Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2014 Sep;17(3):196-200. 10.5223/pghn.2014.17.3.196.
How Should the Pyloric Submucosal Mass Coexisting with Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis Be Treated?: A Case of Pyloric Ectopic Pancreas with Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatric Surgery, Pusan National University Children's Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea.
- 2Department of Pediatric Surgery, Seoul National University Children's Hospital, Seoul, Korea. spkhy02@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1803121
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2014.17.3.196
Abstract
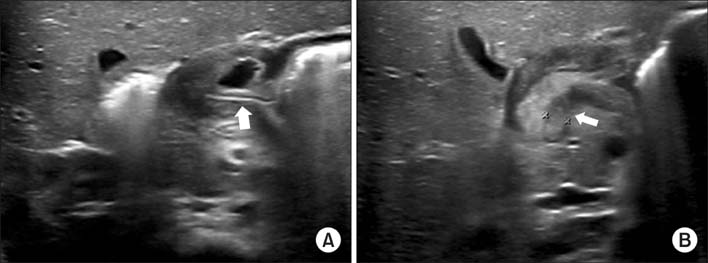
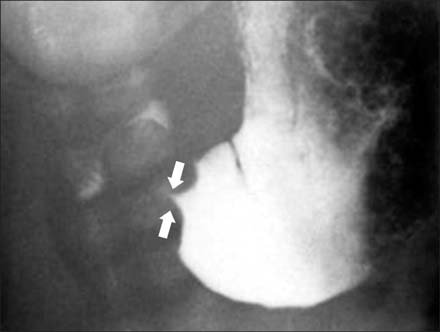
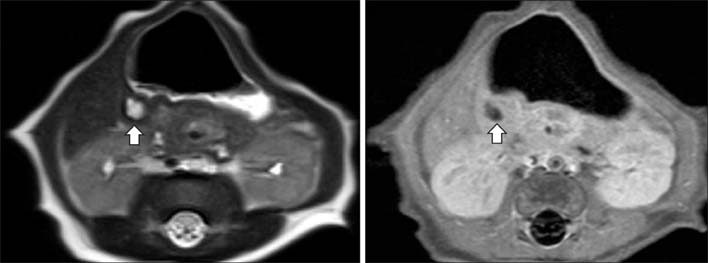
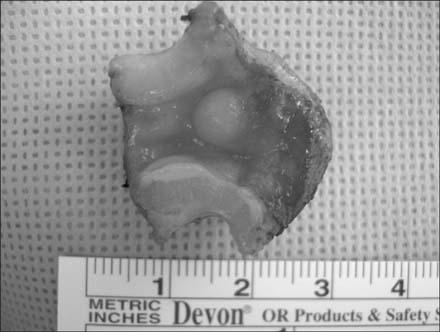
- Co-existing pyloric submucosal masses with hypertrophic pyloric stenosis (HPS) are very rare and treating these lesions is always a problem. A 20-day-old boy presented with recurrent episodes of projectile non-bilious vomiting lasting for 5 days. HPS was suspected due to the presenting age and the symptoms. The sonography demonstrated not only circumferential wall thickening of the pylorus, but also a pyloric submucosal mass. At laparotomy, a 0.8 cm sized pyloric submucosal mass was identified along with a hypertrophied pylorus. Pyloric excision was performed due to the possibility of sustaining the symptoms and malignancy. The pathological report of the submucosal mass was ectopic pancreas. Coexisting pyloric lesions can be diagnosed along with HPS, and surgical excision, not just pyloromyotomy, should be considered in these circumstances. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case report of pyloric ectopic pancreas and HPS to be diagnosed concurrently.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chin AC, Radhakrishnan RS, Lloyd J, Reynolds M. Pyloric duplication with communication to the pancreas in a neonate simulating hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. J Pediatr Surg. 2011; 46:1442–1444.
Article2. Takeyama J, Sato T, Tanaka H, Nio M. Adenomyoma of the stomach mimicking infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. J Pediatr Surg. 2007; 42:E11–E12.
Article3. Ozcan C, Celik A, Güçlü C, Balik E. A rare cause of gastric outlet obstruction in the newborn: Pyloric ectopic pancreas. J Pediatr Surg. 2002; 37:119–120.
Article4. Hishiki T, Saito T, Terui K, Mitsunaga T, Nakata M, Matsuura G, et al. A rare presentation in a case of gastric duplication cyst communicating to the pancreatic duct: coincidental detection during pyloromyotomy for hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. J Pediatr Surg. 2008; 43:e1–e3.
Article5. Kim S, Chung CJ, Fordham LA, Specter BB. Coexisting hyperplastic antral polyp and hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. Pediatr Radiol. 1997; 27:912–914.
Article6. Murphy S, Shaw K, Blanchard H. Report of three gastric tumors in children. J Pediatr Surg. 1994; 29:1202–1204.
Article7. Chongsrisawat V, Yimyeam P, Wisedopas N, Viravaidya D, Poovorawan Y. Unusual manifestations of gastric inflammatory fibroid polyp in a child. World J Gastroenterol. 2004; 10:460–462.
Article8. Thompson WM, Kende AI, Levy AD. Imaging characteristics of gastric lipomas in 16 adult and pediatric patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003; 181:981–985.
Article9. Iwasaki M, Nishimura A, Kamimura R, Ura K, Kobayashi H, Saiga T. Pyloric duplication cyst in an infant. Pediatr Int. 2009; 51:146–149.
Article10. Reggoug S, Errabih I, Ouazzani L, Benzzoubeir N, Krami H, Raiss M, et al. Heterotopic pancreas: an unusual cause of epigastric pain. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2010; 34:726–727.
Article11. Mandell GA. Association of antral diaphragms and hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1978; 131:203–206.
Article12. Bell MJ, Ternberg JL, Keating JP, Moedjona S, McAlister W, Shackelford GD. Prepyloric gastric antral web: a puzzling epidemic. J Pediatr Surg. 1978; 13:307–313.
Article13. Lee SY, Ko JS. Gastric duplication cyst with ectopic pancreas in a child. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2012; 60:391–393.
Article14. The Information Committee of the Korean Gastric Cancer Association. 2005~2006 Nationwide gastric submucosal tumor report in Korea. J Korean Gastric Cancer Assoc. 2008; 8:104–109.15. Ogata H, Oshio T, Ishibashi H, Takano S, Yagi M. Heterotopic pancreas in children: review of the literature and report of 12 cases. Pediatr Surg Int. 2008; 24:271–275.
Article16. Christodoulidis G, Zacharoulis D, Barbanis S, Katsogridakis E, Hatzitheofilou K. Heterotopic pancreas in the stomach: a case report and literature review. World J Gastroenterol. 2007; 13:6098–6100.
Article17. Ueno S, Ishida H, Hayashi A, Kamagata S, Morikawa M. Heterotopic pancreas as a rare cause of gastrointestinal hemorrhage in the newborn: report of a case. Surg Today. 1993; 23:269–272.
Article18. Tomita S, Kang J, Ghassemi M. Heterotopic pancreas-an unusual cause of melena in a pediatric patient. J Pediatr Surg. 2009; 44:2432–2433.
Article19. Malek MM, Gittes GK. Lesions of the pancreas. In : Holcomb GW, Murphy JP, editors. Ashcraft's pediatric surgery. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders;2010. p. 605–615.20. DeBord JR, Majarakis JD, Nyhus LM. An unusual case of heterotopic pancreas of the stomach. Am J Surg. 1981; 141:269–273.
Article21. Chu UM, Seo KW, Kim HS, Joo JK, Park YK, Ryu SY, et al. Clinical significance of a pylorus-preserving gastrectomy for early gastric cancer. J Korean Gastric Cancer Assoc. 2006; 6:11–17.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A clinical analysis of the congenital hypertrophic pyloric stenosis according to the pyloric muscle thickness
- Infantile Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis
- A clinical study of congenital hypertropic pyloric stenosis
- A clinical study ofcongenital hypertrophic pyloric stenosis
- A ultrasonographic study of infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis