Ann Surg Treat Res.
2015 Feb;88(2):77-85. 10.4174/astr.2015.88.2.77.
Astrocyte elevated gene-1 overexpression in hepatocellular carcinoma: an independent prognostic factor
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Soonchunhyang University Cheonan Hospital, Cheonan, Korea. ssurge@sch.ac.kr
- 2Department of Surgery, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea.
- 3Department of Medical Science Research Institute, Soonchunhyang University, Cheonan, Korea.
- 4Department of Pathology, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea.
- 5Department of Pathology, Soonchunhyang University Cheonan Hospital, Cheonan, Korea.
- KMID: 1804124
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2015.88.2.77
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) plays important roles in tumorigenesis such as proliferation, invasion, metastasis, angiogenesis, and chemoresistance. We examined the expression of AEG-1 in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
METHODS
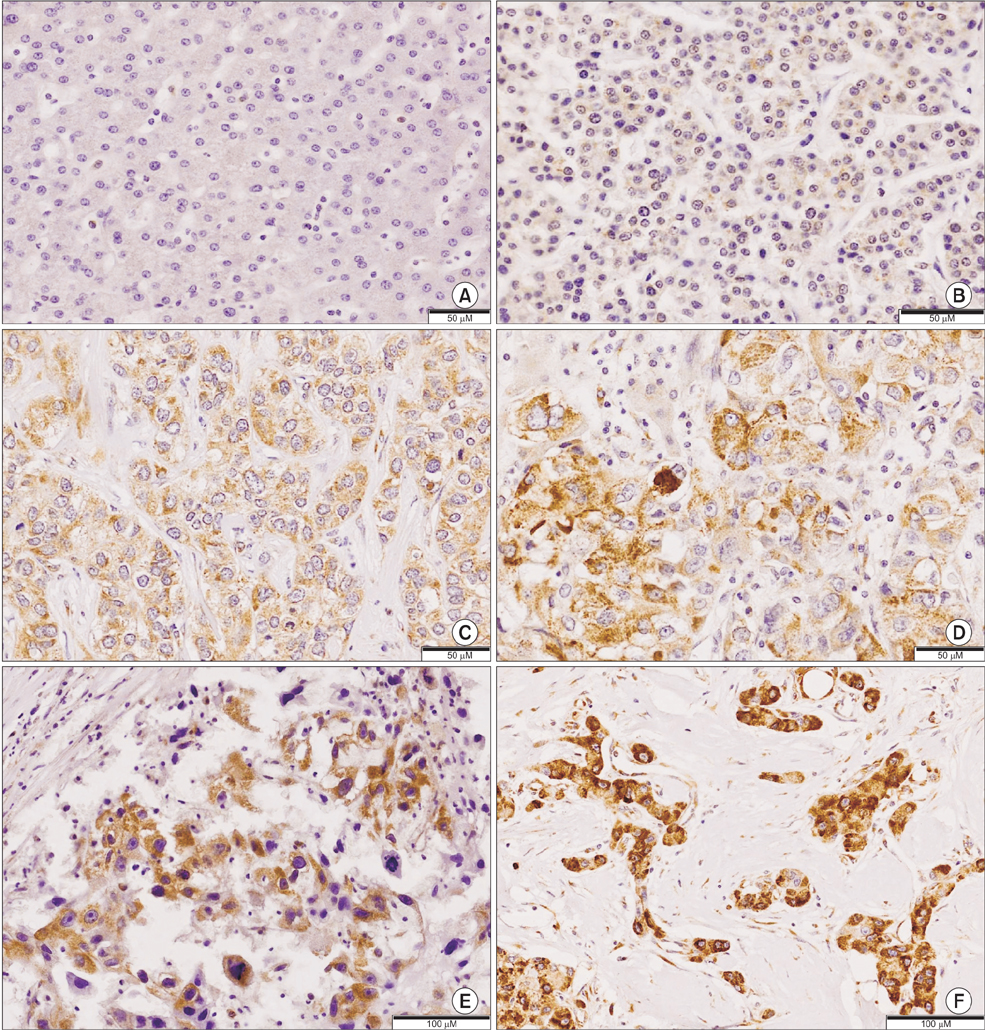
Eighty-five samples were collected from patients with HCC who underwent surgery and were histopathologically confirmed to have HCC. Two independent pathologists, experienced in evaluating immunohistochemistry and blinded to the clinical outcomes of the patients, reviewed all samples. They determined AEG-1 expression semiquantitatively by assessing the percentage of positively stained immunoreactive cells and staining intensity. Clinicopathological data were analyzed in association with prognosis.
RESULTS
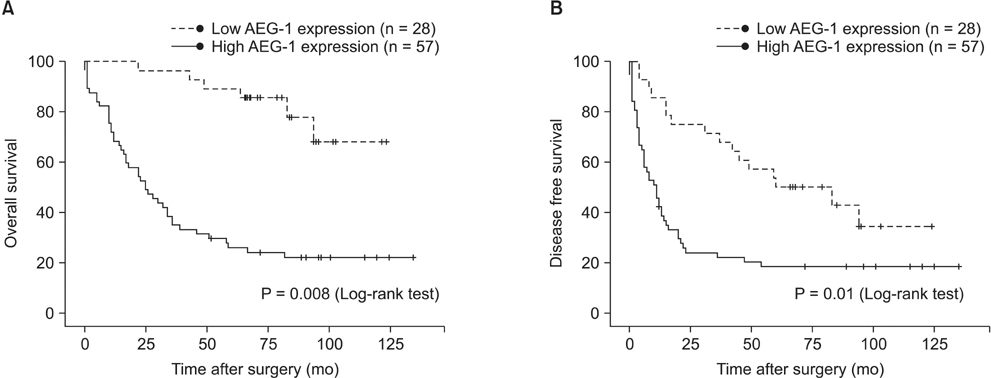
The association was estimated by univariate and multivariate analyses with Cox regression. Tumor size (hazard ratio [HR], 2.285; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.175-4.447; P = 0.015), microvascular invasion (HR, 6.754; 95% CI, 1.631-27.965; P = 0.008), and AEG-1 expression (HR, 4.756; 95% CI, 1.697-13.329; P = 0.003) were independent prognostic factors for overall survival. Those for disease-free survival rate were tumor size (HR, 2.245; 95% CI, 1.282-3.933; P = 0.005) and AEG-1 expression (HR, 1.916; 95% CI, 1.035-3.545; P = 0.038). The cumulative 5-year survival and recurrence rates were 89.2% and 50.0% in the low-expressing group and 24.5% and 82.4% in the high-expressing group, respectively.
CONCLUSION
The results suggest that AEG-1 overexpression could serve as a valuable prognostic marker in patients with HCC.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. El-Serag HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2011; 365:1118–1127.2. Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013; 63:11–30.3. Korea Central Cancer Registry. Cancer reference information [Internet]. Goyang: Korea Central Cancer Registry;2012. cited 2012 Dec 27. Available from: http://www.cancer.go.kr.4. Llovet JM, Burroughs A, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2003; 362:1907–1917.5. Sarkar D. AEG-1/MTDH/LYRIC in liver cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 2013; 120:193–221.6. Britt DE, Yang DF, Yang DQ, Flanagan D, Callanan H, Lim YP, et al. Identification of a novel protein, LYRIC, localized to tight junctions of polarized epithelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 2004; 300:134–148.7. Su ZZ, Kang DC, Chen Y, Pekarskaya O, Chao W, Volsky DJ, et al. Identification and cloning of human astrocyte genes displaying elevated expression after infection with HIV-1 or exposure to HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein by rapid subtraction hybridization, RaSH. Oncogene. 2002; 21:3592–3602.8. Hu G, Chong RA, Yang Q, Wei Y, Blanco MA, Li F, et al. MTDH activation by 8q22 genomic gain promotes chemoresistance and metastasis of poor-prognosis breast cancer. Cancer Cell. 2009; 15:9–20.9. Sarkar D, Fisher PB. AEG-1/MTDH/LYRIC: clinical significance. Adv Cancer Res. 2013; 120:39–74.10. Yoo BK, Emdad L, Su ZZ, Villanueva A, Chiang DY, Mukhopadhyay ND, et al. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma development and progression. J Clin Invest. 2009; 119:465–477.11. Lee SG, Su ZZ, Emdad L, Sarkar D, Fisher PB. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) is a target gene of oncogenic Ha-ras requiring phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and c-Myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006; 103:17390–17395.12. Guo J, Xia B, Meng F, Lou G. miR-137 suppresses cell growth in ovarian cancer by targeting AEG-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013; 441:357–363.13. Yang Y, Wu J, Guan H, Cai J, Fang L, Li J, et al. MiR-136 promotes apoptosis of glioma cells by targeting AEG-1 and Bcl-2. FEBS Lett. 2012; 586:3608–3612.14. He XX, Chang Y, Meng FY, Wang MY, Xie QH, Tang F, et al. MicroRNA-375 targets AEG-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma and suppresses liver cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene. 2012; 31:3357–3369.15. Yoo BK, Emdad L, Lee SG, Su ZZ, Santhekadur P, Chen D, et al. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1): A multifunctional regulator of normal and abnormal physiology. Pharmacol Ther. 2011; 130:1–8.16. Ma J, Xie SL, Geng YJ, Jin S, Wang GY, Lv GY. In vitro regulation of hepatocellular carcinoma cell viability, apoptosis, invasion, and AEG-1 expression by LY294002. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2014; 38:73–80.17. Li C, Chen K, Cai J, Shi QT, Li Y, Li L, et al. Astrocyte elevated gene-1: a novel independent prognostic biomarker for metastatic ovarian tumors. Tumour Biol. 2014; 35:3079–3085.18. Chen X, Dong K, Long M, Lin F, Wang X, Wei J, et al. Serum anti-AEG-1 auto-antibody is a potential novel biomarker for malignant tumors. Oncol Lett. 2012; 4:319–323.19. Jian-bo X, Hui W, Yu-long H, Chang-hua Z, Long-juan Z, Shi-rong C, et al. Astrocyteelevated gene-1 overexpression is associated with poor prognosis in gastric cancer. Med Oncol. 2011; 28:455–462.20. Song H, Li C, Li R, Geng J. Prognostic significance of AEG-1 expression in colorectal carcinoma. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2010; 25:1201–1209.21. Deng H, Zhou Z, Tu W, Xia Y, Huang H, Tian D. Knockdown of astrocyte elevated gene-1 inhibits growth through suppression of IL-6 secretion in HepG2 human hepatoma cells. Oncol Lett. 2014; 7:101–106.22. Zheng J, Li C, Wu X, Yang Y, Hao M, Sheng S, et al. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 is a novel biomarker of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma in two China regions. Tumour Biol. 2014; 35:2265–2269.23. Zheng J, Li C, Wu X, Liu M, Sun X, Yang Y, et al. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) shRNA sensitizes Huaier polysaccharide (HP)-induced anti-metastatic potency via inactivating downstream P13K/Akt pathway as well as augmenting cell-mediated immune response. Tumour Biol. 2014; 35:4219–4224.24. Srivastava J, Siddiq A, Emdad L, Santhekadur PK, Chen D, Gredler R, et al. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 promotes hepatocarcinogenesis: novel insights from a mouse model. Hepatology. 2012; 56:1782–1791.25. Llovet JM, Bru C, Bruix J. Prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: the BCLC staging classification. Semin Liver Dis. 1999; 19:329–338.26. Yoo BK, Gredler R, Vozhilla N, Su ZZ, Chen D, Forcier T, et al. Identification of genes conferring resistance to 5-fluorouracil. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009; 106:12938–12943.27. Llovet JM, Bruix J. Molecular targeted therapies in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2008; 48:1312–1327.28. Villanueva A, Llovet JM. Targeted therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2011; 140:1410–1426.29. Caron M, Choquet-Kastylevsky G, Joubert-Caron R. Cancer immunomics using autoantibody signatures for biomarker discovery. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2007; 6:1115–1122.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Amplification and Overexpression of Cyclin D1 in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas
- A gene expression signature of FOXM1 predicts the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Prognostic Significance of p53 Overexpression after Hepatic Resection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Impact of prognostic nutritional index on the recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after a curative resection
- The Study of p53 Expression and DNA Ploidy in Colorectal Carcinoma