J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg.
2012 Sep;14(3):157-163. 10.7461/jcen.2012.14.3.157.
Clinical and Angiographic Outcomes of Wingspan Stent Placement for Treatment of Symptomatic Intracranial Stenosis: Single Center Experience with 19 Cases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Institute of Wonkwang Medical Science, School of Medicine, Wonkwang University, Iksan, Korea. kimdw@wku.ac.kr
- KMID: 1808449
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2012.14.3.157
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The limitations of medical management of symptomatic intracranial arterial stenosis (ICS) have prompted development of new strategies, including endovascular treatment. However, stenting of symptomatic ICS remains investigational. Here, we have reported and analyzed a series of 19 endovascular procedures involving placement of a Wingspan stent.
METHODS
We conducted a retrospective review of a series of ICS in which patients were treated with percutaneous transarterial balloon angioplasty and stent placement (PTAS). Patients included in the study were diagnosed as symptomatic ICS between May 2010 and September 2011.
RESULTS
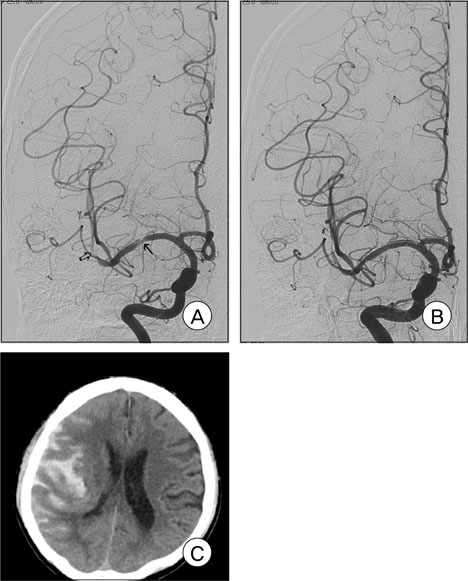
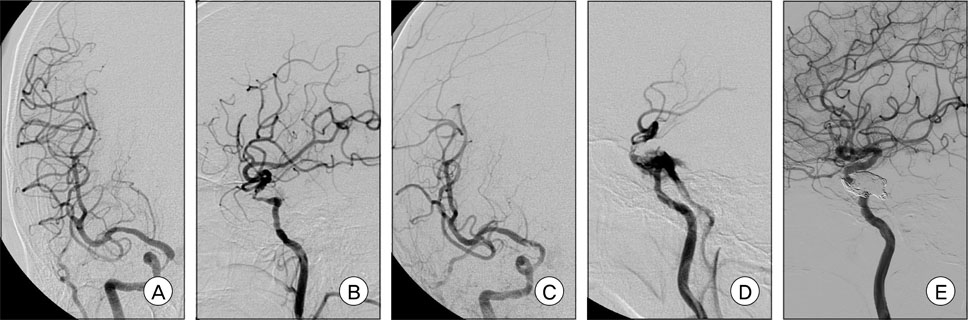
Nineteen patients (median age, 65 years; 12 males, seven women) were treated with the Wingspan stent system for symptomatic ICS ranging from 50% to 99%. The technical success rate was 100%. The location of ICS included the internal carotid (n = 5; 1 petrous, 3 cavernous, and 1 clinoid segments), vertebral (n = 1; V4 segment), basilar (n = 1), and middle cerebral (n = 12; 9 M1, 3 M2) arteries. There was no occurrence of procedure-related mortality. Periprocedural morbidity occurred in two cases (10.5%), including carotid-cavernous fistula (n = 1) and subarachnoid hemorrhage (n = 1). No ipsilateral stroke was recorded beyond 30 days during a mean follow-up period of 13.2 months (range 9-19 months). Restenosis (> 50%) was observed in one patient (6.3%), who was asymptomatic, on follow-up imaging.
CONCLUSION
Wingspan stent for symptomatic ICS can be performed with a high rate of technical success and acceptable periprocedural morbidity rates. Our initial experience indicates that this procedure represents a viable treatment option for this patient population.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Comparison of Drug-eluting Coronary Stents, Bare Coronary Stents and Self-expanding Stents in Angioplasty of Middle Cerebral Artery Stenoses
Jong-Hyeog Lee, Sung-Min Jo, Kwang-Deog Jo, Moon-Kyu Kim, Sang-Youl Lee, Seung-Hoon You
J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg. 2013;15(2):85-95. doi: 10.7461/jcen.2013.15.2.85.
Reference
-
1. Berg-Dammer E, Henkes H, Weber W, Berlit P, Kuhne D. Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty of intracranial artery stenosis: clinical results in 24 patients. Neurosurg Focus. 1998. 10. 5(4):e13.
Article2. Betriu A, Masotti M, Serra A, Alonso J, Fernández-Avilés F, Gimeno F, et al. Randomized comparison of coronary stent implantation and balloon angioplasty in the treatment of de novo coronary artery lesions (START): a four-year follow-up. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1999. 11. 34(5):1498–1506.3. Chimowitz MI, Kokkinos J, Strong J, Brown MB, Levine SR, Silliman S, et al. The warfarin-aspirin symptomatic intracranial disease study. Neurology. 1995. 08. 45(8):1488–1493.
Article4. Feldmann E, Daneault N, Kwan E, Ho KJ, Pessin MS, Langenberg P, et al. Chinese-white differences in the distribution of occlusive cerebrovascular disease. Neurology. 1990. 10. 40(10):1541–1545.
Article5. Fiorella D, Levy EI, Turk AS, Albuquerque FC, Niemann DB, Aagaard-Kienitz B, et al. US multicenter experience with the wingspan stent system for the treatment of intracranial atheromatous disease: periprocedural results. Stroke. 2007. 03. 38(3):881–887.
Article6. Gupta R, Schumacher HC, Mangla S, Meyers PM, Duong H, Khandji AG, et al. Urgent endovascular revascularization for symptomatic intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis. Neurology. 2003. 12. 61(12):1729–1735.
Article7. Henkes H, Miloslavski E, Lowens S, Reinartz J, Liebig T, Kühne D. Treatment of intracranial atherosclerotic stenoses with balloon dilatation and self-expanding stent deployment (WingSpan). Neuroradiology. 2005. 03. 47(3):222–228.
Article8. Kasner SE, Chimowitz MI, Lynn MJ, Howlett-Smith H, Stern BJ, Hertzberg VS, et al. Predictors of ischemic stroke in the territory of a symptomatic intracranial arterial stenosis. Circulation. 2006. 01. 113(4):555–563.
Article9. Kim JS, Kim J, Choi D, Lee CJ, Lee SH, Ko YG, et al. Efficacy of high-dose atorvastatin loading before primary percutaneous coronary intervention in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: the STATIN STEMI trial. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2010. 03. 3(3):332–339.10. Lylyk P, Cohen JE, Ceratto R, Ferrario A, Miranda C. Angioplasty and stent placement in intracranial atherosclerotic stenoses and dissections. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002. 03. 23(3):430–436.11. Marks MP, Marcellus ML, Do HM, Schraedley-Desmond PK, Steinberg GK, Tong DC, et al. Intracranial angioplasty without stenting for symptomatic atherosclerotic stenosis: long-term follow-up. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005. 03. 26(3):525–530.12. Marks MP, Marcellus M, Norbash AM, Steinberg GK, Tong D, Albers GW. Outcome of angioplasty for atherosclerotic intracranial stenosis. Stroke. 1999. 05. 30(5):1065–1069.
Article13. Marks MP, Wojak JC, Al-Ali F, Jayaraman M, Marcellus ML, Connors JJ, et al. Angioplasty for symptomatic intracranial stenosis: clinical outcome. Stroke. 2006. 04. 37(4):1016–1020.14. Mazighi M, Yadav JS, Abou-Chebl A. Durability of endovascular therapy for symptomatic intracranial atherosclerosis. Stroke. 2008. 06. 39(6):1766–1769.
Article15. Powers WJ, Clarke WR, Grubb RL Jr, Videen TO, Adams HP Jr, Derdeyn CP, et al. Extracranial-intracranial bypass surgery for stroke prevention in hemodynamic cerebral ischemia: the Carotid Occlusion Surgery Study randomized trial. JAMA. 2011. 11. 306(18):1983–1992.16. Rahme RJ, Aoun SG, Batjer HH, Bendok BR. SAMMPRIS; end of intracranial stenting for atherosclerosis or back to the drawing board? Neurosurgery. 2011. 12. 69(6):N16–N18.17. Sacco RL, Kargman DE, Gu Q, Zamanillo MC. Race-ethnicity and determinants of intracranial atherosclerotic cerebral infarction. The Northern Manhattan Stroke Study. Stroke. 1995. 01. 26(1):14–20.18. Suryapranata H, van't Hof AW, Hoorntje JC, de Boer MJ, Zijlstra F. Randomized comparison of coronary stenting with balloon angioplasty in selected patients with acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 1998. 06. 97(25):2502–2505.
Article19. The EC/IC Bypass Study Group. Failure of extracranial-intracranial arterial bypass to reduce the risk of ischemic stroke. Results of an international randomized trial. N Engl J Med. 1985. 11. 313(19):1191–1200.20. The SSYLVIA study investigators. Stenting of symptomatic atherosclerotic lesions in the vertebral or intracranial arteries (SSYLVIA): Study results. Stroke. 2004. 06. 35(6):1388–1392.21. The Warfarin-Aspirin Symptomatic Intracranial Disease (WASID) Study Group. Prognosis of patients with symptomatic vertebral or basilar artery stenosis. Stroke. 1998. 07. 29(7):1389–1392.22. Tsumoto T, Terada T, Tsuura M, Matsumoto H, Masuo O, Yamaga H, et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging abnormalities after percutaneous transluminal angioplasty and stenting for intracranial atherosclerotic disease. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005. 02. 26(2):385–389.23. Wityk RJ, Lehman D, Klag M, Coresh J, Ahn H, Litt B. Race and sex differences in the distribution of cerebral atherosclerosis. Stroke. 1996. 11. 27(11):1974–1980.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Wingspan Stenting for Symptomatic Severe In-Stent Stenosis of a Closed-Cell Stent after Stent-Assisted Coiling of a Ruptured Intracranial Aneurysm
- Coincidental Occurrence of Acute In-stent Thrombosis and Iatrogenic Vessel Perforation During a Wingspan Stent Placement: Management with a Stent In-stent Technique
- The WingSpan Stent System for the Treatment of Intracranial Atherosclerotic Stenoses: A Single Center Experience
- Delayed Remote Intracerebral Hemorrhage after Wingspan Stenting for Internal Carotid Artery Stenosis Following the On-Label Usage Guidelines
- Bench-Top Comparison of Three Different Types of Stents Used for Treatment of Intracranial Atherosclerotic Stenosis