Korean J Urol.
2007 Jun;48(6):620-626. 10.4111/kju.2007.48.6.620.
Dextranomer/Hyaluronic Acid Copolymer (Deflux(R)) Injection for Vesicoureteral Reflux in Children: the Efficacy and Safety
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kwang@plaza. snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1885544
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2007.48.6.620
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: We evaluated the efficacy and safety of Deflux injection for treating vesicoureteral reflux (VUR) in children.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
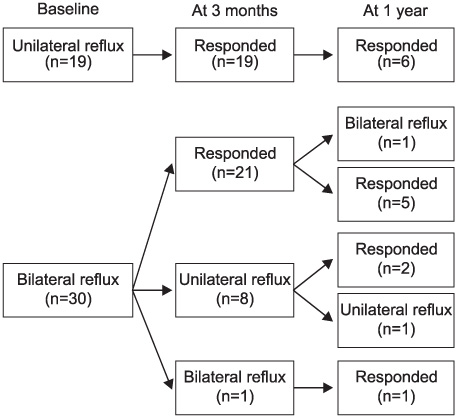
Between January 2004 and May 2006, 49 children (28 boys and 21 girls) with a mean age of 51 months (5-182) underwent Deflux injection. VUR was unilateral in 19 cases (38.8%) and bilateral in 30 (61.2%), affecting 79 ureters. VUR was grades II to V in 26 cases (32.9%), 24 (30.4%), 16 (20.3%), and 4 (5.1%), respectively. Our clinical protocol involved ultrasonography at 6 weeks to evaluate the development of hydronephrosis and the creation of submucosal mound, and VCUG or RIVCU at 3 months to assess the VUR.
RESULTS
The median follow-up was 8.0 months (1-22). The cure rate at 3 months by the ureter was 81.6% (88.9% for grade I, 100% for grade II, 79.2% for grade III, 75.0% for grade IV, and 50.0% for grade V) and the cure rate was 84.8% for the total patients (100% for the unilateral cases and 80% for the bilateral cases). There were 16 patients with 1 year of follow-up and the cure rate was 88.5% by the ureter and 87.5% for the total patient. The severity of VUR (p=0.035) and the concomitant voiding dysfunction (p=0.001) were the significant predictors of a successful outcome. One patient complained of gross hematuria resolved within a few days.
CONCLUSIONS
Deflux injection was safe and efficacious with a low complication rate. The severity of VUR and the concomitant voiding dysfunction had significant adverse effects on the cure rate.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jacobson SH, Hansson S, Jakobsson B. Vesico-ureteric reflux: occurrence and long-term risks. Acta Paediatr. 1999. 88:Suppl. 22–30.2. Elder JS. Guidelines for consideration for surgical repair of vesicoureteral reflux. Curr Opin Urol. 2000. 10:579–585.3. Bailey RR, Maling TM, Swainson CP. Schrier RW, Gottschalk CW, editors. Vesicoureteric reflux and reflux nephropathy. Diseases of the kidney. 1993. 5th ed. Boston: Little, Brown & Co.;689–727.4. Arant BS Jr. Medical management of mild and moderate vesicoureteral reflux: follow-up studies of infants and young children. A preliminary report of the Southwest Pediatric Nephrology Study Group. J Urol. 1992. 148:1683–1687.5. Capozza N, Caione P. Dextranomer/hyaluronic acid copolymer implantation for vesico-ureteral reflux: a randomized comparison with antibiotic prophylaxis. J Pediatr. 2002. 140:230–234.6. International Reflux Study Committee. Medical versus surgical treatment of primary vesicoureteral reflux: a prospective International Reflux Study in children. J Urol. 1981. 125:277–283.7. O'Donnell B, Puri P. Treatment of vesicoureteral reflux by endoscopic injection of Teflon. Br Med J. 1984. 289:7–9.8. Chertin B, Calhoun E, Velayudham M, Puri P. Endoscopic treatment of vesicoureteral reflux: 11 to 17 years of followup. J Urol. 2002. 167:1443–1446.9. Malizia AA Jr, Reiman HM, Myers RP, Sande JR, Barham SS, Benson RC Jr, et al. Migration and granulomatous reaction after periurethral injection of polytef (Teflon). JAMA. 1984. 251:3277–3281.10. Steyaert H, Sattonnet C, Bloch C, Jaubert F, Galle P, Valla JS. Migration of PTFE paste particles to the kidney after treatment for vesicoureteral reflux. BJU Int. 2000. 85:168–169.11. Leonard MP, Canning DA, Peters CA, Gearhart JP, Jeffs RD. Endoscopic injection of glutaraldehyde cross-linked bovine dermal collagen for correction of vesicoureteral reflux. J Urol. 1991. 145:115–119.12. Dodat H, Valmelle AF, Weidmann JD, Collet F, Pelizzo G, Dubois R. Endoscopic treatment of vesicoureteral reflux in children. Five-year assessment of the use of Macroplastique®. Prog Urol. 1998. 8:1001–1006.13. Herz D, Hafez A, Bagli D, Capolicchio G, McLorie G, Khoury A. Efficacy of endoscopic subureteral polydimethylsiloxane injection for treatment of vesicoureteral reflux in children: a North American Clinical Report. J Urol. 2001. 166:1880–1886.14. Stenberg AM, Sundia A, Larsson BS, Lackgren G, Stenberg A. Lack of distant migration after injection of a 125iodine labeled dextranomer based implant into the rabbit bladder. J Urol. 1997. 158:1937–1941.15. Puri P, Chertin B, Velayudham M, Dass L, Colhoun E. Treatment of vesicoureteral reflux by endoscopic injection of dex tranomer/hyaluronic acid copolymer: preliminary results. J Urol. 2003. 170:1541–1544.16. Kirsch AJ, Perez-Brayfield MR, Scherz HC. Minimally invasive treatment of vesicoureteral reflux with endoscopic injection of dextranomer/hyaluronic acid copolymer: the Children's Hospitals of Atlanta experience. J Urol. 2003. 170:211–215.17. Lackgren G, Wahlin N, Skoldenberg E, Stenberg A. Long-term followup of children treated with dextranomer/hyaluronic acid copolymer for vesicoureteral reflux. J Urol. 2001. 166:1887–1892.18. Capozza N, Lais A, Matarazzo E, Nappo S, Patricolo M, Caione P. Influence of voiding dysfunction on the outcome of endoscopic treatment for vesicoureteral reflux. J Urol. 2002. 168:1695–1698.19. Lavelle MT, Conlin MJ, Skoog SJ. Subureteral injection of Deflux for correction of reflux: analysis of factors predicting success. Urology. 2005. 65:564–567.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Endoscopic Subureteral Injection for the Treatment of Vesicoureteral Reflux in Children: Polydimethylsiloxane (Macroplastique(R)) versus Dextranomer/Hyaluronic Acid Copolymer (Deflux(R))
- Endoscopic injection therapy
- Efficacy of Dextranomer/Hyaluronic Acid Copolymer (Deflux(R)) Injection for Vesicoureteral Reflux in Children
- Overall Outcomes and Factors Predicting the Success of Endoscopic Dextranomer/Hyaluronic Acid Copolymer Injection for Vesicoureteral Reflux
- Risk Factors for Treatment Failure after Endoscopic Subureteral Injection of Dextranomer/Hyaluronic Acid Copolymer (Deflux(R)) for Vesicoureteral Reflux