J Korean Surg Soc.
2012 Aug;83(2):115-118. 10.4174/jkss.2012.83.2.115.
Successful aspiration and thrombolytic therapy for acute superior mesenteric artery occlusion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endo-Vascular Surgery, Department of Surgery, Wonkwang University College of Medicine, Iksan, Korea. sbjun@wku.ac.kr
- KMID: 1820098
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2012.83.2.115
Abstract
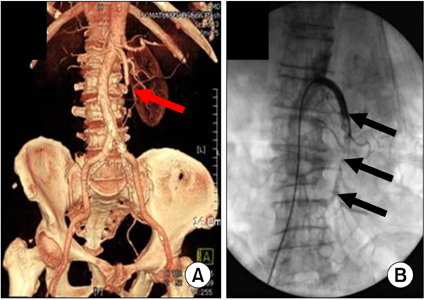
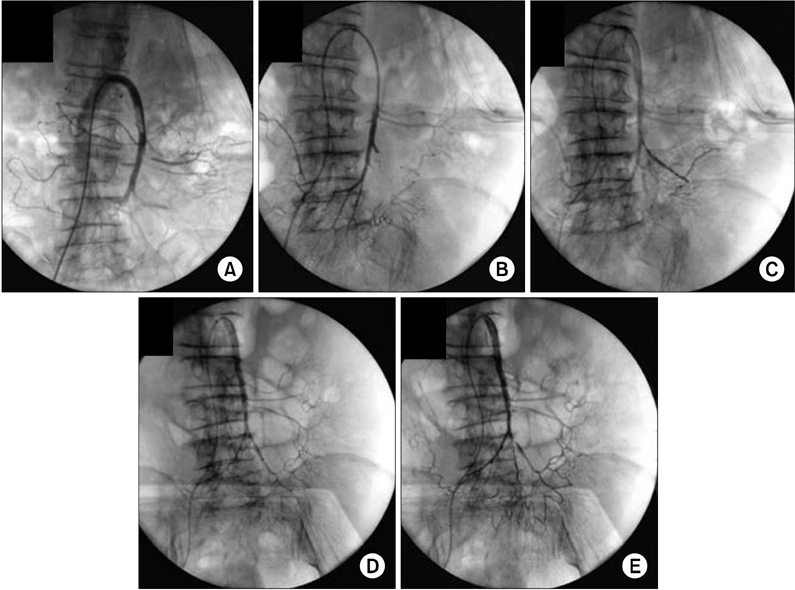
- To report a case of acute superior mesenteric artery (SMA) embolism successfully treated with aspiration and pharmacological thrombolysis. A 74-year-old female was admitted to the hospital with acute abdominal pain 5 hours in duration. Computed tomography angiography revealed a complete embolic occlusion distal to the first jejunal branch of the SMA. Aspiration and local continuous thrombolysis with urokinase resulted in near complete revascularization of the mesenteric flow after 4 hours and almost complete restoration after 20 hours. The patient made a complete recovery and continues to do well on warfarin therapy after treatment. Aspiration and thrombolytic therapy can be an alternative treatment modality in surgical high risk patient.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Acosta-Merida MA, Marchena-Gomez J, Hemmersbach-Miller M, Roque-Castellano C, Hernandez-Romero JM. Identification of risk factors for perioperative mortality in acute mesenteric ischemia. World J Surg. 2006. 30:1579–1585.2. Jamieson AC, Thomas RJ, Cade JF. Lysis of a superior mesenteric artery embolus following local infusion of streptokinase and heparin. Aust N Z J Surg. 1979. 49:355–356.3. Katsuki M, Yoshio S, Kentaro T, Takanobu K. Intraarterial infusion of urokinase for acute superior mesenteric artery occlusion: a report of two cases. Jpn J Gastroenterol Surg. 2001. 34:495–499.4. Miyazawa T, Ueki K, Wakakuwa R. A case of acute superior mesenteric artery occlusion treated by intraarterial infusion of urokinase and prostaglandin E1. J Jpn Surg Assoc. 2004. 65:3293–3296.5. Acosta S, Sonesson B, Resch T. Endovascular therapeutic approaches for acute superior mesenteric artery occlusion. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2009. 32:896–905.6. Badiola CM, Scoppetta DJ. Rapid revascularization of an embolic superior mesenteric artery occlusion using pulse-spray pharmacomechanical thrombolysis with urokinase. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1997. 169:55–57.7. Oh SK, Whang CW. A case report of superior mesenteric artery embolism. J Korean Surg Soc. 1986. 31:60–63.8. Barakate MS, Cappe I, Curtin A, Engel KD, Li-Kim-Moy J, Poon MS, et al. Management of acute superior mesenteric artery occlusion. ANZ J Surg. 2002. 72:25–29.9. McNamara TO, Fischer JR. Thrombolysis of peripheral arterial and graft occlusions: improved results using high-dose urokinase. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1985. 144:769–775.10. Katsuhiko M, Kouzou I, Minako S, Hirohumi T, Sadahiro N, Tadayoshi K, et al. Acute superior mesenteric arterial occlusion. Occlusion sites and its clinical course. J Abd Emerg Med. 1996. 16:427–432.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Portal and Superior Mesenteric Venous Thrombosis Treated with Urokinase Infusion via Superior Mesenteric Artery
- One Case Report with the Occlusion of the Superior Mesenteric Artery and Left Renal Artery Complicated in the Mitral Stenosis
- A Case of Superior Mesenteric Artery Thrombosis Treated with Intra-arterial Urokinase Infusion and Intraluminal Stent Insertion
- Superior Mesenteric Artery Occlusion in Acute Cardioembolic Stroke
- Successful Cross-circulation Stent-Retriever Embolectomy Through Posterior Communicating Artery for Acute MCA Occlusion by Using Trevo XP ProVue