Lab Med Online.
2013 Jan;3(1):50-55. 10.3343/lmo.2013.3.1.50.
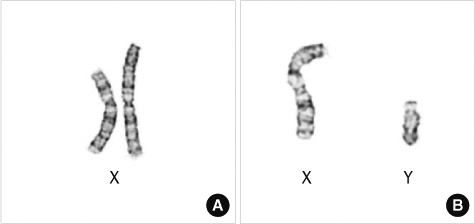
Prenatal Diagnosis of der(X)t(X;Y)(p22.31;q11.22) in a Male Fetus by Using Array Comparative Genomic Hybridization
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Ulsan University of Medical College and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. ejseo@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Asan Institute for Life Sciences, Ulsan University of Medical College and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Ulsan University of Medical College and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Pediatrics, Ulsan University of Medical College and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1845397
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/lmo.2013.3.1.50
Abstract
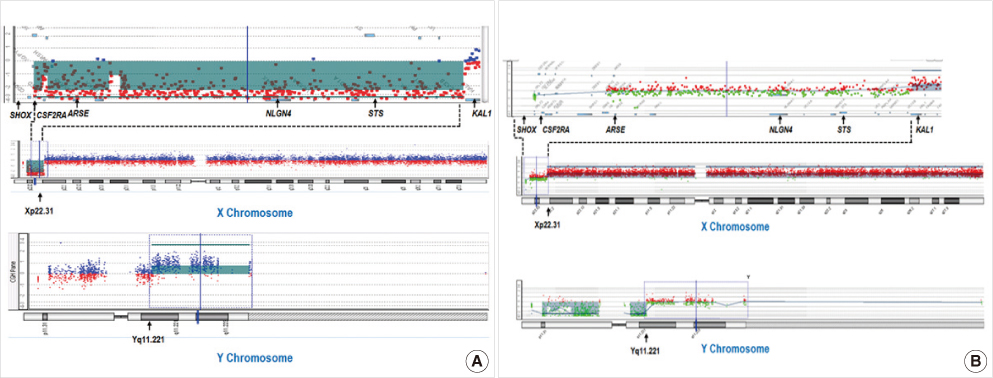
- Xp/Yq translocations are rare chromosomal rearrangements, and the phe-notype of male carriers varies according to the segment of the Xp region that is deleted. In this case report, we describe a der(X)t(X;Y)(p22.31;q11.22) translocation, detected by conventional cytogenetic analysis, in a male fetus at a gestational age of 16 weeks. Chromosomal analysis of parental blood confirmed that this chromosomal aberration had been maternally inherited. Array comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) analysis of fetal blood further indicated a nullisomy of Xp22.31-pter and a breakpoint between the STS and KAL1 genes. The STS, NLGN4, ARSE, CSF2RA, and SHOX genes are present in the region that was deleted, and are known to be related to conditions such as X-linked ichthyosis, chondrodysplasia punctata, mental retardation, and facial dysmorphism in humans. Prenatal ultrasonographic findings and autopsy results were consistent with Xp22.31-pter deletion phenotypes. Genetic counseling was provided for the mother. The observations from this case study indicate that advanced molecular techniques can provide a more precise prenatal diagnosis of chromosomal anomalies than conventional cytogenetics can.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Burnside RD, Mikhail FM, Cosper PC. A prenatally ascertained X;Y translocation characterized using conventional and molecular cytogenetics. Am J Med Genet A. 2008. 146A:1221–1224.
Article2. Ballabio A, Andria G. Deletions and translocations involving the distal short arm of the human X chromosome: review and hypotheses. Hum Mol Genet. 1992. 1:221–227.
Article3. Bardoni B, Floridia G, Guioli S, Peverali G, Anichini C, Cisternino M, et al. Functional disomy of Xp22-pter in three males carrying a portion of Xp translocated to Yq. Hum Genet. 1993. 91:333–338.
Article4. Ballabio A, Bardoni B, Carrozzo R, Andria G, Bick D, Campbell L, et al. Contiguous gene syndromes due to deletions in the distal short arm of the human X chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989. 86:10001–10005.
Article5. Hsu LY. Phenotype/karyotype correlations of Y chromosome aneuploidy with emphasis on structural aberrations in postnatally diagnosed cases. Am J med Genet. 1994. 53:108–140.
Article6. Ha JS, Ryoo NH, Jeon DS, Kim JR, Cho YJ, Kim EJ, et al. A case of X;Y translocation with complex minor anomalies and mental retardation: 46,Y,der(X)t(X;Y)(p22.3;q11.2)mat. Korean J Clin Pathol. 2002. 22:125–129.7. Shaffer LGSM, Campbell LJ, editors. ISCN 2009: An international system for human cytogenetic nomenclature. 2009. Bssel: S.Karger.8. Morel F, Fellmann F, Roux C, Bresson JL. Meiotic segregation analysis by FISH investigation of spermatozoa of a 46,Y,der(X),t(X;Y)(qter-->p22::q11-->qter) carrier. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 2001. 92:63–68.
Article9. Yen PH, Tsai SP, Wenger SL, Steele MW, Mohandas TK, Shapiro LJ. X/Y translocations resulting from recombination between homologous sequences on Xp and Yq. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991. 88:8944–8948.
Article10. Bukvic N, Carri VD, Di Cosola ML, Pustorino G, Cesarano C, Chetta M, et al. Familial X;Y translocation with distinct phenotypic consequences: Characterization using FISH and array CGH. Am J Med Genet A. 2010. 152A:1730–1734.
Article11. Fujita PA, Rhead B, Zweig AS, Hinrichs AS, Karolchik D, Cline MS, et al. The UCSC Genome Browser database: update 2011. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. 39:D876–D882.
Article12. Bonifas JM, Morley BJ, Oakey RE, Kan YW, Epstein EH Jr. Cloning of a cDNA for steroid sulfatase: frequent occurrence of gene deletions in patients with recessive X chromosome-linked ichthyosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987. 84:9248–9251.
Article13. Doherty MJ, Glass IA, Bennett CL, Cotter PD, Watson NF, Mitchell AL, et al. An Xp; Yq translocation causing a novel contiguous gene syndrome in brothers with generalized epilepsy, ichthyosis, and attention deficits. Epilepsia. 2003. 44:1529–1535.
Article14. van Steensel MA, Vreeburg M, Engelen J, Ghesquiere S, Stegmann AP, Herbergs J, et al. Contiguous gene syndrome due to a maternally inherited 8.41 Mb distal deletion of chromosome band Xp22.3 in a boy with short stature, ichthyosis, epilepsy, mental retardation, cerebral cortical heterotopias and Dandy-Walker malformation. Am J Med Genet A. 2008. 146A:2944–2949.
Article15. Petit C, Melki J, Levilliers J, Serville F, Weissenbach J, Maroteaux P. An interstitial deletion in Xp22.3 in a family with X-linked recessive chondrodysplasia punctata and short stature. Hum Genet. 1990. 85:247–250.
Article16. Jamain S, Quach H, Betancur C, Råstam M, Colineaux C, Gillberg IC, et al. Mutations of the X-linked genes encoding neuroligins NLGN3 and NLGN4 are associated with autism. Nat Genet. 2003. 34:27–29.
Article17. Boycott KM, Parslow MI, Ross JL, Miller IP, Bech-Hansen NT, MacLeod PM. A familial contiguous gene deletion syndrome at Xp22.3 characterized by severe learning disabilities and ADHD. Am J Med Genet A. 2003. 122A:139–147.
Article18. Melichar VO, Guth S, Hellebrand H, Meindl A, von der Hardt K, Kraus C, et al. A male infant with a 9.6 Mb terminal Xp deletion including the OA1 locus: Limit of viability of Xp deletions in males. Am J Med Genet A. 2007. 143:135–141.19. Suzuki T, Sakagami T, Rubin BK, Nogee LM, Wood RE, Zimmerman SL, et al. Familial pulmonary alveolar proteinosis caused by mutations in CSF2RA. J Exp Med. 2008. 205:2703–2710.
Article20. Ross JL, Scott C Jr, Marttila P, Kowal K, Nass A, Papenhausen P, et al. Phenotypes Associated with SHOX Deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001. 86:5674–5680.
Article21. Calabrese G, Fischetto R, Stuppia L, Capodiferro F, Mingarelli R, Causio F, et al. X/Y translocation in a family with Leri-Weill dyschondrosteosis. Hum Genet. 1999. 105:367–368.
Article22. Seo EJ. Clinical Applications of Chromosomal Microarray Analysis. J Genet Med. 2010. 7:111–118.
Article23. Hillman SC, Pretlove S, Coomarasamy A, McMullan DJ, Davison EV, Maher ER, et al. Additional information from array comparative genomic hybridization technology over conventional karyotyping in prenatal diagnosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2011. 37:6–14.
Article24. ACOG Committee Opinion No. 446: array comparative genomic hybridization in prenatal diagnosis. Obstet Gynecol. 2009. 114:1161–1163.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Next generation sequencing and array-based comparative genomic hybridization for molecular diagnosis of pediatric endocrine disorders
- Prenatal chromosomal microarray analysis of fetus with increased nuchal translucency
- The Wolf-Hirschhorn Syndrome in Fetal Autopsy: A Case Report
- Current Status and Future Clinical Applications of Array.based Comparative Genomic Hybridization
- Characterization of a prenatally diagnosed de novo der(X)t(X;Y)(q27;q11.23) of fetus