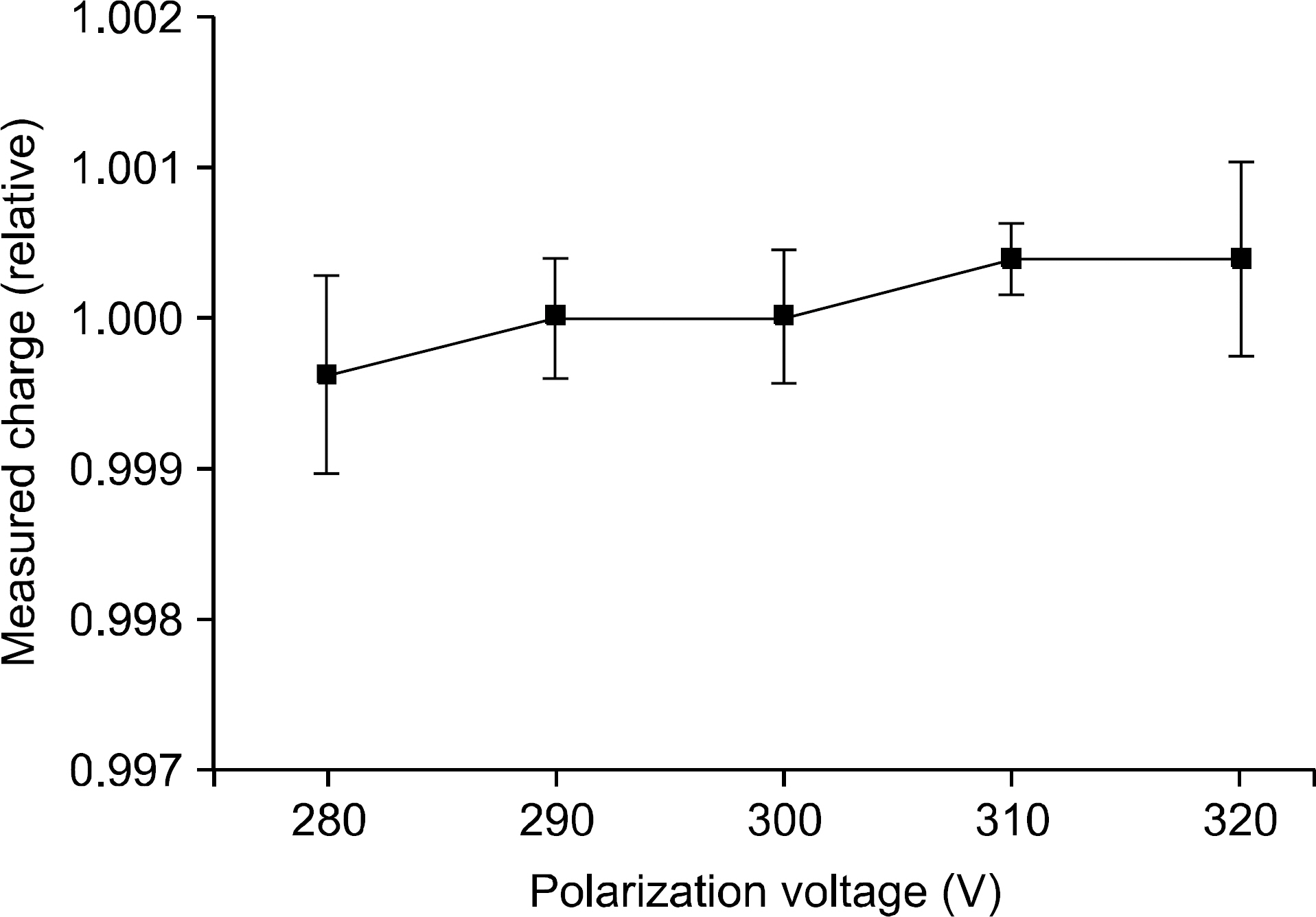
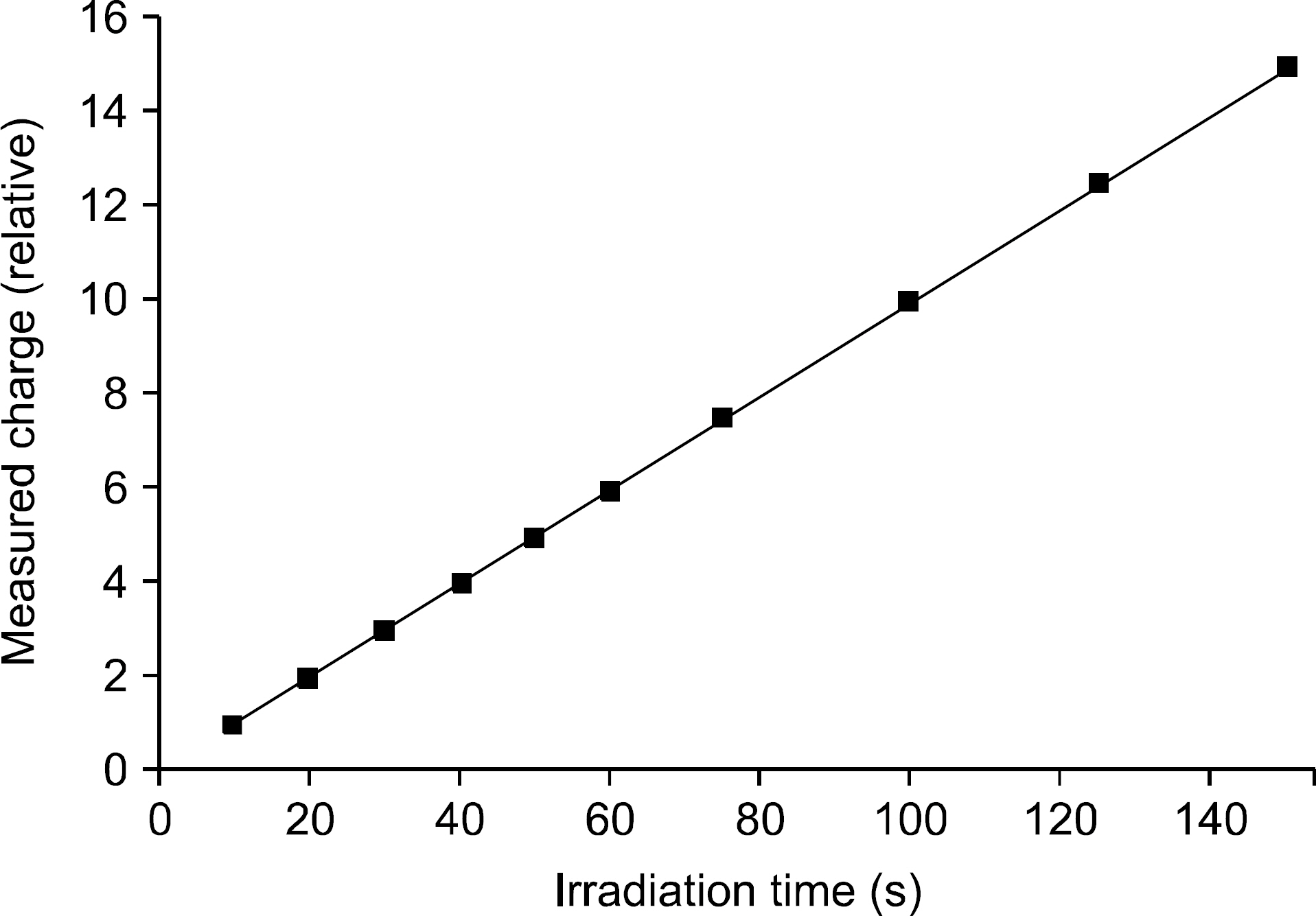
- The monitor chamber is a real time dosimetry device for the measurement and the control of radiation beam intensity of the linac system. The monitor chamber prototype was developed for monitoring and controlling radiation beam from the linac based radiation generator. The thin flexible printed circuit boards were used for electrodes of the two independent plane-parallel ionization chambers to minimize the attenuation of radiation beam. The dosimetric characteristics, saturation and linearity of the measured charge, were experimentally evaluated with the Co-60 gamma rays. The performance of the developed monitor chamber prototype was in an acceptable range and this study shows the possibility of the further development of the chamber with additional functions.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Greene D, Williams PC. Linear Accelerators for Radiation Therapy. 2nd ed.Taylor & Francis Group;New York: 1997. ), pp.p. 94–107.2. Podgorsak EB. Review of Radiation Oncology Physics: A Handbook for Teachers and Students. International Atomic Energy Agency;Vienna, Austria: 2003. ), pp.p. 125–126.3. Khan FM. The Physics of Radiation Therapy. 4th ed.Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;Philadelphia: 2010. ), pp.p. 162–163.4. ICRP Ref-32/147/07. Preventing Accidental Exposures from New External Beam Radiation Therapy Technologies. International Commission on Radiological Protection;Ottawa, Canada: 2009. ), pp.p. 51–51.5. MaShani G. Radiation Dosimetry. 2nd ed.CRC Press;New York: 2000. ): pp.p. 85–220.6. IEC 60977: Medical electrical equipment-Medical electron accelerators-Guidelines for functional performance characteristics. edition 2. .0, International Electrotechnical Commission, Geneva, Switzerland (. 2008.7. IEC 60731: Medical electrical equipment-Dosimeters with ionization chambers as used in radiotherapy. International Electrotechnical Commission, Geneva, Switzerland (. 2011.8. ARPNSA Fact Sheet 24: Specifying the polarity of the polarizing voltage of an ionisation chamber. Australian Radiation Profection and Nuclear Safety Agency (. 2011.9. Keithley 6517B–901–01: Model 6517B Reference Manual. Rev. B, Keithley Instruments, Inc, Ohio (. 2009. ), pp.93–93.10. Macleod P. A Review of Flexible Circuit Technology and its Applications. PRIME Faraday Partnership;Loughborough University, UK: 2002. ): pp.p. 1–5.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Measurement of Electron Beam Output for the Prototype Compact Linac
- Design and Evaluation of a Prototype HL7 Message Server for Data Sharing across and within Medical Institutions
- Preliminary Report about the Efficacy of Prototype Pressure Sensor for the Real-Time Intravesical Pressure Monitoring in the Rabbit
- Design and Evaluation of a Prototype Algorithm for 12 Channel Computer ECG Analysis
- Preclinical evaluation of prototype products