Tuberc Respir Dis.
2012 Sep;73(3):174-177. 10.4046/trd.2012.73.3.174.
Endobronchial Schwannoma Treated by Rigid Bronchoscopy with Argon Plasma Coagulation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Hospital, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. yskwon@chonnam.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Chonnam National University Hospital, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 1842913
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2012.73.3.174
Abstract
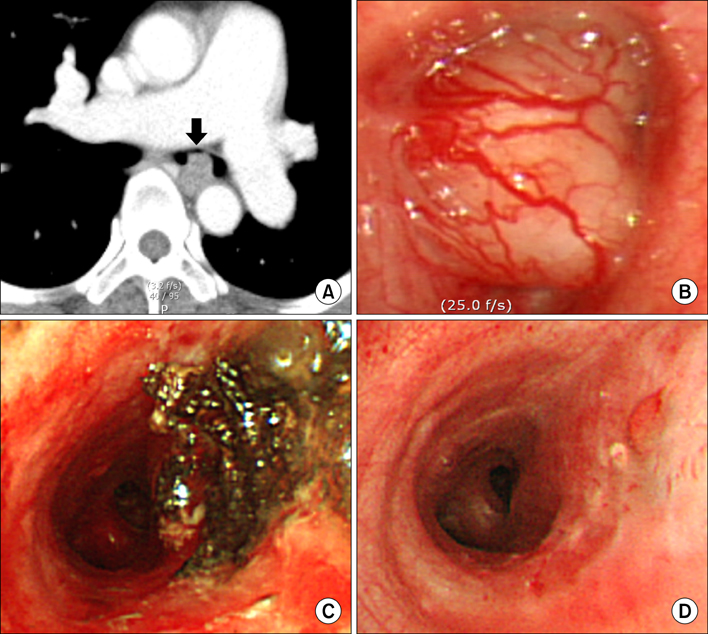
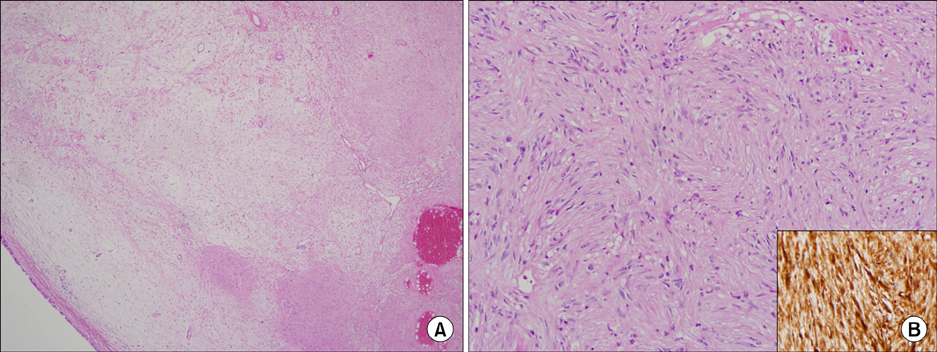
- Primary endobronchial schwannomas are extremely rare tumors that originate from Schwann cells. We report a case of primary endobronchial schwannoma. A 44-year-old woman, without respiratory symptoms, was presented with a nodule in the left main bronchus on her chest computed tomography scan. The nodule was removed by a rigid bronchoscopy with argon plasma coagulation. Biopsy confirmed the diagnosis of schwannoma. There was no recurrence during her 4-month follow-up.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Shah H, Garbe L, Nussbaum E, Dumon JF, Chiodera PL, Cavaliere S. Benign tumors of the tracheobronchial tree. Endoscopic characteristics and role of laser resection. Chest. 1995. 107:1744–1751.2. Kasahara K, Fukuoka K, Konishi M, Hamada K, Maeda K, Mikasa K, et al. Two cases of endobronchial neurilemmoma and review of the literature in Japan. Intern Med. 2003. 42:1215–1218.3. Kwon YS, Kim H, Koh WJ, Suh GY, Chung MP, Kwon OJ, et al. Clinical characteristics and efficacy of bronchoscopic intervention for tracheobronchial leiomyoma. Respirology. 2008. 13:908–912.4. Suzuki H, Sekine Y, Motohashi S, Chiyo M, Suzuki M, Haga Y, et al. Endobronchial neurogenic tumors treated by transbronchial electrical snaring and Nd-YAG laser abrasion: report of three cases. Surg Today. 2005. 35:243–246.5. Straus GD, Guckien JL. Schwannoma of the tracheobronchial tree. A case report. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1951. 60:242–246.6. Kurtkaya-Yapicier O, Scheithauer B, Woodruff JM. The pathobiologic spectrum of Schwannomas. Histol Histopathol. 2003. 18:925–934.7. Ko JM, Jung JI, Park SH, Lee KY, Chung MH, Ahn MI, et al. Benign tumors of the tracheobronchial tree: CT-pathologic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006. 186:1304–1313.8. Takeda S, Miyoshi S, Minami M, Matsuda H. Intrathoracic neurogenic tumors: 50 years' experience in a Japanese institution. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2004. 26:807–812.9. Bolliger CT, Sutedja TG, Strausz J, Freitag L. Therapeutic bronchoscopy with immediate effect: laser, electrocautery, argon plasma coagulation and stents. Eur Respir J. 2006. 27:1258–1271.10. Ernst A, Simoff M, Ost D, Goldman Y, Herth FJ. Prospective risk-adjusted morbidity and mortality outcome analysis after therapeutic bronchoscopic procedures: results of a multi-institutional outcomes database. Chest. 2008. 134:514–519.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Usefulness of Rigid Bronchoscopic Intervention Using Argon Plasma Coagulation for Central Airway Tumors
- Two Cases of Central Airway Obstruction Treated with an Insulation-Tipped Diathermic Knife-2
- A case of gastric antral vascular ectasia treated with argon plasma coagulation
- A Case of Argon Plasma Coagulation Therapy for Hemorrhagic Radiation-induced Gastritis
- A Case of Huge Gastric Angiodysplasia Treated with Argon Plasma Coagulation