Tuberc Respir Dis.
2009 Mar;66(3):211-215. 10.4046/trd.2009.66.3.211.
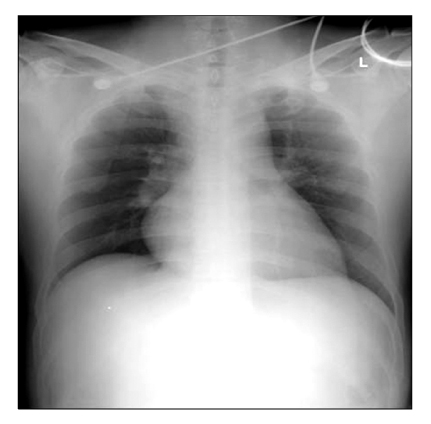
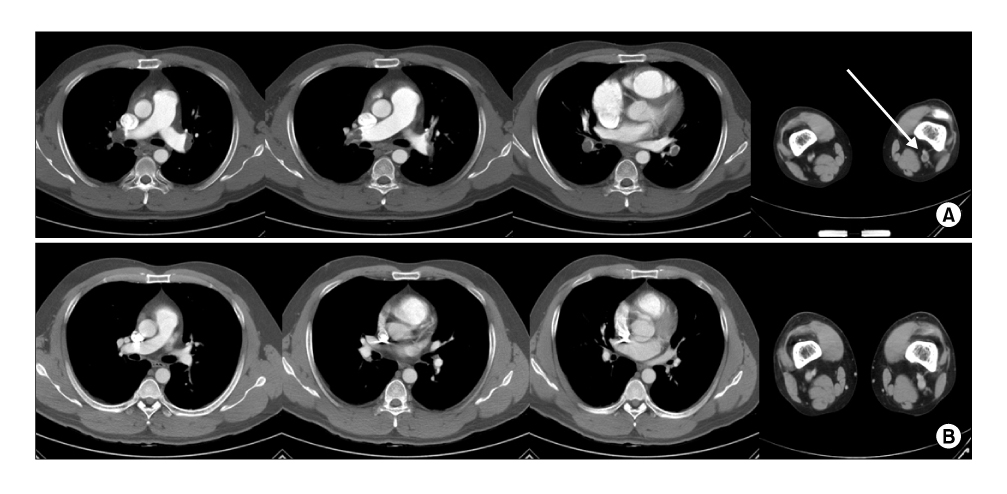
A Case of Massive Pulmonary Thromboembolism in a Young Man Attribute to Computer Gaming
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea. ymshin@chungbuk.ac.kr
- KMID: 1846382
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2009.66.3.211
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Heit JA, Silverstein MD, Mohr DN, Petterson TM, O'Fallon WM, Melton LJ 3rd. Risk factors for deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism: a population-based case-control study. Arch Intern Med. 2000. 160:809–815.2. Francis CW. Clinical practice. Prophylaxis for thromboembolism in hospitalized medical patients. N Engl J Med. 2007. 356:1438–1444.3. Beasley R, Raymond N, Hill S, Nowitz M, Hughes R. eThrombosis: the 21st century variant of venous thromboembolism associated with immobility. Eur Respir J. 2003. 21:374–376.4. Rosendaal FR, Koster T, Vandenbroucke JP, Reitsma PH. High risk of thrombosis in patients homozygous for factor V Leiden (activated protein C resistance). Blood. 1995. 85:1504–1508.5. Bick RL. Coagulation abnormalities in malignancy: a review. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1992. 18:353–372.6. Kucher N, Goldhaber SZ. Management of massive pulmonary embolism. Circulation. 2005. 112:e28–e32.7. Dalen JE. Pulmonary Embolism: what have we learned since Virchow? Natural history, pathophysiology, and diagnosis. Chest. 2002. 122:1440–1456.8. Simpson K. Shelter deaths form pulmonary embolism. Lancet. 1940. I:744.9. Homans J. Thrombosis of the deep leg veins due to prolonged sitting. N Engl J Med. 1954. 250:148–149.10. Cruickshank JM, Gorlin R, Jennett B. Air travel and thrombotic episodes: the economy class syndrome. Lancet. 1988. 2:497–498.11. Alberty-Ryöppy A, Juntunen J, Salmi T. Femoral neuropathy following anticoagulant therapy for "economy class syndrome" in a young woman. Acta Chir Scand. 1985. 151:643–645.12. Lee H. A new case of fatal pulmonary thromboembolism associated with prolonged sitting at computer in Korea. Yonsei Med J. 2004. 45:349–351.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Pulmonary Embolism Associated with Prolonged Seated Immobility during Computer Work
- The Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation in the Massive Pulmonary Thromboemolism: The Use of t-PA in 2 Cases
- Fatal Pulmonary Thromboembolism Associated with Prolonged Sitting at Computer
- A case of rescuing a patient with acute cardiovascular instability from sudden and massive intraoperative pulmonary thromboembolism by extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
- A Case of Percutaneous Catheter Thrombectomy in a Patient With Massive Pulmonary Thromboembolism