Cancer Res Treat.
2012 Dec;44(4):275-278.
Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma in The External Auditory Canal: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Hanyang University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kytae@hanyang.ac.kr
Abstract
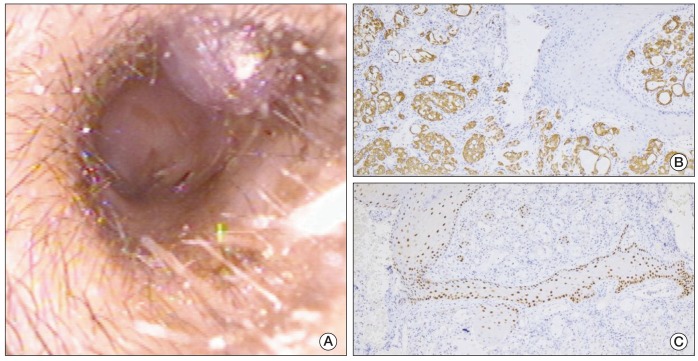
- Mucoepidermoid carcinoma in the external auditory canal is extremely rare. Strategies used for treatment of mucoepidermoid carcinoma remain controversial. We present a case of mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the external auditory canal. The patient underwent lateral temporal bone resection and the surgical defect was obliterated with temporal muscle. He is currently disease-free, four years after surgery. Proper diagnostic measures and strategy for treatment of mucoepidermoid carcinoma are discussed.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bared A, Dave SP, Garcia M, Angeli SI. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the external auditory canal (EAC). Acta Otolaryngol. 2007; 127:280–284. PMID: 17364365.
Article2. Rancic D, Nihailovic D, Mijovic Z. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the external auditory canal: case report. Arch Oncol. 2003; 11:27–29.3. Magliulo G, Fusconi M, Pulice G. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the external auditory canal: case report. Am J Otolaryngol. 2003; 24:274–277. PMID: 12884224.4. Magliulo G, Ciniglio Appiani M. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the external auditory canal. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010; 142:624–625. PMID: 20304291.
Article5. Yoon YH, Park HT, Kim EH, Park YH. A case of mucoepidermoid carcinoma occurring in external auditory canal. Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2008; 51:822–824.6. Arriaga M, Curtin H, Takahashi H, Hirsch BE, Kamerer DB. Staging proposal for external auditory meatus carcinoma based on preoperative clinical examination and computed tomography findings. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1990; 99(9 Pt 1):714–721. PMID: 2396807.
Article7. Marsh M, Jenkins H. Cummings CW, Flint PW, Harker LA, Haughey BH, Richardson MA, Robbins KT, editors. Temporal bone neoplasms and lateral cranialbase surgery. Cummings otolaryngology: head and neck surgery. 2005. 4th ed. St. Louis: Elsevier Mosby;p. 3699–3737.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma Occurring in External Auditory Canal
- A Case of Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Situ Occurredin the External Auditory Canal
- A Case of Osteoma with Cholesteatoma in the External Auditory Canal
- Ceruminous Gland Tumors: 5 cases report
- A Case of Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis involving the External Auditory Canal