J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2013 Aug;54(2):118-124. 10.3340/jkns.2013.54.2.118.
Factors Related to Outcomes of Subthalamic Deep Brain Stimulation in Parkinson's Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Brain Korea 21 Project for Medical Science, Brain Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jchang@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Neurology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurosurgery, Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 4Department of Neurosurgery, Pusan University Hospital, Pusan University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 1814248
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2013.54.2.118
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Subthalamic nucleus (STN) deep brain stimulation (DBS) is an effective treatment of choice for patients with advanced idiopathic Parkinson's disease (PD) who have motor complication with medication. The objectives of this study are to analyze long-term follow-up data of STN DBS cases and to identify the factors related to outcomes.
METHODS
Fifty-two PD patients who underwent STN DBS were followed-up for more than 3 years. The Unified Parkinsons Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) and other clinical profiles were assessed preoperatively and during follow-up. A linear regression model was used to analyze whether factors predict the results of STN DBS. We divided the study individuals into subgroups according to several factors and compared subgroups.
RESULTS
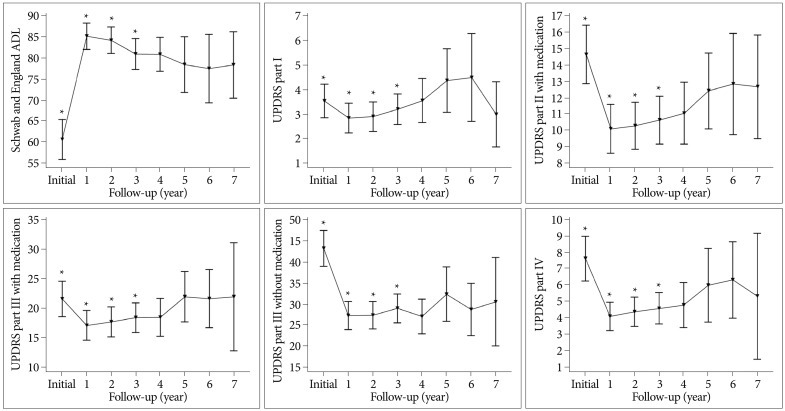
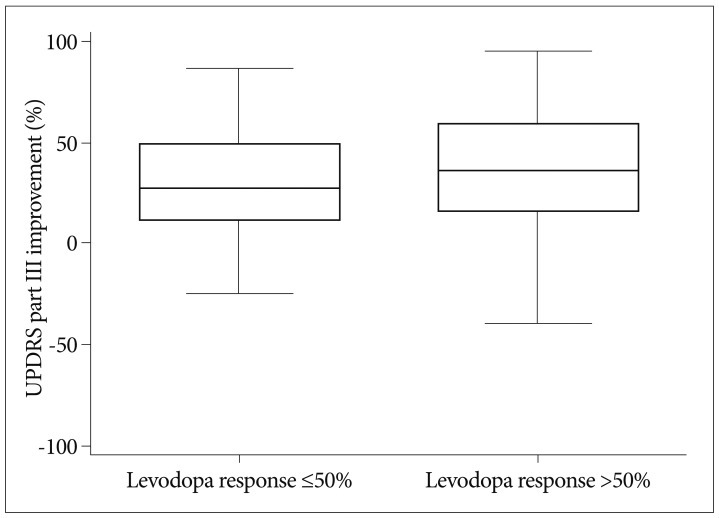
Preoperative activity of daily living (ADL) and the magnitude of preoperative levodopa response were shown to predict the improvement in UPDRS part II without medication, and preoperative ADL and levodopa equivalent dose (LED) were shown to predict the improvement in UPDRS part II with medication. In UPDRS part III with medication, the magnitude of preoperative levodopa response was a predicting factor.
CONCLUSION
The intensity of preoperative levodopa response was a strong factor for motor outcome. And preoperative ADL and LED were strong factors for ADL improvement. More vigorous studies should be conducted to elucidate how levodopa-induced motor complications are ameliorated after STN DBS.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Accolla E, Caputo E, Cogiamanian F, Tamma F, Mrakic-Sposta S, Marceglia S, et al. Gender differences in patients with Parkinson's disease treated with subthalamic deep brain stimulation. Mov Disord. 2007; 22:1150–1156. PMID: 17469208.
Article2. Bejjani BP, Gervais D, Arnulf I, Papadopoulos S, Demeret S, Bonnet AM, et al. Axial parkinsonian symptoms can be improved : the role of levodopa and bilateral subthalamic stimulation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2000; 68:595–600. PMID: 10766889.
Article3. Benabid AL, Chabardes S, Mitrofanis J, Pollak P. Deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Lancet Neurol. 2009; 8:67–81. PMID: 19081516.
Article4. Cenci MA, Lindgren HS. Advances in understanding L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2007; 17:665–671. PMID: 18308560.
Article5. Chang WS, Kim HY, Kim JP, Park YS, Chung SS, Chang JW. Bilateral subthalamic deep brain stimulation using single track microelectrode recording. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2011; 153:1087–1095. PMID: 21311918.
Article6. Derost PP, Ouchchane L, Morand D, Ulla M, Llorca PM, Barget M, et al. Is DBS-STN appropriate to treat severe Parkinson disease in an elderly population? Neurology. 2007; 68:1345–1355. PMID: 17452578.
Article7. Deuschl G, Schade-Brittinger C, Krack P, Volkmann J, Schäfer H, Bötzel K, et al. A randomized trial of deep-brain stimulation for Parkinson's disease. N Engl J Med. 2006; 355:896–908. PMID: 16943402.
Article8. Erola T, Heikkinen ER, Haapaniemi T, Tuominen J, Juolasmaa A, Myllylä VV. Efficacy of bilateral subthalamic nucleus (STN) stimulation in Parkinson's disease. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2006; 148:389–394. PMID: 16284705.
Article9. Erola T, Karinen P, Heikkinen E, Tuominen J, Haapaniemi T, Koivukangas J, et al. Bilateral subthalamic nucleus stimulation improves health-related quality of life in Parkinsonian patients. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2005; 11:89–94. PMID: 15734666.
Article10. Follett KA. Comparison of pallidal and subthalamic deep brain stimulation for the treatment of levodopa-induced dyskinesias. Neurosurg Focus. 2004; 17:E3. PMID: 15264772.
Article11. Gervais-Bernard H, Xie-Brustolin J, Mertens P, Polo G, Klinger H, Adamec D, et al. Bilateral subthalamic nucleus stimulation in advanced Parkinson's disease : five year follow-up. J Neurol. 2009; 256:225–233. PMID: 19242649.
Article12. Guehl D, Cuny E, Benazzouz A, Rougier A, Tison F, Machado S, et al. Side-effects of subthalamic stimulation in Parkinson's disease : clinical evolution and predictive factors. Eur J Neurol. 2006; 13:963–971. PMID: 16930362.
Article13. Hariz GM, Lindberg M, Hariz MI, Bergenheim AT. Gender differences in disability and health-related quality of life in patients with Parkinson's disease treated with stereotactic surgery. Acta Neurol Scand. 2003; 108:28–37. PMID: 12807390.
Article14. Jankovic J. Motor fluctuations and dyskinesias in Parkinson's disease : clinical manifestations. Mov Disord. 2005; 20(Suppl 11):S11–S16. PMID: 15822109.15. Kaiser I, Kryspin-Exner I, Brücke T, Volc D, Alesch F. Long-term effects of STN DBS on mood : psychosocial profiles remain stable in a 3-year follow-up. BMC Neurol. 2008; 8:43. PMID: 19014430.16. Kleiner-Fisman G, Fisman DN, Sime E, Saint-Cyr JA, Lozano AM, Lang AE. Long-term follow up of bilateral deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in patients with advanced Parkinson disease. J Neurosurg. 2003; 99:489–495. PMID: 12959435.
Article17. Kleiner-Fisman G, Herzog J, Fisman DN, Tamma F, Lyons KE, Pahwa R, et al. Subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation : summary and meta-analysis of outcomes. Mov Disord. 2006; 21(Suppl 14):S290–S304. PMID: 16892449.18. Krack P, Batir A, Van Blercom N, Chabardes S, Fraix V, Ardouin C, et al. Five-year follow-up of bilateral stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in advanced Parkinson's disease. N Engl J Med. 2003; 349:1925–1934. PMID: 14614167.
Article19. Marceglia S, Mrakic-Sposta S, Foffani G, Cogiamanian F, Caputo E, Egidi M, et al. Gender-related differences in the human subthalamic area : a local field potential study. Eur J Neurosci. 2006; 24:3213–3222. PMID: 17156382.
Article20. Ory-Magne F, Brefel-Courbon C, Simonetta-Moreau M, Fabre N, Lotterie JA, Chaynes P, et al. Does ageing influence deep brain stimulation outcomes in Parkinson's disease? Mov Disord. 2007; 22:1457–1463. PMID: 17516457.
Article21. Paek SH, Lee JY, Kim HJ, Kang D, Lim YH, Kim MR, et al. Electrode position and the clinical outcome after bilateral subthalamic nucleus stimulation. J Korean Med Sci. 2011; 26:1344–1355. PMID: 22022189.
Article22. Paek SH, Yun JY, Song SW, Kim IK, Hwang JH, Kim JW, et al. The clinical impact of precise electrode positioning in STN DBS on three-year outcomes. J Neurol Sci. 2013; 327:25–31. PMID: 23465484.
Article23. Rodriguez-Oroz MC, Obeso JA, Lang AE, Houeto JL, Pollak P, Rehncrona S, et al. Bilateral deep brain stimulation in Parkinson's disease : a multicentre study with 4 years follow-up. Brain. 2005; 128(Pt 10):2240–2249. PMID: 15975946.
Article24. Romito LM, Contarino FM, Albanese A. Transient gender-related effects in Parkinson's disease patients with subthalamic stimulation. J Neurol. 2010; 257:603–608. PMID: 19921302.
Article25. Romito LM, Scerrati M, Contarino MF, Iacoangeli M, Bentivoglio AR, Albanese A. Bilateral high frequency subthalamic stimulation in Parkinson's disease : long-term neurological follow-up. J Neurosurg Sci. 2003; 47:119–128. PMID: 14618124.26. Schrag A, Quinn N. Dyskinesias and motor fluctuations in Parkinson's disease. A community-based study. Brain. 2000; 123(Pt 11):2297–2305. PMID: 11050029.27. Schüpbach WM, Chastan N, Welter ML, Houeto JL, Mesnage V, Bonnet AM, et al. Stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in Parkinson's disease : a 5 year follow up. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2005; 76:1640–1644. PMID: 16291886.28. Shapiro MB, Vaillancourt DE, Sturman MM, Metman LV, Bakay RA, Corcos DM. Effects of STN DBS on rigidity in Parkinson's disease. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2007; 15:173–181. PMID: 17601186.
Article29. Simonin C, Tir M, Devos D, Kreisler A, Dujardin K, Salleron J, et al. Reduced levodopa-induced complications after 5 years of subthalamic stimulation in Parkinson's disease : a second honeymoon. J Neurol. 2009; 256:1736–1741. PMID: 19536584.
Article30. Simuni T, Jaggi JL, Mulholland H, Hurtig HI, Colcher A, Siderowf AD, et al. Bilateral stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in patients with Parkinson disease : a study of efficacy and safety. J Neurosurg. 2002; 96:666–672. PMID: 11990805.
Article31. Tagliati M, Miravite J, Koss A, Shils J, Alterman RL. Is advanced age a poor predictor of motor outcome for subthalamic DBS in parkinson's disease? Neurology. 2004; 62(Suppl 5):A395–A396.32. Tsai ST, Lin SH, Chou YC, Pan YH, Hung HY, Li CW, et al. Prognostic factors of subthalamic stimulation in Parkinson's disease : a comparative study between short- and long-term effects. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 2009; 87:241–248. PMID: 19556833.
Article33. Tsai ST, Lin SH, Lin SZ, Chen JY, Lee CW, Chen SY. Neuropsychological effects after chronic subthalamic stimulation and the topography of the nucleus in Parkinson's disease. Neurosurgery. 2007; 61:E1024–E1029. discussion E1029-E1030. PMID: 18091257.
Article34. Weaver FM, Follett K, Stern M, Hur K, Harris C, Marks WJ Jr, et al. Bilateral deep brain stimulation vs best medical therapy for patients with advanced Parkinson disease : a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2009; 301:63–73. PMID: 19126811.
Article35. Welter ML, Houeto JL, Tezenas du Montcel S, Mesnage V, Bonnet AM, Pillon B, et al. Clinical predictive factors of subthalamic stimulation in Parkinson's disease. Brain. 2002; 125(Pt 3):575–583. PMID: 11872614.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Microelectrode Recording-Guided Deep Brain Stimulation in Patients with Movement Disorders
- Deep Brain Stimulation of the Subthalamic and Pedunculopontine Nucleus in a Patient with Parkinson's Disease
- Deep Brain Stimulation of the Subthalamic Area for Dystonic Tremor
- Subthalamic Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson's Disease
- Benefits of Levodopa-Carbidopa Intestinal Gel Infusion in Patients with Parkinson's Disease Experiencing Gait Dysfunction Following Subthalamic Deep Brain Stimulation