J Korean Soc Radiol.
2014 Dec;71(6):278-287. 10.3348/jksr.2014.71.6.278.
Radiation Dose and Imaging Quality of Abdominal Computed Tomography before and after Scan Protocol Adjustment: Single-Institution Experience in Three Years
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. dumkycji@gmail.com
- KMID: 1801550
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2014.71.6.278
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To compare radiation dose and image quality of abdominal CT for patients who underwent repeated CT examinations before and after adjustment of scan protocol.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
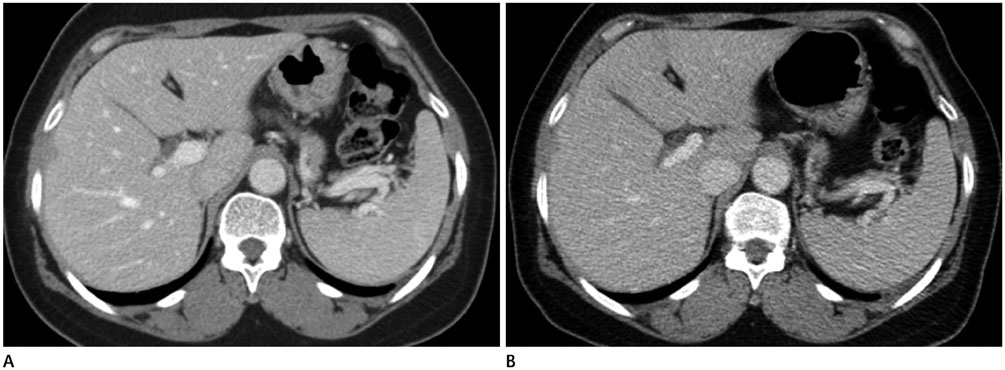
We compared radiation dose and image quality of repeated abdominal CT scans (at three-year-interval) of 50 patients with chronic liver disease, 50 patients with early gastric cancer, and 50 patients with uterine cancer. To reduce radiation dose, we optimized CT protocols by omitting unnecessary pre-contrast phase, reducing kVp, and setting higher noise index. Data of dose reports were collected. Objective image quality was evaluated for noise level, signal to noise ratio (SNR), and contrast noise ratio (CNR). For subjective image quality, we evaluated image noise, contrast, and overall diagnostic acceptability.
RESULTS
The mean values of dose length product of 2011 CT scans compared to those of 2008 CT scans were 27.6% to 45.7%. The image noise level, SNR, and CNR were significantly (p < 0.05) worse in 2011 CT scans compared to 2008 CT scans. For subjective image quality, image noise was also significantly (p < 0.05) worse in 2011. However, CNR and diagnostic acceptability showed variable results. No CT scans were considered as unacceptable image.
CONCLUSION
We modified abdominal CT protocols to reduce radiation exposure while trying to maintain diagnostic acceptability.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mettler FA Jr, Bhargavan M, Faulkner K, Gilley DB, Gray JE, Ibbott GS, et al. Radiologic and nuclear medicine studies in the United States and worldwide: frequency, radiation dose, and comparison with other radiation sources--1950-2007. Radiology. 2009; 253:520–531.2. Hricak H, Brenner DJ, Adelstein SJ, Frush DP, Hall EJ, Howell RW, et al. Managing radiation use in medical imaging: a multifaceted challenge. Radiology. 2011; 258:889–905.3. Hamberg LM, Rhea JT, Hunter GJ, Thrall JH. Multi-detector row CT: radiation dose characteristics. Radiology. 2003; 226:762–772.4. Kalra MK, Naz N, Rizzo SM, Blake MA. Computed tomography radiation dose optimization: scanning protocols and clinical applications of automatic exposure control. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2005; 34:171–181.5. Murazaki H, Funama Y, Sugaya Y, Miyazaki O, Tomiguchi S, Awai K. Optimal setting of automatic exposure control based on image noise and contrast on iodine-enhanced CT. Acad Radiol. 2012; 19:478–484.6. Nyman U, Ahl TL, Kristiansson M, Nilsson L, Wettemark S. Patient-circumference-adapted dose regulation in body computed tomography. A practical and flexible formula. Acta Radiol. 2005; 46:396–340.7. Rizzo S, Kalra M, Schmidt B, Dalal T, Suess C, Flohr T, et al. Comparison of angular and combined automatic tube current modulation techniques with constant tube current CT of the abdomen and pelvis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006; 186:673–679.8. Starck G, Lönn L, Cederblad A, Forssell-Aronsson E, Sjöström L, Alpsten M. A method to obtain the same levels of CT image noise for patients of various sizes, to minimize radiation dose. Br J Radiol. 2002; 75:140–150.9. Winklehner A, Karlo C, Puippe G, Schmidt B, Flohr T, Goetti R, et al. Raw data-based iterative reconstruction in body CTA: evaluation of radiation dose saving potential. Eur Radiol. 2011; 21:2521–2526.10. Brenner DJ, Hall EJ. Computed tomography--an increasing source of radiation exposure. N Engl J Med. 2007; 357:2277–2284.11. Borgen L, Stranden E, Espeland A. Clinicians' justification of imaging: do radiation issues play a role? Insights Imaging. 2010; 1:193–200.12. Dougeni E, Faulkner K, Panayiotakis G. A review of patient dose and optimisation methods in adult and paediatric CT scanning. Eur J Radiol. 2012; 81:e665–e683.13. Kalra MK, Maher MM, Kamath RS, Horiuchi T, Toth TL, Halpern EF, et al. Sixteen-detector row CT of abdomen and pelvis: study for optimization of Z-axis modulation technique performed in 153 patients. Radiology. 2004; 233:241–249.14. Hur S, Lee JM, Kim SJ, Park JH, Han JK, Choi BI. 80-kVp CT using Iterative Reconstruction in Image Space algorithm for the detection of hypervascular hepatocellular carcinoma: phantom and initial clinical experience. Korean J Radiol. 2012; 13:152–164.15. Hwang HJ, Seo JB, Lee JS, Song JW, Kim SS, Lee HJ, et al. Radiation dose reduction of chest CT with iterative reconstruction in image space - Part II: assessment of radiologists' preferences using dual source CT. Korean J Radiol. 2012; 13:720–727.16. Hwang HJ, Seo JB, Lee JS, Song JW, Kim SS, Lee HJ, et al. Radiation dose reduction of chest CT with iterative reconstruction in image space - Part I: studies on image quality using dual source CT. Korean J Radiol. 2012; 13:711–719.17. Kim M, Lee JM, Yoon JH, Son H, Choi JW, Han JK, et al. Adaptive iterative dose reduction algorithm in CT: effect on image quality compared with filtered back projection in body phantoms of different sizes. Korean J Radiol. 2014; 15:195–204.18. Shin HJ, Chung YE, Lee YH, Choi JY, Park MS, Kim MJ, et al. Radiation dose reduction via sinogram affirmed iterative reconstruction and automatic tube voltage modulation (CARE kV) in abdominal CT. Korean J Radiol. 2013; 14:886–893.19. Kanal KM, Stewart BK, Kolokythas O, Shuman WP. Impact of operator-selected image noise index and reconstruction slice thickness on patient radiation dose in 64-MDCT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007; 189:219–225.20. Kambadakone AR, Prakash P, Hahn PF, Sahani DV. Low-dose CT examinations in Crohn's disease: impact on image quality, diagnostic performance, and radiation dose. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010; 195:78–88.21. Tamm EP, Rong XJ, Cody DD, Ernst RD, Fitzgerald NE, Kundra V. Quality initiatives: CT radiation dose reduction: how to implement change without sacrificing diagnostic quality. Radiographics. 2011; 31:1823–1832.22. Feinstein AR, Cicchetti DV. High agreement but low kappa: I. The problems of two paradoxes. J Clin Epidemiol. 1990; 43:543–554.23. Shuryak I, Sachs RK, Brenner DJ. Cancer risks after radiation exposure in middle age. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2010; 102:1628–1636.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Is It Better to Enter a Volume CT Dose Index Value before or after Scan Range Adjustment for Radiation Dose Optimization of Pediatric Cardiothoracic CT with Tube Current Modulation?
- Initial Clinical Experience With Coronary CT Angiography Performed on Dual Source Photon Counting CT Using Different Cardiac Scan Modes-Analysis of Image Quality and Radiation Dose
- A study on radiation exposure dose at brain CT
- Pediatric CT: Understanding of Radiation Dose and Optimization of Imaging Techniques
- 100 kVp Low-Tube Voltage Abdominal CT in Adults: Radiation Dose Reduction and Image Quality Comparison of 120 kVp Abdominal CT