Tuberc Respir Dis.
2009 Mar;66(3):241-245. 10.4046/trd.2009.66.3.241.
Delayed Diagnosis of a Traumatic Diaphragmatic Injury
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kimch2002@hallym.or.kr
- 2Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1846388
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2009.66.3.241
Abstract
- Traumatic diaphragmatic rupture is uncommon, but requires a prompt diagnosis and repair. Diaphragmatic injury is most commonly associated with automobile accidents. The diagnosis is difficult and may be delayed because there are no specific symptoms, signs, or radiographic studies that are pathognomic for diaphragmatic injury. The most important factor in the diagnosis is a high suspicion and the use of proper diagnostic studies. We report a case involving the delayed presentation of diaphragmatic rupture in a 54 year old man, requiring surgical repair 12 days following multiple blunt trauma. It should be noted that early recognition for diaphragmatic injury is important in patients with multiple trauma to avoid the potential fatal complications.
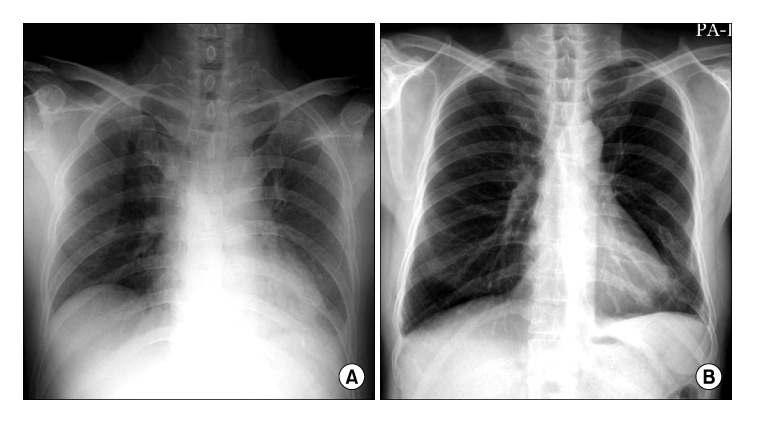
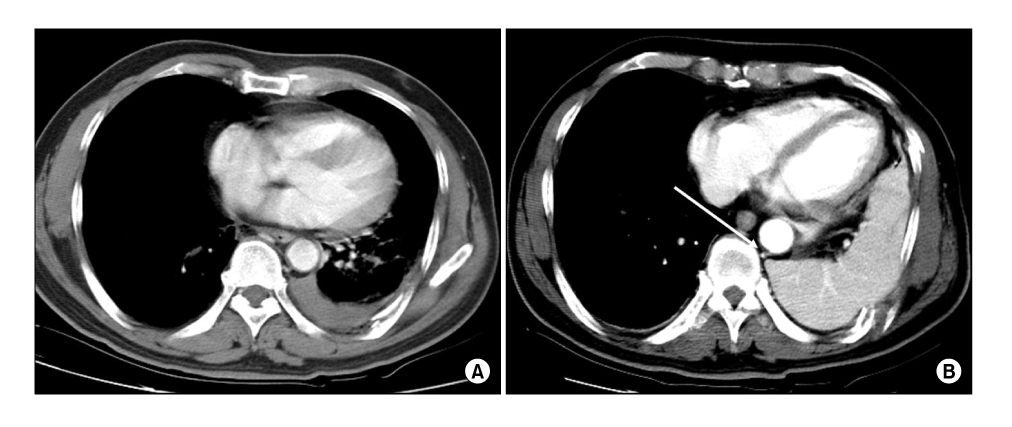
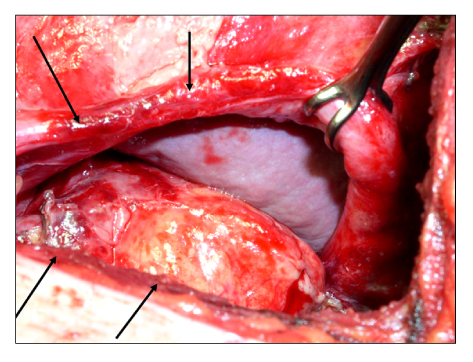
Figure
Reference
-
1. Brandt ML, Luks FI, Spigland NA, DiLorenzo M, Laberge JM, Ouimet A. Diaphragmatic injury in children. J Trauma. 1992. 32:298–301.2. Park SS, Kang JG, Chung JM. Clinical review and evaluation of the blunt traumatic diaphragmatic injury. J Korean Soc Emerg Med. 1997. 8:217–227.3. Flancbaum L, Dauber M, Demas C, Boyarsky AH, Trooskin SZ. Early diagnosis and treatment of blunt diaphragmatic injury. Am Surg. 1988. 54:195–199.4. Rappaport WD, Lee S, Coates S, McIntyre K. Diagnosis of diaphragmatic injury using intraperitoneal technetium. Am Surg. 1989. 55:621–624.5. Shah R, Sabanathan S, Mearns AJ, Choudhury AK. Traumatic rupture of diaphragm. Ann Thorac Surg. 1995. 60:1444–1449.6. Kim YW, Ah SH, Ryu SY, Kim HY, Jeon BM. Clinical evaluation of traumatic diaphragmatic injury. J Korean Soc Traumatol. 2001. 14:108–118.7. Athanassiadi K, Kalavrouziotis G, Athanassiou M, Vernikos P, Skrekas G, Poultsidi A, et al. Blunt diaphragmatic rupture. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 1999. 15:469–474.8. Cerón Navarro J, Peñalver Cuesta JC, Padilla Alarcón J, Jordá Aragón C, Escrivá Peiró J, Calvo Medina V, et al. Traumatic rupture of the diaphragm. Arch Bronconeumol. 2008. 44:197–203.9. Goh BK, Wong AS, Tay KH, Hoe MN. Delayed presentation of a patient with a ruptured diaphragm complicated by gastric incarceration and perforation after apparently minor blunt trauma. CJEM. 2004. 6:277–280.10. Haciibrahimoglu G, Solak O, Olcmen A, Bedirhan MA, Solmazer N, Gurses A. Management of traumatic diaphragmatic rupture. Surg Today. 2004. 34:111–114.11. Crandall M, Popowich D, Shapiro M, West M. Posttraumatic hernias: historical overview and review of the literature. Am Surg. 2007. 73:845–850.12. Kozak O, Mentes O, Harlak A, Yigit T, Kilbas Z, Aslan I, et al. Late presentation of blunt right diaphragmatic rupture (hepatic hernia). Am J Emerg Med. 2008. 26:638e3–e5.13. Reber PU, Schmied B, Seiler CA, Baer HU, Patel AG, Bühler MW. Missed diaphragmatic injuries and their long-term sequelae. J Trauma. 1998. 44:183–188.14. Matsevych OY. Blunt diaphragmatic rupture: four year's experience. Hernia. 2008. 12:73–78.15. Sadeghi N, Nicaise N, DeBacker D, Struyven J, Van Gansbeke D. Right diaphragmatic rupture and hepatic hernia: an indirect sign on computed tomography. Eur Radiol. 1999. 9:972–974.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Delayed presenting traumatic diaphragmatic hernia: four case reports
- Traumatic Diaphragmatic Hernia with Delayed Presentation in an Adult
- Delayed Presentarion of Traumatic Diaphragmatic Rupture
- A Case of Late Presentation of Traumatic Diaphragmatic Hernia in a Child
- Traumatic Diaphragmatic Hernia with a Delayed Presentation: A Report on Two Cases of Omental Herniation that Simulated Pleural Effusion