Infect Chemother.
2012 Dec;44(6):481-484. 10.3947/ic.2012.44.6.481.
Two Cases of Invasive Infections Caused by Arcanobacterium haemolyticum in Immunocompetent Adult
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, University of Dongguk College of Medicine, Gyeongju, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, University of Dongguk College of Medicine, Gyeongju, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, University of Dongguk College of Medicine, Gyeongju, Korea. rocky@dumc.or.kr
- KMID: 1806938
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2012.44.6.481
Abstract
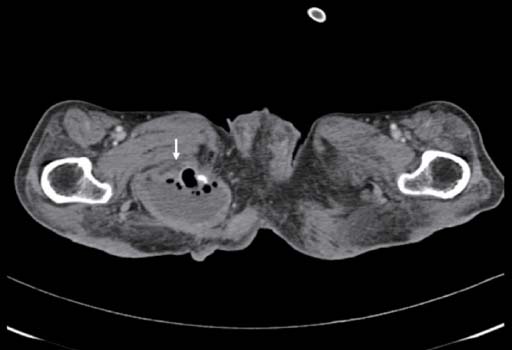
- Arcanobacterium haemolyticum is a gram-positive bacillus that is most commonly implicated in pharyngitis and infections of the skin and soft tissue. Systemic and deep-seated infections caused by this organism are rarely reported in the literature. Recently, we encountered two cases of invasive infections caused by A. haemolyticum. We describe two cases, one with vertebral osteomyelitis with an epidural abscess and the other with a buttock abscess with bacteremia.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Maclean PD, Liebow AA, Rosenberg AA. A hemolytic corynebacterium resembling Corynebacterium ovis and Corynebacterium pyogenes in man. J Infect Dis. 1946. 79:69–90.
Article2. Ceilley RI. Foot ulceration and vertebral osteomyelitis with Corynebacterium haemolyticum. Arch Dermatol. 1977. 113:646–647.
Article3. Skov RL, Sanden AK, Danchell VH, Robertsen K, Ejlertsen T. Systemic and deep-seated infections caused by Arcanobacterium haemolyticum. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1998. 17:578–582.
Article4. Vargas J, Hernandez M, Silvestri C, Jiménez O, Guevara N, Carballo M, Rojas N, Riera J, Alayo E, Fernández M, Rodriguez-Morales AJ, Silva M. Brain abscess due to Arcanobacterium haemolyticum after dental extraction. Clin Infect Dis. 2006. 42:1810–1811.
Article5. Therriault BL, Daniels LM, Carter YL, Raasch RH. Severe sepsis caused by Arcanobacterium haemolyticum: a case report and review of the literature. Ann Pharmacother. 2008. 42:1697–1702.
Article6. Choi SM, Lee HK, Kim YR, Park KS, Jeon HK, Moon SW, Park YJ, Shin WS. A case of subactue infective endocarditis caused by Arcanobacterium haemolyticum in a patient with mitral valve prolapse. Infect Chemother. 2007. 39:104–107.7. Jun KR, Chun SH, Park SJ, Kim DJ, Bae HG, Kim MN. A case of Arcanobacterium haemolyticum sepsis. Korean J Lab Med. 2005. 25:56–60.8. Funke G, von Graevenitz A, Clarridge JE 3rd, Bernard KA. Clinical microbiology of coryneform bacteria. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1997. 10:125–159.
Article9. Miller RA, Brancato F, Holmes KK. Corynebacterium hemolyticum as a cause of pharyngitis and scarlatiniform rash in young adults. Ann Intern Med. 1986. 105:867–872.
Article10. Collins MD, Jones D, Schofield GM. Reclassification of 'Corynebacterium haemolyticum' (MacLean, Liebow & Rosenberg) in the genus Arcanobacterium gen.nov. as Arcanobacterium haemolyticum nom.rev., comb.nov. J Gen Microbiol. 1982. 128:1279–1281.
Article11. Fernández-Suárez A, Benítez JM, Vidal AM, Iglesias JM. Lemierre's syndrome and septicaemia caused solely by Arcanobacterium haemolyticum in a young immunocompetent patient. J Med Microbiol. 2009. 58:1645–1648.
Article12. Ouriemchi W, Jeddi D, Ziane Y, El Quessar A, Benouda A. Arcanobacterium haemolyticum brain abscess mimicking a brain tumor. Med Mal Infect. 2011. 41:397–399.13. Wong V, Turmezei T, Cartmill M, Soo S. Infective endocarditis caused by Arcanobacterium haemolyticum: a case report. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2011. 10:17.
Article14. Lundblom K, Jung K, Kalin M. Lemierre syndrome caused by co-infection by Arcanobacterium haemolyticum and Fusobacterium necrophorum. Infection. 2010. 38:427–429.
Article15. Bae SY, Choi S, Kang SJ, Jang HC, Park KH, Jung SI, Shin JH. A case of Arcanobacterium haemolyticum bacteremia and osteomyelitis diagnosed by16s rRNA sequencing. Infect Chemother. 2010. 42:241–243.
Article16. Lee S, Roh KH, Kim CK, Yong D, Choi JY, Lee JW, Lee K, Chong Y. A case of necrotizing fasciitis due to Streptococcus agalactiae, Arcanobacterium haemolyticum, and Finegoldia magna in a dog-bitten patient with diabetes. Korean J Lab Med. 2008. 28:191–195.
Article17. Kim YC, Kim JS, Park JY, Kang SH, Cho HC, Bang JW, Kim EC. Five cases of Arcanobacterium haemolyticum isolated from skin ulcer and peritonsillar abscess. Korean J Lab Med. 2004. 24:392–395.18. Tan TY, Ng SY, Thomas H, Chan BK. Arcanobacterium haemolyticum bacteraemia and soft-tissue infections: case report and review of the literature. J Infect. 2006. 53:e69–e74.19. Parija SC, Kaliaperumal V, Kumar SV, Sujatha S, Babu V, Balu V. Arcanobacterium haemolyticum associated with pyothorax: case report. BMC Infect Dis. 2005. 5:68.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Lemierre Syndrome Caused by Arcanobacterium haemolyticum Alone in a Healthy Man
- A Case of Diabetic Foot Ulcer Caused by Arcanobacterium haemolyticum and Streptococcus agalactiae
- A Case of Subacute Infective Endocarditis Caused by Arcanobacterium haemolyticum in a Patient with Mitral Valve Prolapse
- A Case of Arcanobacterium haemolyticum Bacteremia and Osteomyelitis Diagnosed by 16s rRNA Sequencing
- Five Cases of Arcanobacterium haemolyticum Isolated from Skin Ulcer and Peritonsillar Abscess