J Clin Neurol.
2007 Jun;3(2):112-115. 10.3988/jcn.2007.3.2.112.
Pure Sensory Deficit at the T4 Sensory Level as an Isolated Manifestation of Lateral Medullary Infarction
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea. ks1007@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 1851024
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2007.3.2.112
Abstract
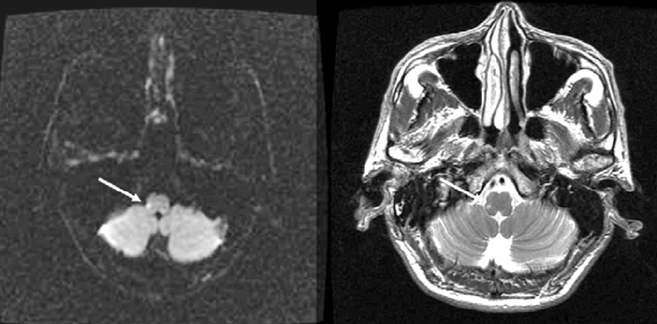
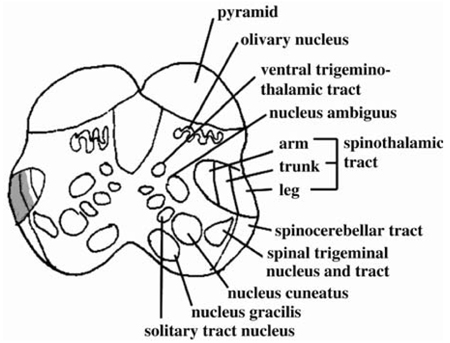
- In rare cases restricted sensory deficits along the somatotopic topography of the spinothalamic tract can develop from a lateral medullary infarction. To our knowledge, isolated dermatomal sensory deficit as a single manifestation of a lateral medullary infarction has not been reported previously. A 58-year-old man presenting with sudden left-sided paresthesia complained of sensory deficit of pain and temperature below the left T4 sensory level without other neurologic deficits. Diffuse- and T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain showed high signal intensities in the right lower medulla oblongata, whereas thoracic-spine MRI and somatosensory evoked potentials produced normal findings.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sacco RL, Freddo L, Bello JA, Odel JG, Onesti ST, Mohr JP. Wallenberg's lateral medullary syndrome: clinicalmagnetic resonance imaging correlations. Arch Neurol. 1993. 50:609–614.2. Kim JS, Lee JH, Lee MC. Patterns of sensory dysfunction in lateral medullary infarction: clinical-MRI correlation. Neurology. 1997. 49:1557–1563.
Article3. Blitshteyn S, Rubino FA. Pure sensory stroke as an isolated manifestation of the lateral medullary infarction. J Neuroimaging. 2005. 15:82–84.
Article4. Park JW, Rha JH, Kim BS. A case of lateral medullary syndrome presenting as sensory-motor stroke. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 1997. 15:200–203.5. Kim JS, Lee JH, Suh DC, Lee MC. Spectrum of lateral medullary syndrome. Correlation between clinical findings and magnetic resonance imaging in 33 subjects. Stroke. 1994. 25:1405–1410.
Article6. Vuadens P, Bogousslavsky J. Face-arm-trunk-leg sensory loss limited to the contralateral side in lateral medullary infarction: a new variant. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1998. 65:255–257.
Article7. Fisher CM. Pure sensory stroke and allied conditions. Stroke. 1982. 13:434–447.
Article8. Kim JS. Restricted acral sensory syndrome following minor stroke. Further observation with special reference to differential severity of symptoms among individual digits. Stroke. 1994. 25:2497–2502.
Article9. Lee SH, Kim DE, Song EC, Roh JK. Sensory dermatomal representation in the medial lemniscus. Arch Neurol. 2001. 58:649–651.
Article10. Phan TG, Wijdicks EFM. A sensory level on the trunk and sparing the face from vertebral artery dissection: how much more subtle can we get? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1999. 66:691–692.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- MRI Findings in Lateral Medullary Syndrome According to the Patterns of Sensory Deficits
- Pure Limb Ataxia as Isolated Manifestation in Lateral Medullary Infarction
- Isolated Axial Lateropulsion in Lateral Medullary Infarction
- Isolated Body Lateropulsion as a Presenting Symptom of Lateral Medullary Infarction
- Restricted Spinothalamic Sensory Loss Below Thoracic Dermatomal Level Caused by Pontine Infarction