J Gynecol Oncol.
2012 Oct;23(4):226-234. 10.3802/jgo.2012.23.4.226.
Comparison of outcomes between radical hysterectomy followed by tailored adjuvant therapy versus primary chemoradiation therapy in IB2 and IIA2 cervical cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jhnam@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Radiation Oncology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Radiation Oncology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1810119
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3802/jgo.2012.23.4.226
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To compare survival outcomes and treatment-related morbidities between radical hysterectomy (RH) and primary chemoradiation therapy (CRT) in patients with bulky early-stage cervical cancer.
METHODS
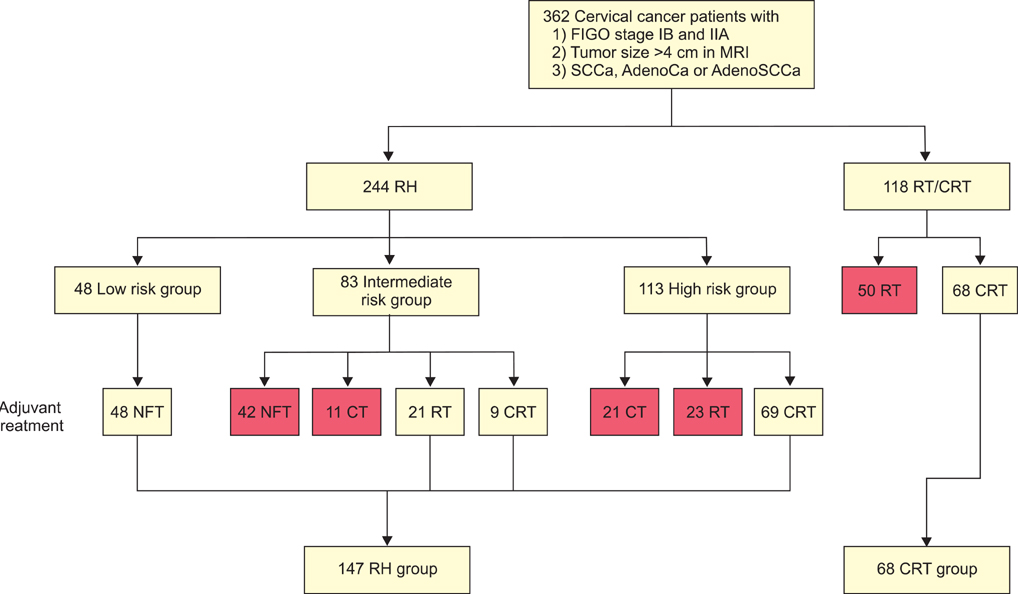
We selected 215 patients with stage IB2 and IIA2 cervical cancer (tumor diameter > 4 cm on magnetic resonance imaging) who underwent RH followed by tailored adjuvant therapy (n=147) or primary CRT (n=68) at two tertiary referral centers between 2001 and 2010.
RESULTS
About twenty nine percent of patients were cured by RH alone and these patients experienced the best survival outcomes with the lowest morbidity rates. After the median follow-up times of 40 months, 27 RH (18.4%) and 20 CRT (29.4%) patients had recurrence (p=0.068) and 23 (15.6%) and 17 (25%) patients died of disease (p=0.101). The 5-year progression-free survival were 77% and 66% (p=0.047), and the 5-year overall survival were 78% and 67% (p=0.048) after RH and primary CRT, respectively. In multivariate analysis, patients who received primary CRT was at higher risk for tumor recurrence (odds ratio [OR], 2.26; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.24 to 4.14; p=0.008) and death (OR, 3.02; 95% CI, 1.53 to 5.98; p=0.001) than those who received RH. Grade 3-4, early (17% vs. 30.9%, p=0.021) and late (1.4% vs. 8.8%, p=0.007) complications were significantly less frequent after RH than primary CRT.
CONCLUSION
Thirty percent of patients were cured by RH alone. A treatment outcome was better in this retrospective study in terms of morbidity and survival. Randomized trials are needed to confirm this result.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Surgical Outcomes of Robotic Radical Hysterectomy Using Three Robotic Arms versus Conventional Multiport Laparoscopy in Patients with Cervical Cancer
Ga Won Yim, Sang Wun Kim, Eun Ji Nam, Sunghoon Kim, Hee Jung Kim, Young Tae Kim
Yonsei Med J. 2014;55(5):1222-1230. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2014.55.5.1222.An Alternative Triage Strategy Based on Preoperative MRI for Avoiding Trimodality Therapy in Stage IB Cervical Cancer
Jung-Yun Lee, Jina Youm, Jae Weon Kim, Kidong Kim, Hak Jae Kim, Jeong Yeon Cho, Min A Kim, Noh Hyun Park, Yong-Sang Song
Cancer Res Treat. 2016;48(1):259-265. doi: 10.4143/crt.2014.370.
Reference
-
1. Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011. 61:69–90.2. Jung KW, Park S, Kong HJ, Won YJ, Lee JY, Park EC, et al. Cancer statistics in Korea: incidence, mortality, survival, and prevalence in 2008. Cancer Res Treat. 2011. 43:1–11.3. Piver MS, Ghomi A. The twenty-first century role of Piver-Rutledge type III radical hysterectomy and FIGO stage IA, IB1, and IB2 cervical cancer in the era of robotic surgery: a personal perspective. J Gynecol Oncol. 2010. 21:219–224.4. Ryu HS, Kang SB, Kim KT, Chang KH, Kim JW, Kim JH. Efficacy of different types of treatment in FIGO stage IB2 cervical cancer in Korea: results of a multicenter retrospective Korean study (KGOG-1005). Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2007. 17:132–136.5. Landoni F, Maneo A, Colombo A, Placa F, Milani R, Perego P, et al. Randomised study of radical surgery versus radiotherapy for stage Ib-IIa cervical cancer. Lancet. 1997. 350:535–540.6. Zivanovic O, Alektiar KM, Sonoda Y, Zhou Q, Iasonos A, Tew WP, et al. Treatment patterns of FIGO Stage IB2 cervical cancer: a single-institution experience of radical hysterectomy with individualized postoperative therapy and definitive radiation therapy. Gynecol Oncol. 2008. 111:265–270.7. Kim WY, Chang SJ, Chang KH, Yoo SC, Chun M, Ryu HS. Treatment patterns and outcomes in bulky stage IB2 cervical cancer patients: a single institution's experience over 14 years. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2011. 71:19–23.8. Bansal N, Herzog TJ, Shaw RE, Burke WM, Deutsch I, Wright JD. Primary therapy for early-stage cervical cancer: radical hysterectomy vs radiation. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2009. 201:485.e1–485.e9.9. Rungruang B, Courtney-Brooks M, Beriwal S, Zorn KK, Richard SD, Olawaiye AB, et al. Surgery versus radiation therapy for stage IB2 cervical carcinoma: a population-based analysis. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2012. 22:484–489.10. Rocconi RP, Estes JM, Leath CA 3rd, Kilgore LC, Huh WK, Straughn JM Jr. Management strategies for stage IB2 cervical cancer: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Gynecol Oncol. 2005. 97:387–394.11. Jewell EL, Kulasingam S, Myers ER, Alvarez Secord A, Havrilesky LJ. Primary surgery versus chemoradiation in the treatment of IB2 cervical carcinoma: a cost effectiveness analysis. Gynecol Oncol. 2007. 107:532–540.12. Pecorelli S, Zigliani L, Odicino F. Revised FIGO staging for carcinoma of the cervix. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2009. 105:107–108.13. Sedlis A, Bundy BN, Rotman MZ, Lentz SS, Muderspach LI, Zaino RJ. A randomized trial of pelvic radiation therapy versus no further therapy in selected patients with stage IB carcinoma of the cervix after radical hysterectomy and pelvic lymphadenectomy: a Gynecologic Oncology Group Study. Gynecol Oncol. 1999. 73:177–183.14. Peters WA 3rd, Liu PY, Barrett RJ 2nd, Stock RJ, Monk BJ, Berek JS, et al. Concurrent chemotherapy and pelvic radiation therapy compared with pelvic radiation therapy alone as adjuvant therapy after radical surgery in high-risk early-stage cancer of the cervix. J Clin Oncol. 2000. 18:1606–1613.15. Piver MS, Rutledge F, Smith JP. Five classes of extended hysterectomy for women with cervical cancer. Obstet Gynecol. 1974. 44:265–272.16. Havrilesky LJ, Leath CA, Huh W, Calingaert B, Bentley RC, Soper JT, et al. Radical hysterectomy and pelvic lymphadenectomy for stage IB2 cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2004. 93:429–434.17. Park JY, Kim DY, Kim JH, Kim YM, Kim YT, Nam JH. Outcomes after radical hysterectomy according to tumor size divided by 2-cm interval in patients with early cervical cancer. Ann Oncol. 2011. 22:59–67.18. Beadle BM, Jhingran A, Yom SS, Ramirez PT, Eifel PJ. Patterns of regional recurrence after definitive radiotherapy for cervical cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010. 76:1396–1403.19. Eifel PJ, Winter K, Morris M, Levenback C, Grigsby PW, Cooper J, et al. Pelvic irradiation with concurrent chemotherapy versus pelvic and para-aortic irradiation for high-risk cervical cancer: an update of radiation therapy oncology group trial (RTOG) 90-01. J Clin Oncol. 2004. 22:872–880.20. Rotman M, Choi K, Guse C, Marcial V, Hornback N, John M. Prophylactic irradiation of the para-aortic lymph node chain in stage IIB and bulky stage IB carcinoma of the cervix, initial treatment results of RTOG 7920. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1990. 19:513–521.21. Delpech Y, Haie-Meder C, Rey A, Zafrani Y, Uzan C, Gouy S, et al. Para-aortic involvement and interest of para-aortic lymphadenectomy after chemoradiation therapy in patients with stage IB2 and II cervical carcinoma radiologically confined to the pelvic cavity. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007. 14:3223–3231.22. Ferrandina G, Distefano M, Ludovisi M, Morganti A, Smaniotto D, D'Agostino G, et al. Lymph node involvement in locally advanced cervical cancer patients administered preoperative chemoradiation versus chemotherapy. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007. 14:1129–1135.23. Houvenaeghel G, Lelievre L, Rigouard AL, Buttarelli M, Jacquemier J, Viens P, et al. Residual pelvic lymph node involvement after concomitant chemoradiation for locally advanced cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2006. 102:74–79.24. Berveling MJ, Langendijk JA, Beukema JC, Mourits MJ, Reyners AK, Pras E. Health-related quality of life and late morbidity in concurrent chemoradiation and radiotherapy alone in patients with locally advanced cervical carcinoma. J Gynecol Oncol. 2011. 22:152–160.25. Gruen A, Musik T, Kohler C, Fuller J, Wendt T, Stromberger C, et al. Adjuvant chemoradiation after laparoscopically assisted vaginal radical hysterectomy (LARVH) in patients with cervical cancer: oncologic outcome and morbidity. Strahlenther Onkol. 2011. 187:344–349.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Recent Management of FIGO stage IB2 Cervical Cancer
- A retrospective comparison of outcome in IB2 and IIA cervical cancer patients treated with primary concurrent chemoradiation versus radical hysterectomy with or without tailored adjuvant therapy
- Treatment of Cervical Cancer
- The influence of number of high risk factors on clinical outcomes in patients with early-stage cervical cancer after radical hysterectomy and adjuvant chemoradiation
- Vaginal evisceration after radical hysterectomy and adjuvant radiation